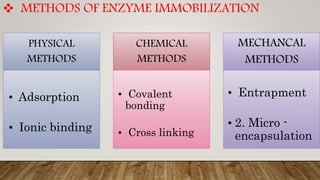
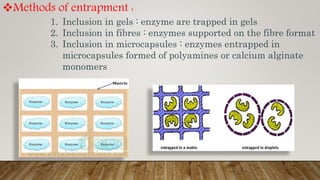
Immobilization is a process where enzymes are attached to an inert, insoluble carrier to stabilize them. This prevents degradation and allows enzymes to be reused. Common carriers include inorganic materials like silica and organic polymers. Enzymes can be immobilized via physical adsorption, ionic binding, covalent bonding, or entrapment. Immobilized enzymes have benefits like enhanced stability and ease of product separation. They find applications in industries like food production, waste treatment, and biodiesel manufacturing.