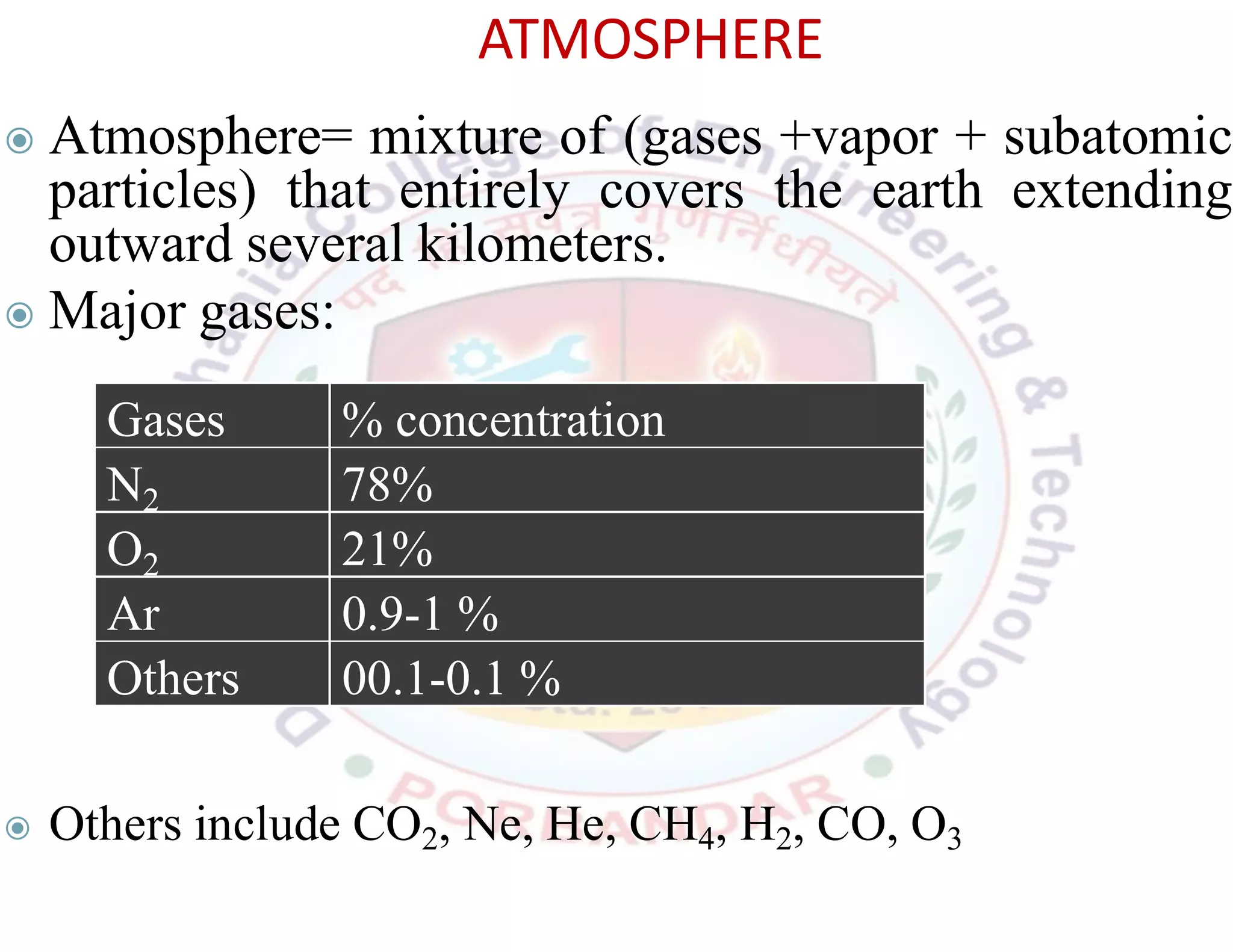
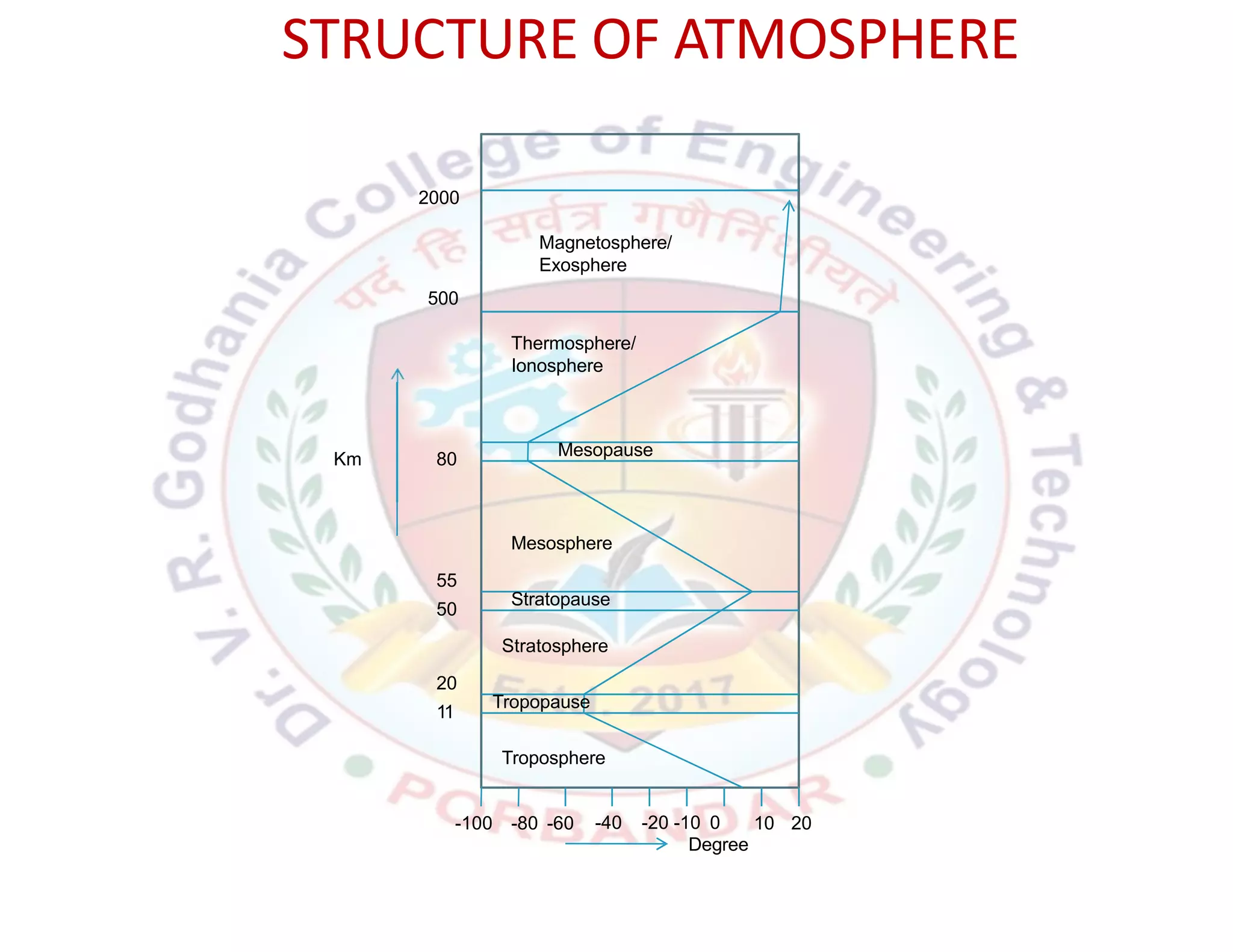
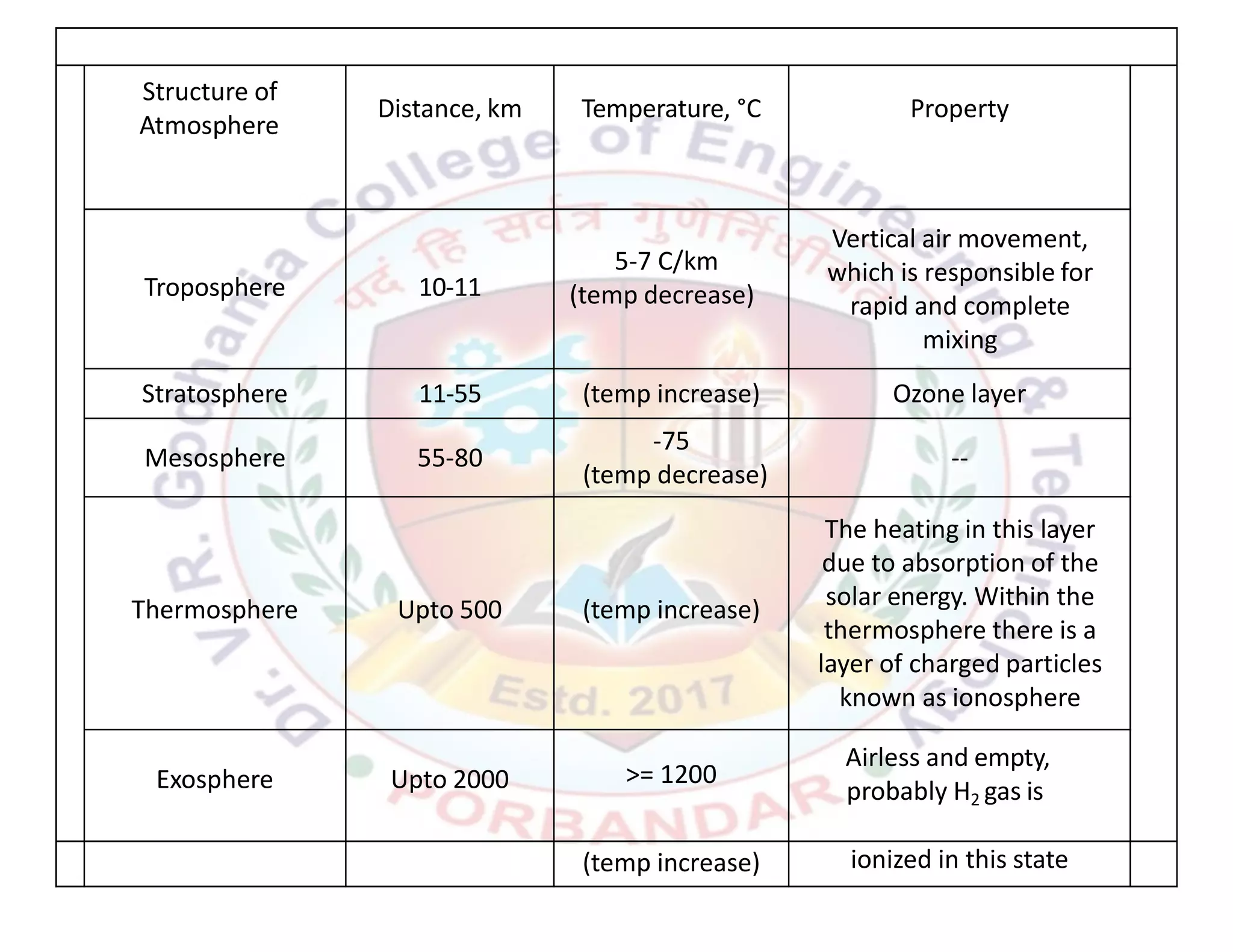
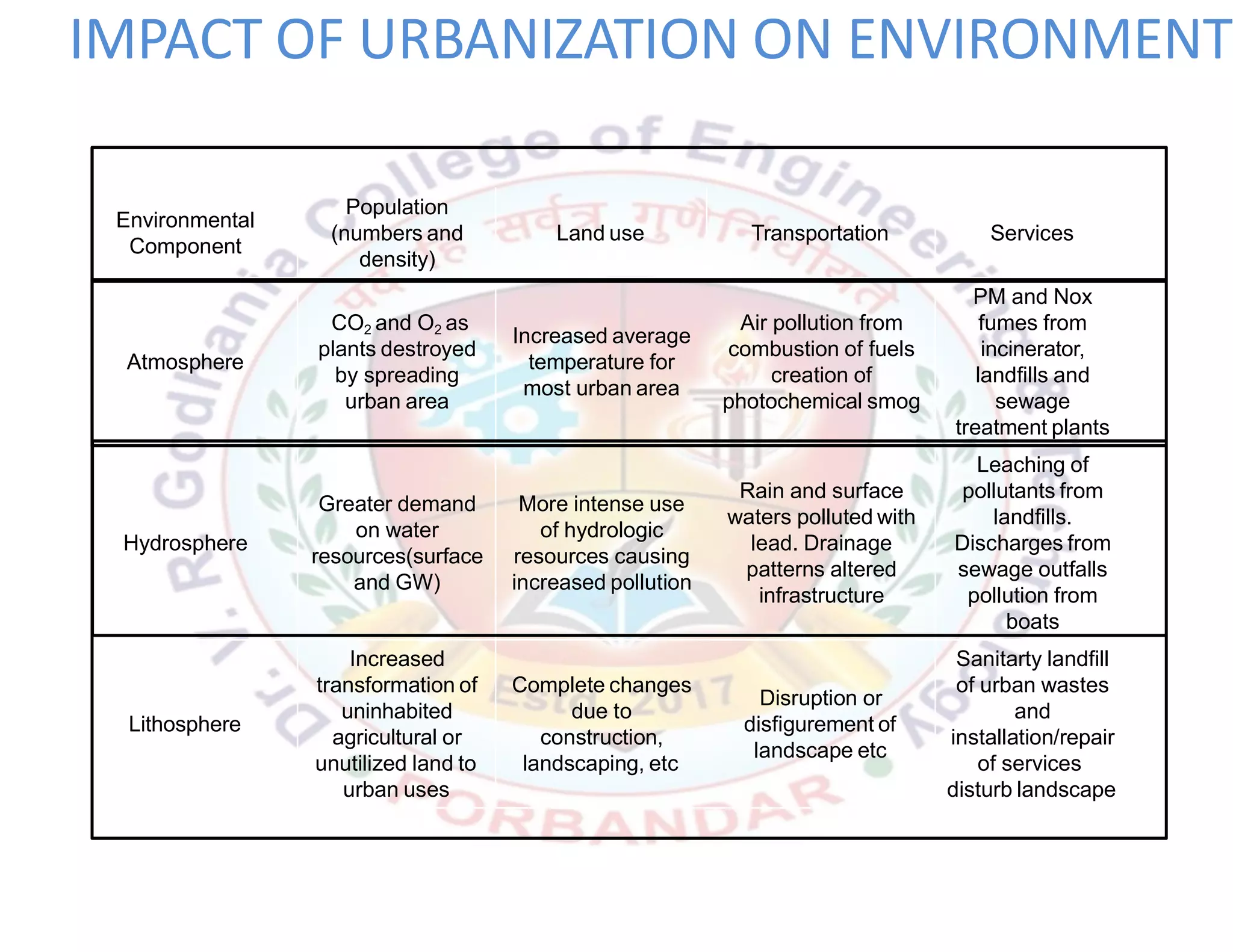
This document provides an introduction to key concepts related to environment, ecology, and ecosystems. It defines environment as the external conditions that surround and influence living organisms. Environment includes biotic factors like other living things and abiotic factors like temperature, soil and minerals. Ecology is defined as the study of the relationships between living organisms and their physical environment. An ecosystem is the complex set of interactions between a community of organisms and their environment. The four main components that make up the environment are the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere, which all interact with each other in a closed, dynamic system.