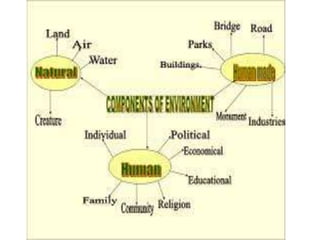
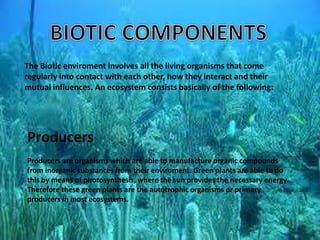
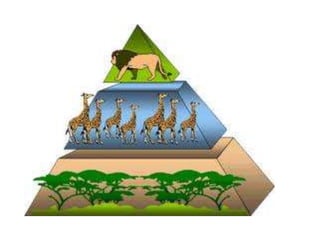
The environment consists of both biotic and abiotic components. Biotic components include living things like plants, animals and humans. Abiotic components are non-living factors such as water, air, soil, rocks and sunlight. Ecosystems involve interactions between living organisms, including producers like plants that produce energy through photosynthesis, primary consumers like herbivores that eat plants, and secondary consumers like carnivores that eat other animals. Abiotic factors also influence ecosystems, with examples being soil, water, air, temperature and sunlight, which different organisms are adapted to in different ways.