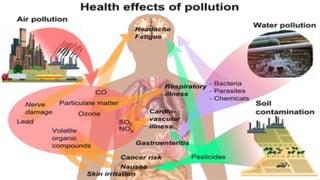
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause adverse effects. There are several types of pollution including air, water, soil, noise, and light pollution. Air pollution is caused by burning fossil fuels and vehicle emissions. Water pollution results from waste, chemicals from agriculture and industry, and oil spills. Soil pollution occurs from leaking tanks, landfills, and excess chemicals from farming. Noise pollution stems from vehicles, machines, and events. Light pollution is caused by excessive artificial lighting. These types of pollution can negatively impact human health, ecosystems, and climate. Prevention methods include sustainable transportation, energy choices, reducing waste, and educating others.