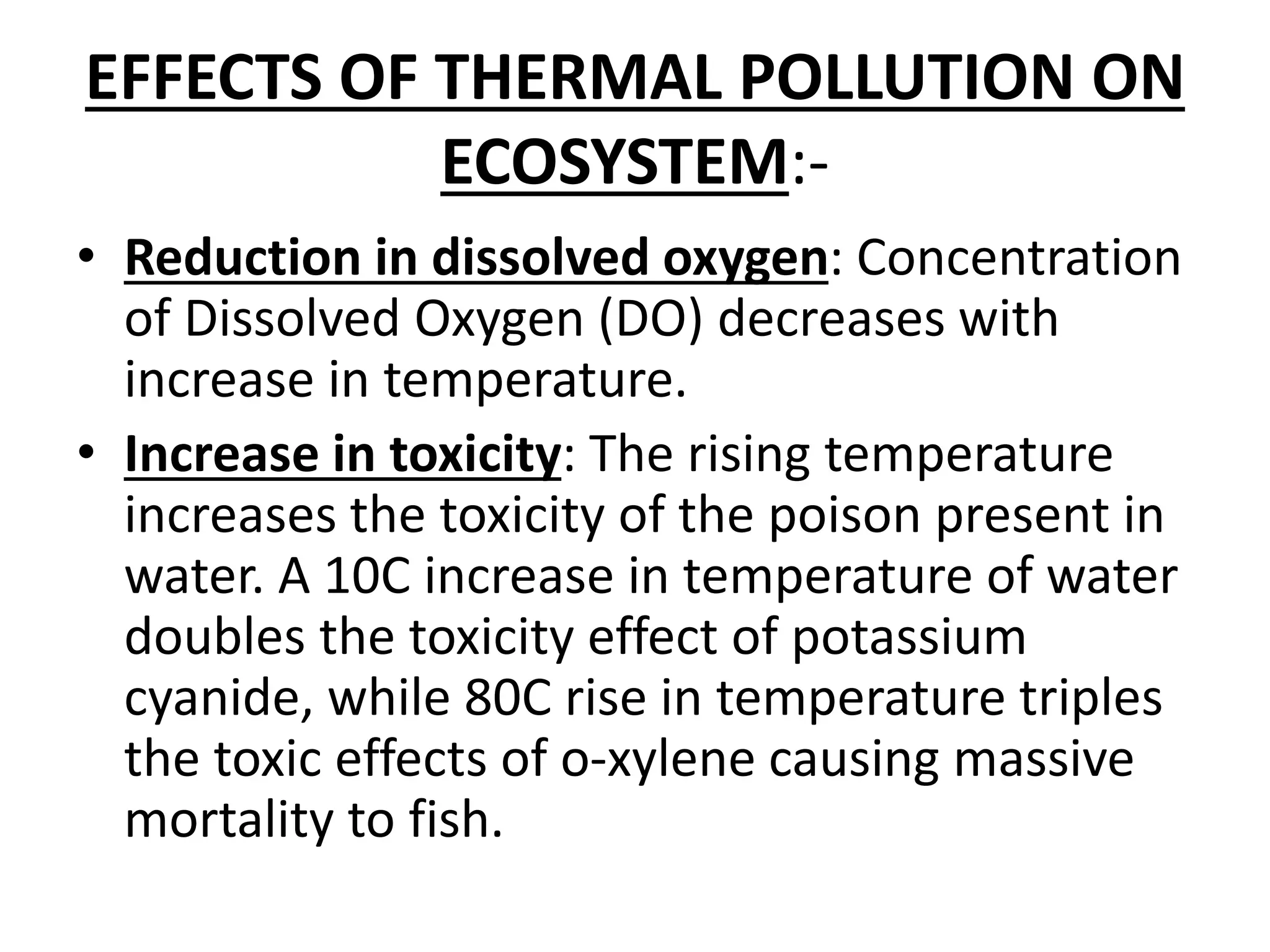
This document discusses various types of environmental pollution including water, air, soil, noise, light, radioactive and thermal pollution. It defines each type of pollution and provides their sources and effects on plants and ecosystems. Soil pollution occurs from chemical spills and leaks, contaminating the soil and making it unsuitable for agriculture. Noise pollution comes from vehicles, construction machinery and other human sources, and can interfere with plant pollination. Light pollution prevents zooplankton from controlling algae blooms. Radioactive pollution from minerals and nuclear accidents can weaken plant seeds and cause mutations. Thermal pollution from power plants and industry raises water temperatures, reducing dissolved oxygen and increasing toxicity, disrupting aquatic ecosystems.