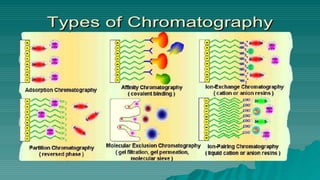
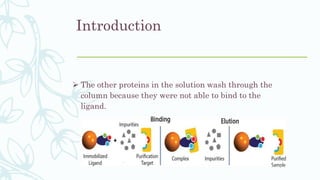
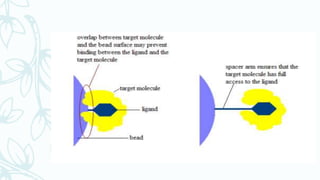
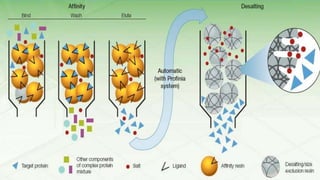
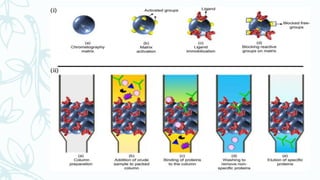
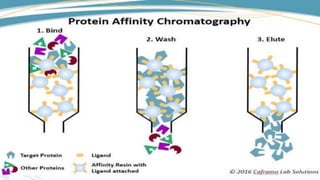
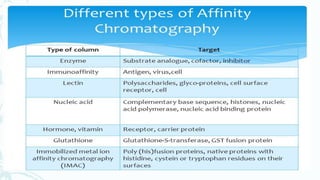
Affinity chromatography is a method that separates molecules based on a highly specific non-covalent biological interaction between the target molecule and an immobilized ligand. The process involves passing a sample mixture over a column containing the ligand, where the desired molecule binds selectively while unbound molecules pass through. The bound molecule can then be eluted and collected by changing conditions like pH or introducing a competitive ligand. Affinity chromatography has various applications like antibody purification, enzyme purification, and nucleic acid separation. It provides high selectivity and purity but ligands can be expensive and columns have a limited lifetime.