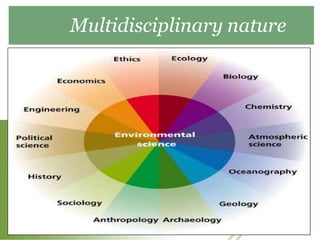
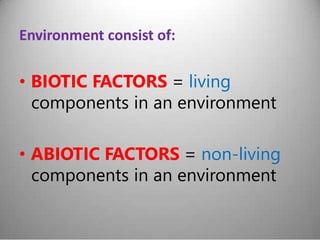
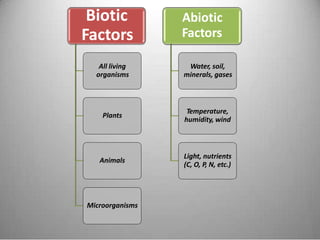
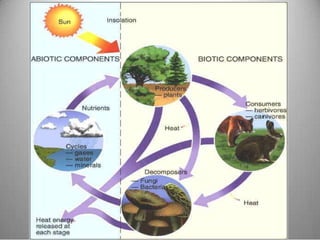
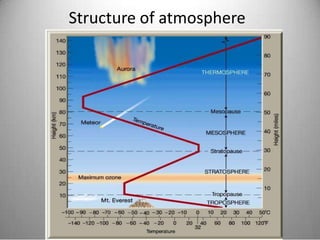
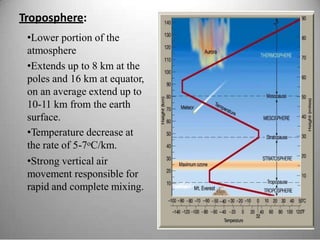
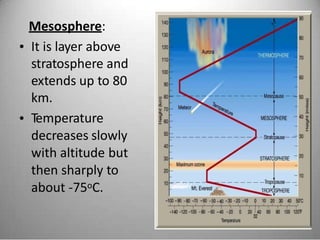
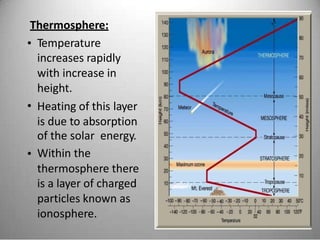
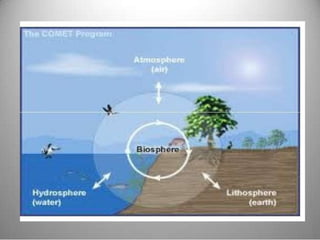
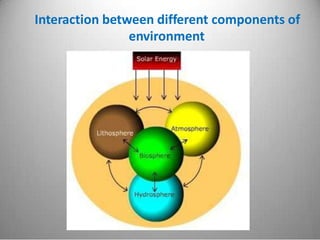
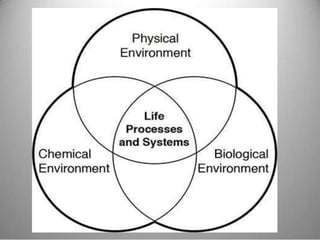
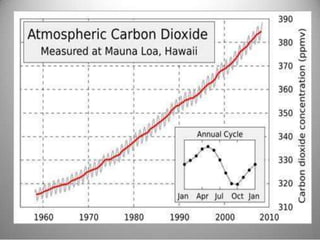
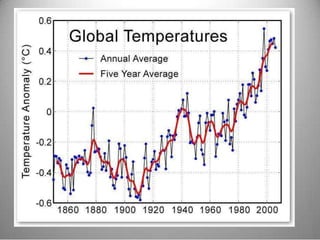
This document provides definitions and overview information about the environment and environmental studies. It defines environment as the sum of surrounding conditions, including both biotic and abiotic factors, that influence living organisms. Environmental science is described as the interdisciplinary study of how living things interact with each other and their non-living surroundings. The key components of the environment - the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere - are also summarized. The document then discusses the relationship between humans and the environment and the impacts of technology before concluding with summaries of environmental degradation and sustainable development.