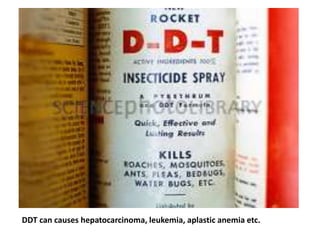
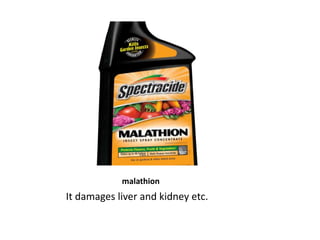
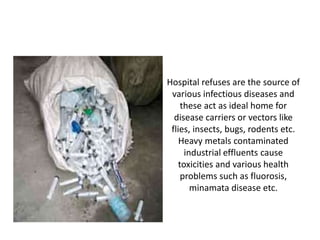
Environmental factors like pollution, overpopulation, urbanization, and degradation of natural resources negatively impact human health. Air pollution causes respiratory issues, water pollution spreads diseases, and solid waste pollution contaminates land. Population growth exacerbates all environmental problems by leading to increased resource exploitation and degradation. Rapid urbanization stresses cities' ability to manage waste and provide healthcare. Loss of biodiversity from deforestation removes natural medicines and destabilizes life-supporting ecosystems. To protect human health and life, a sustainable development model respecting the interdependence of humanity and nature is needed.