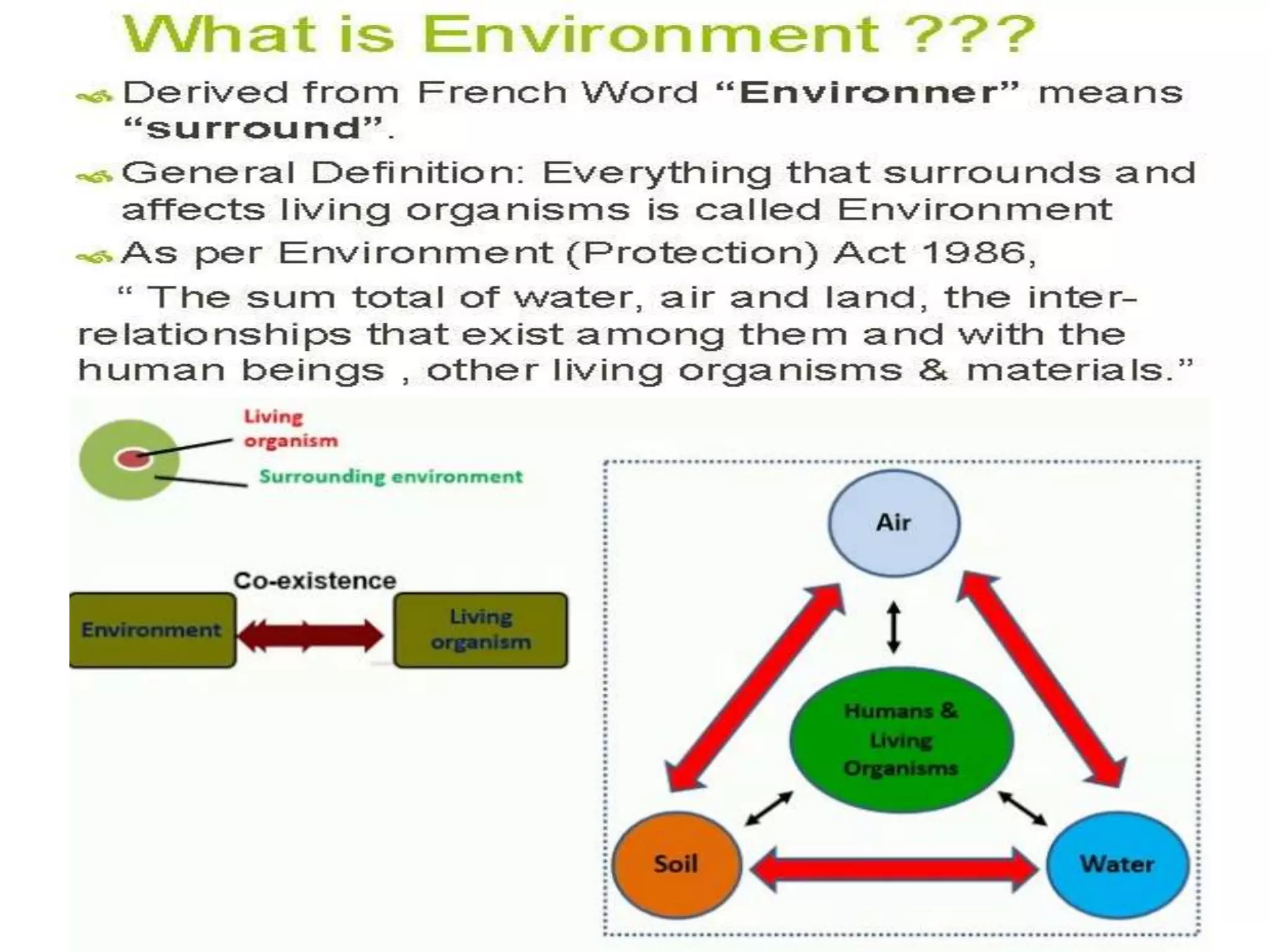
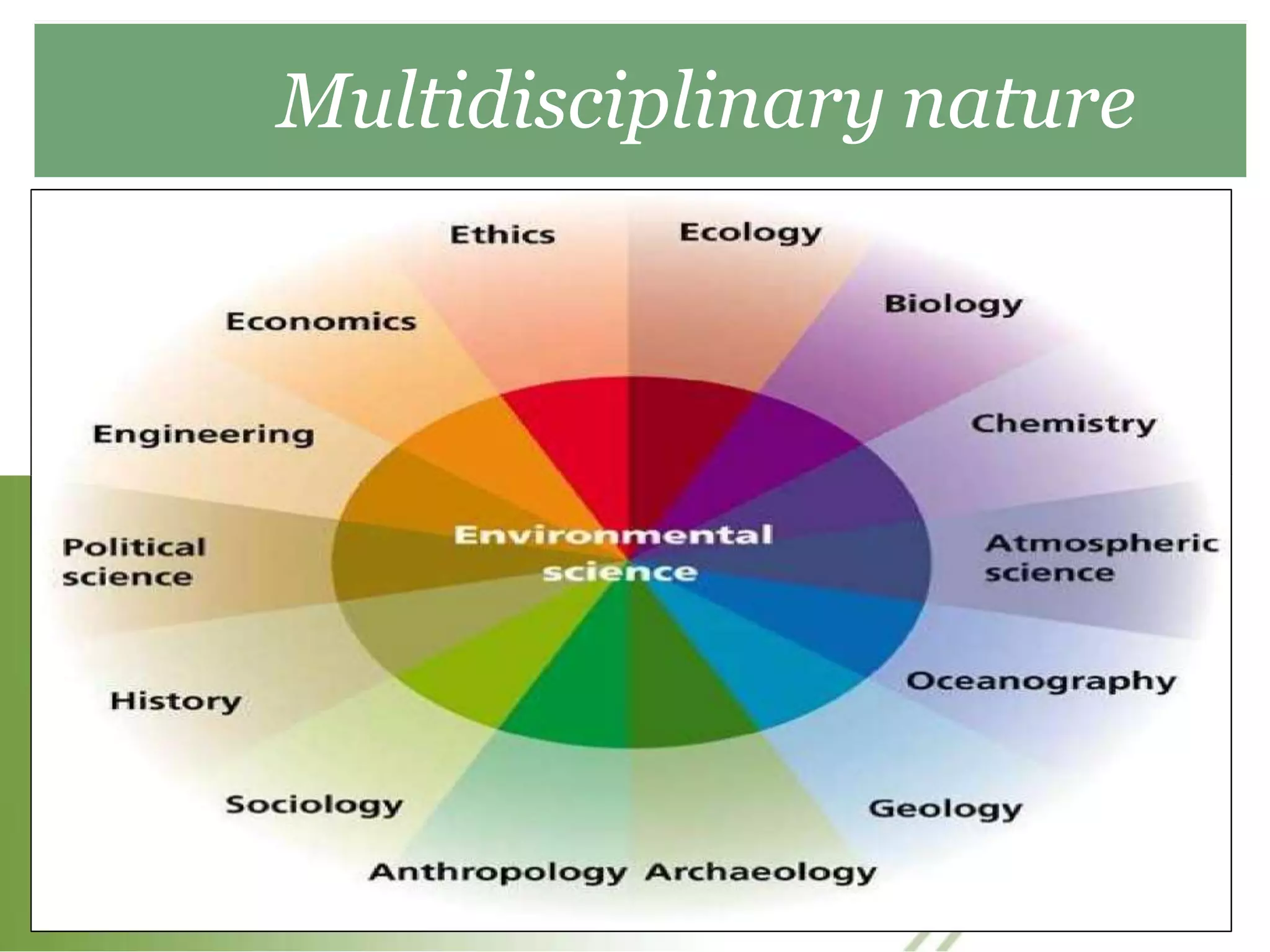
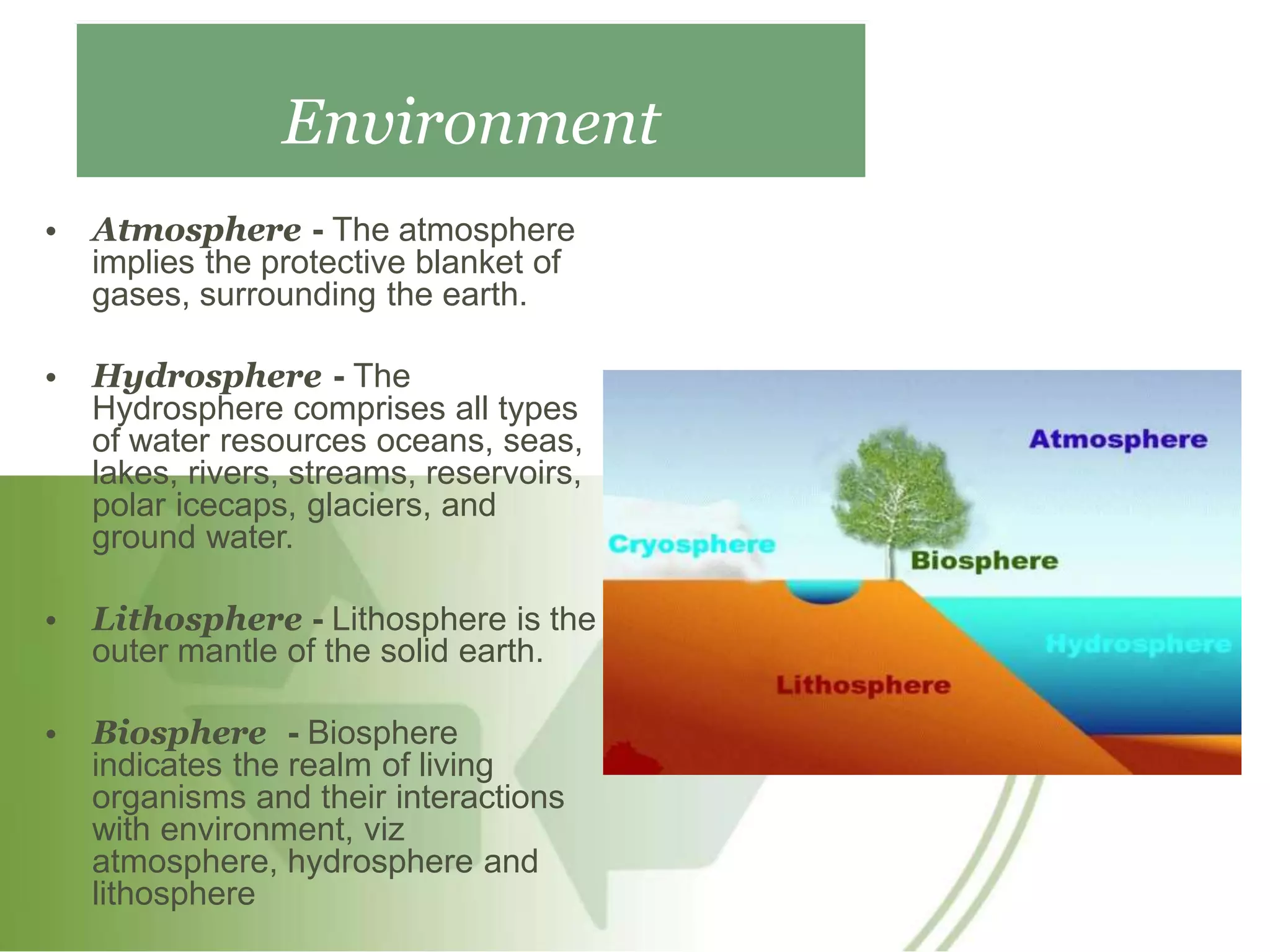
This document provides an introduction and overview of an environmental studies course syllabus. The syllabus covers 5 units: (1) the multidisciplinary nature of environmental science and ecosystems, (2) natural resources, (3) biodiversity and conservation, (4) environmental pollution, and (5) social issues and environmental management. Key topics addressed include different types of ecosystems, natural resources like forests and water, biodiversity threats and conservation, various forms of pollution and their impacts, and approaches to addressing social and environmental issues. The course aims to educate students on interactions between the environment and human activities from diverse perspectives.