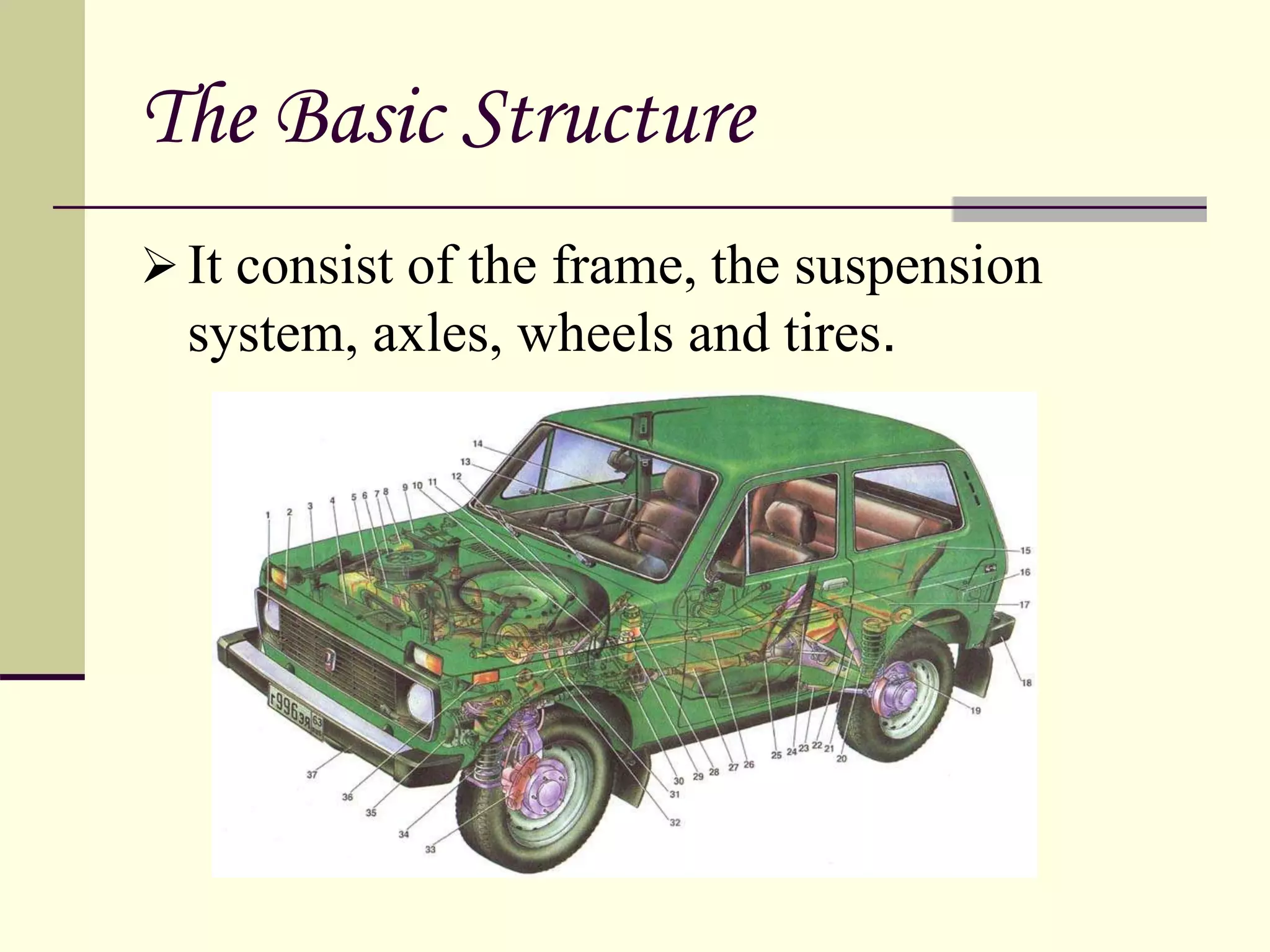
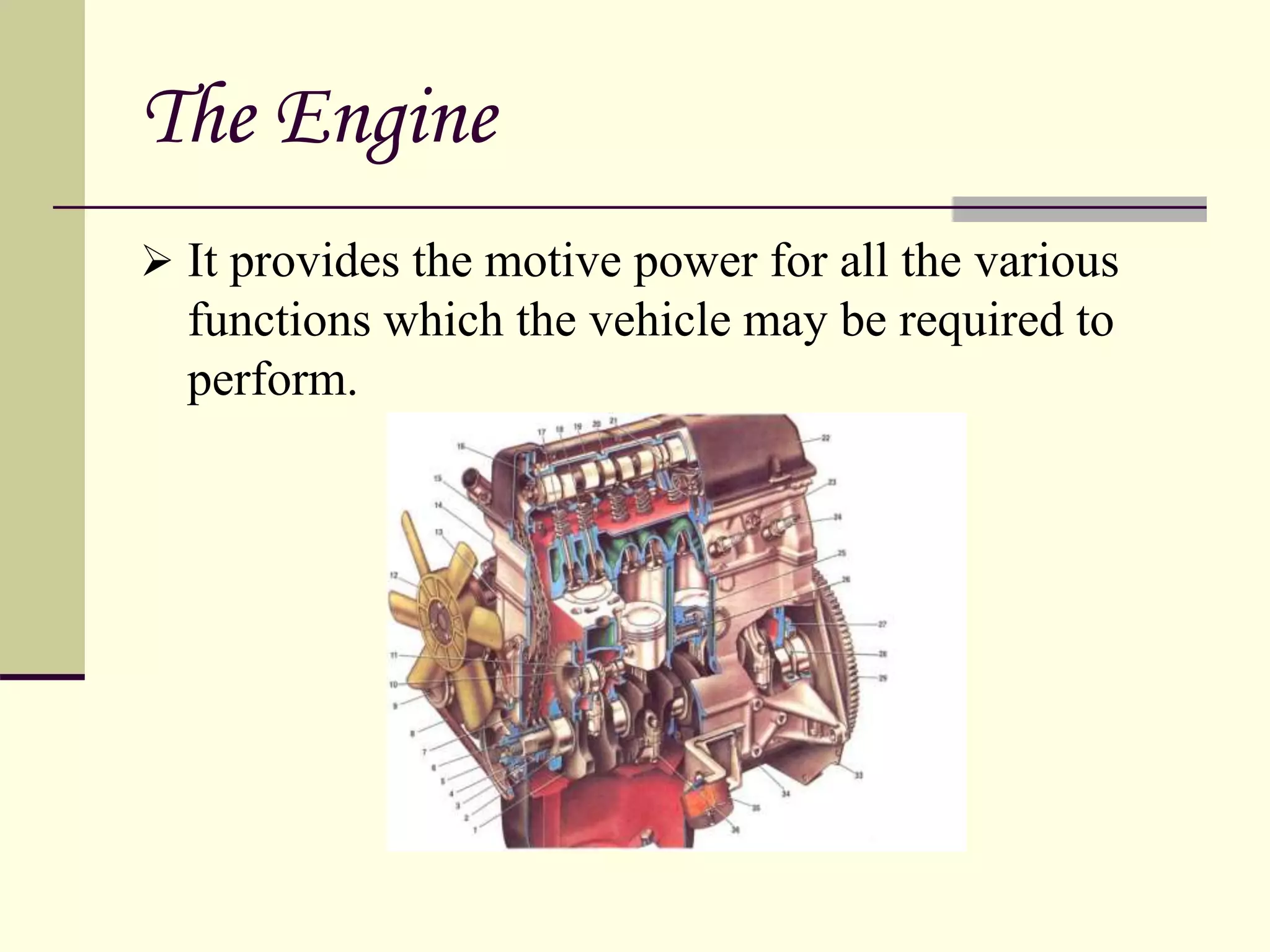
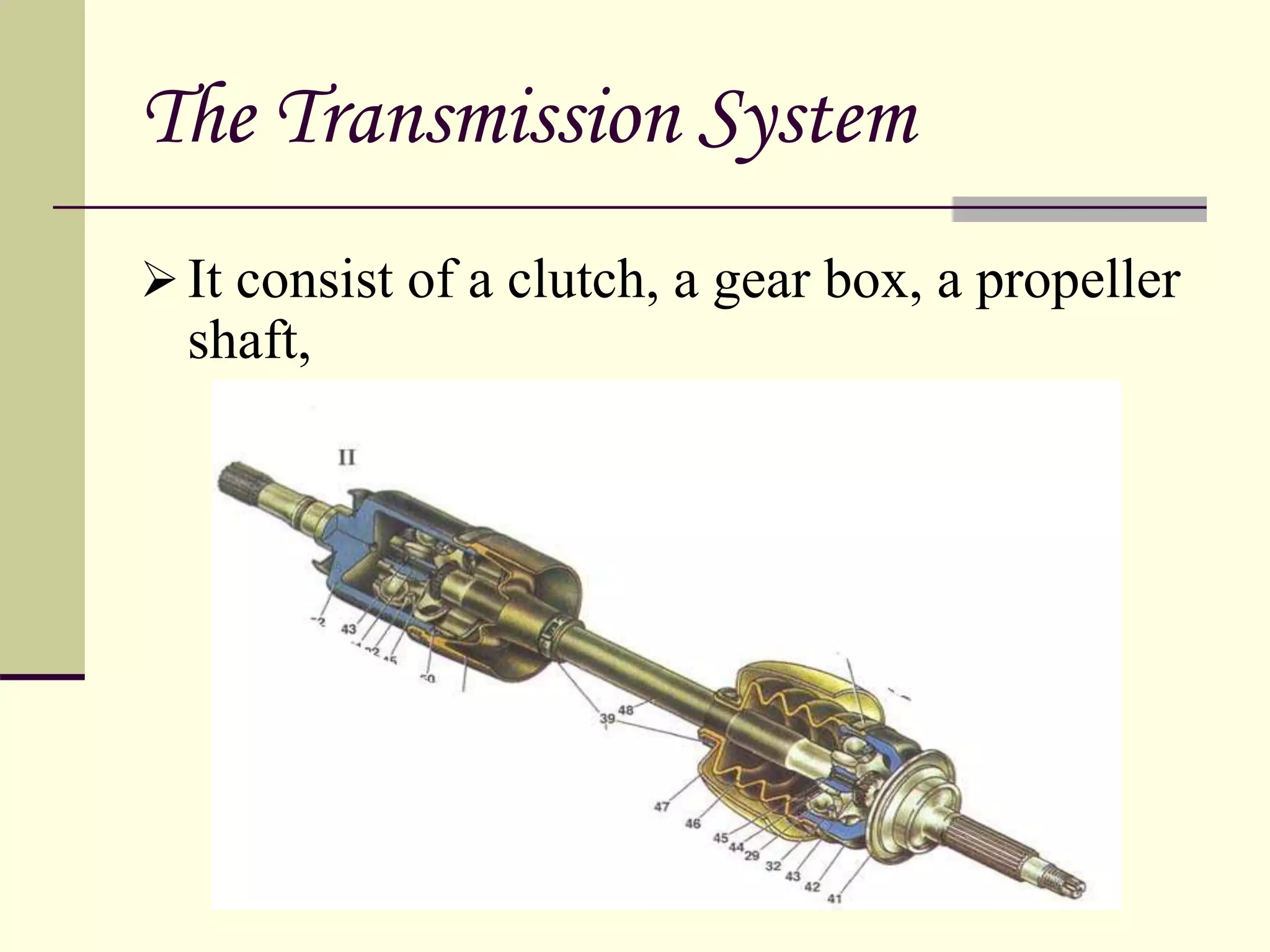
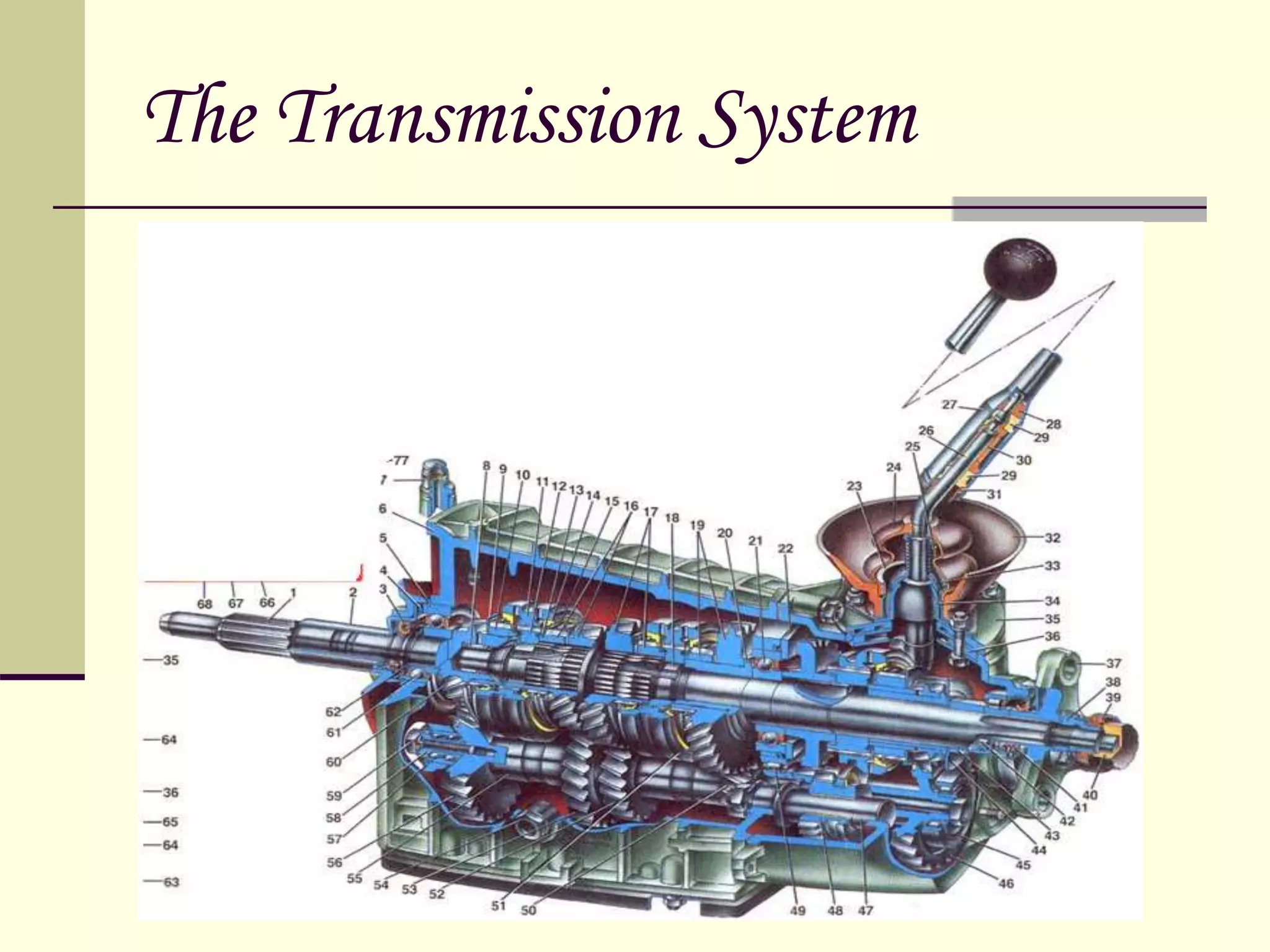
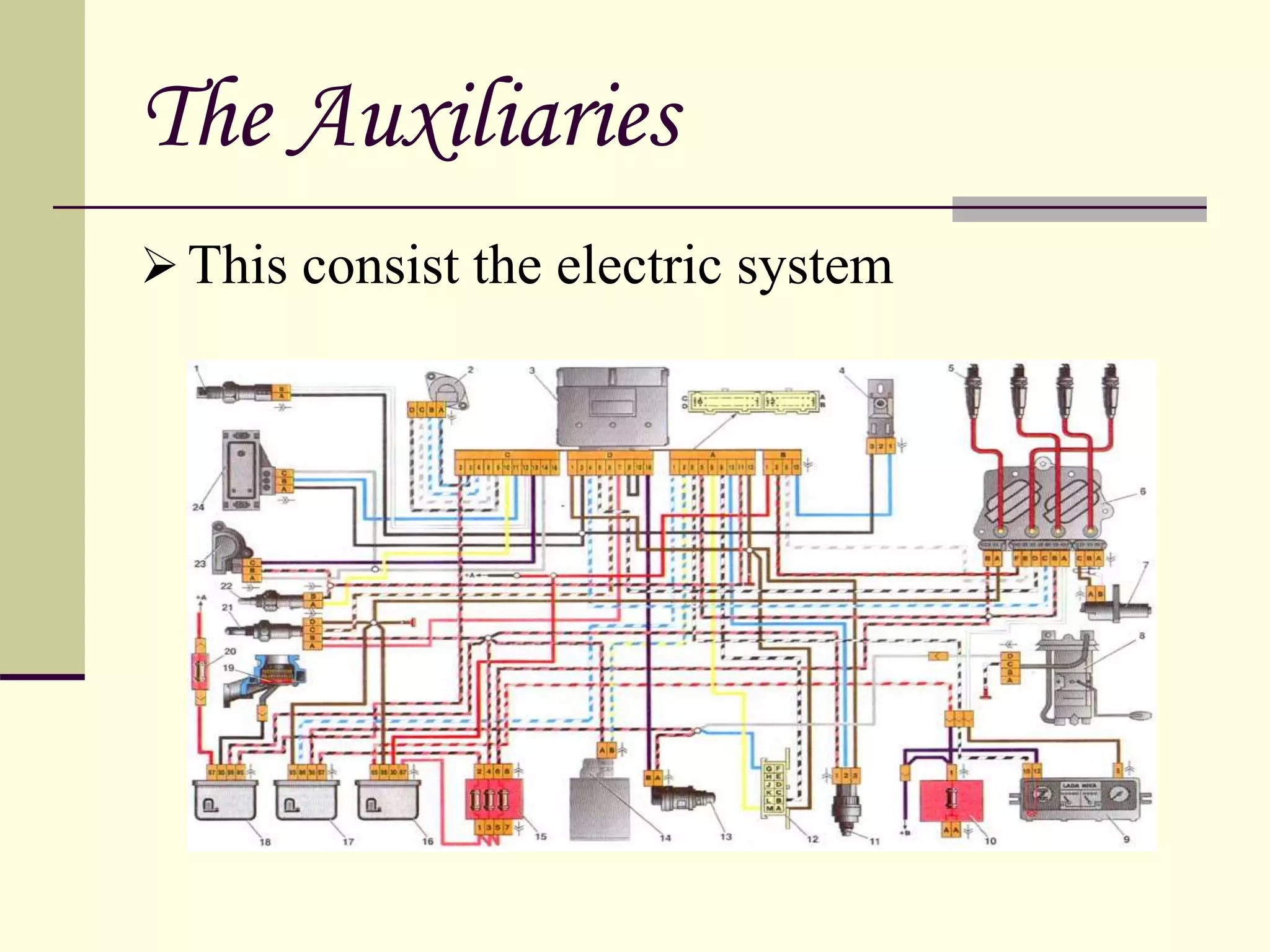
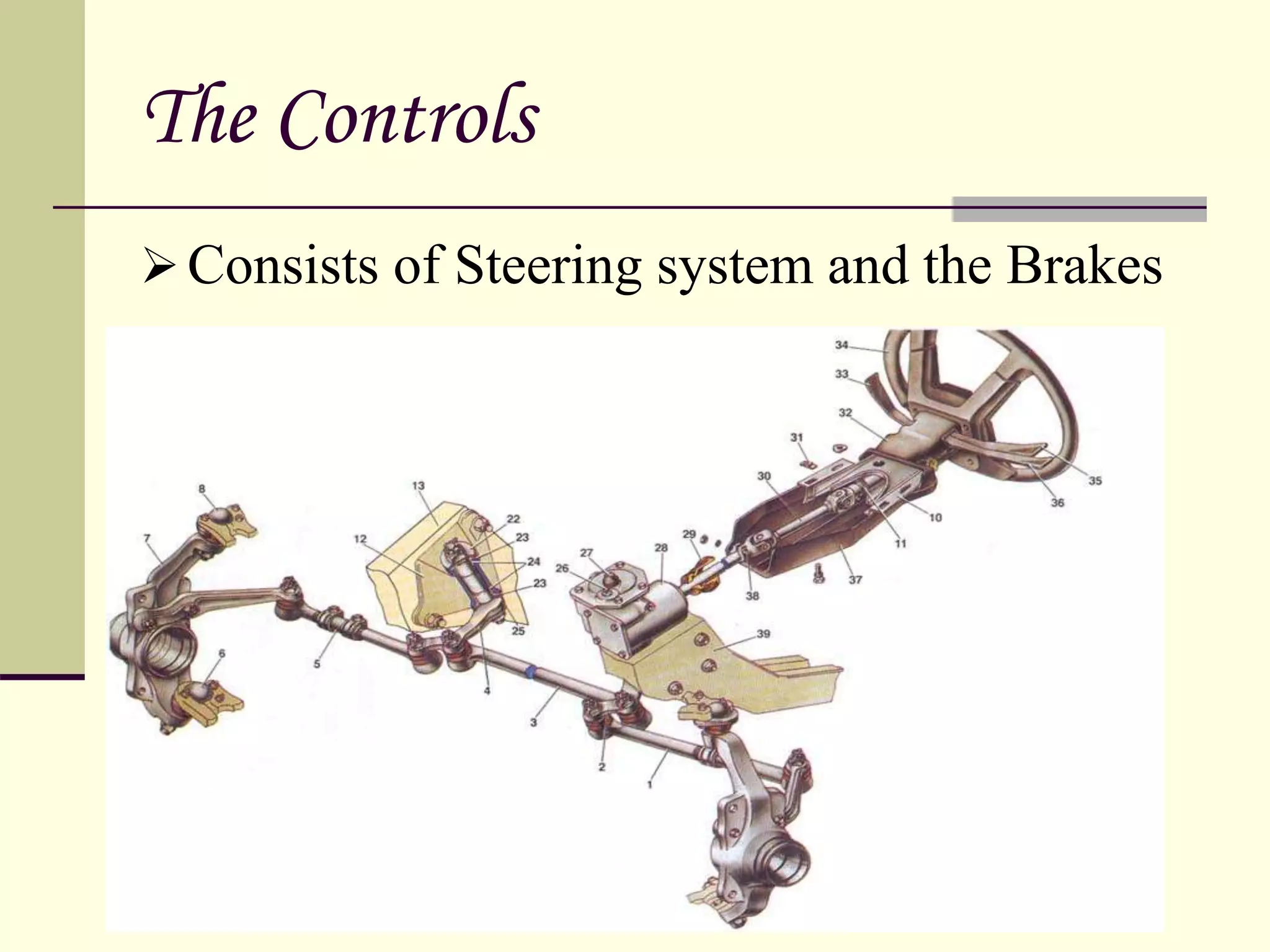
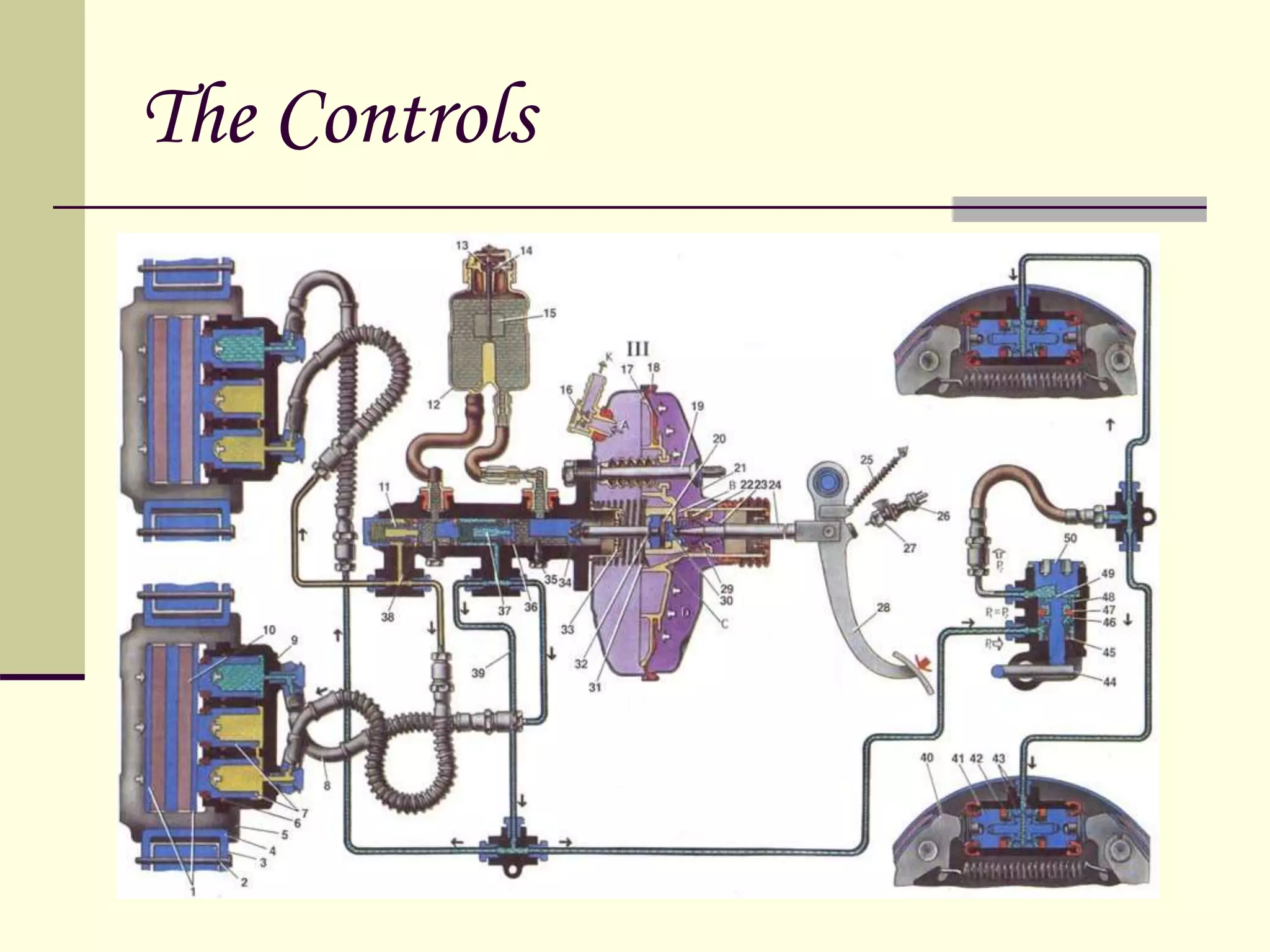
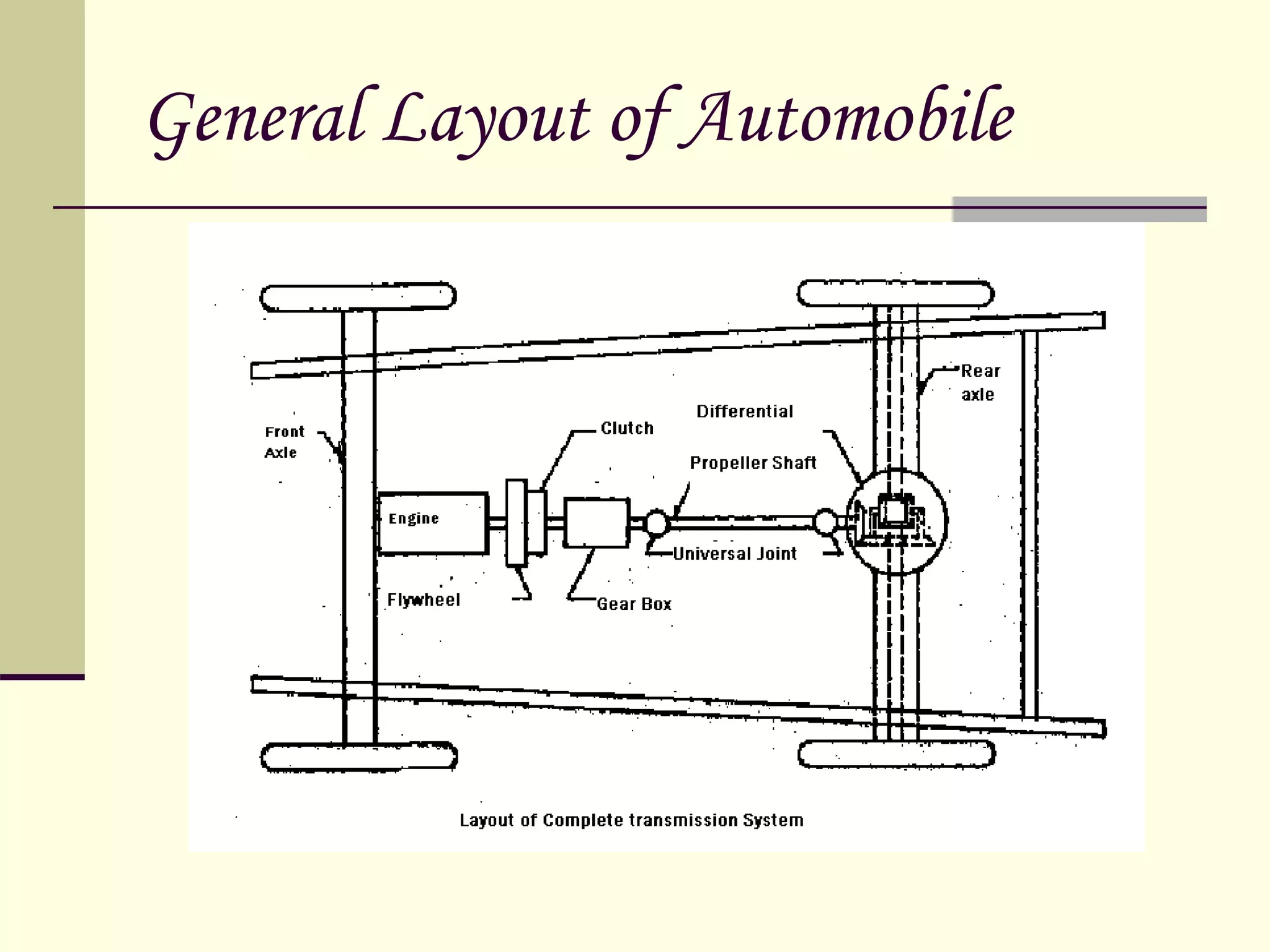
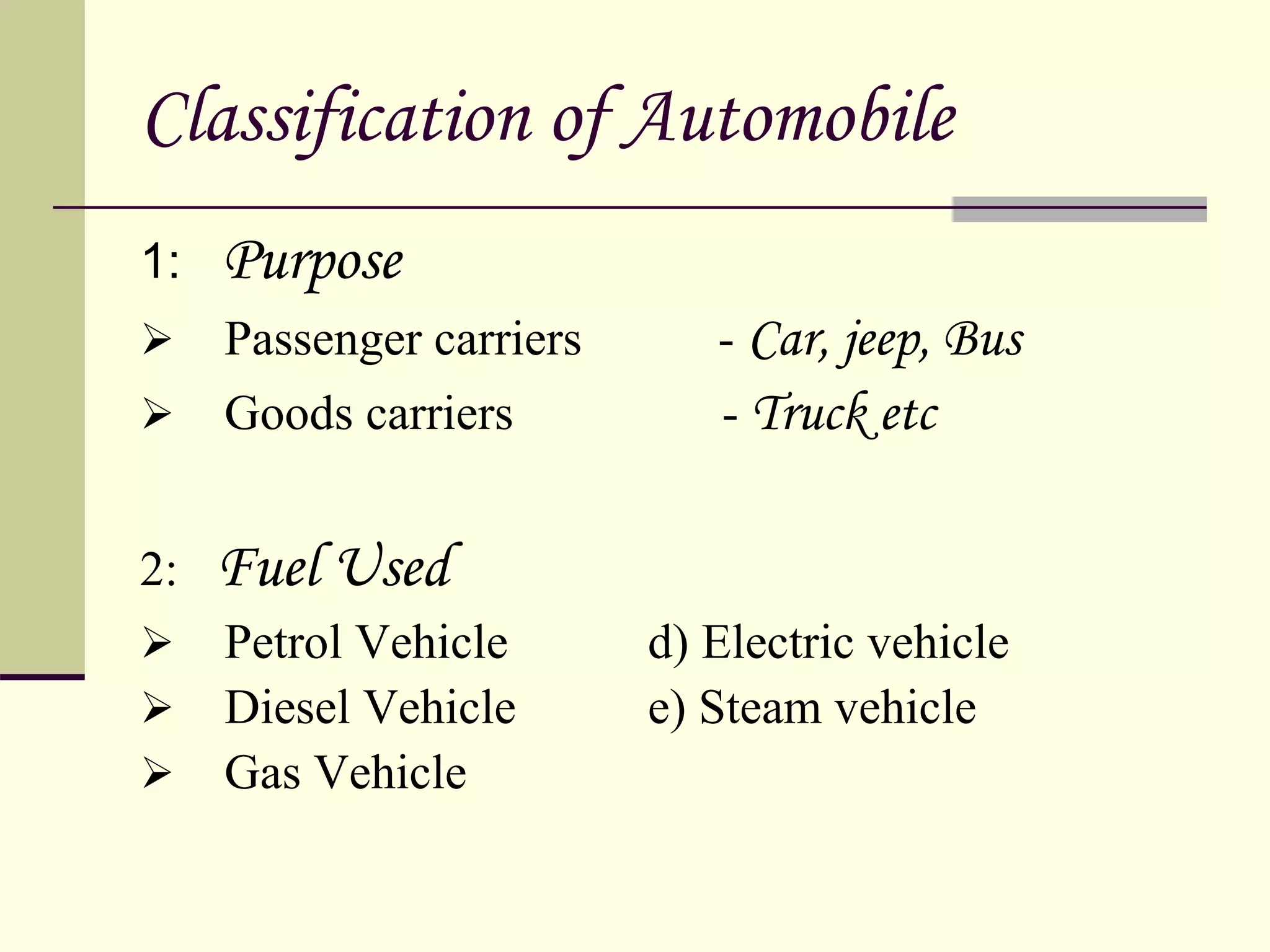
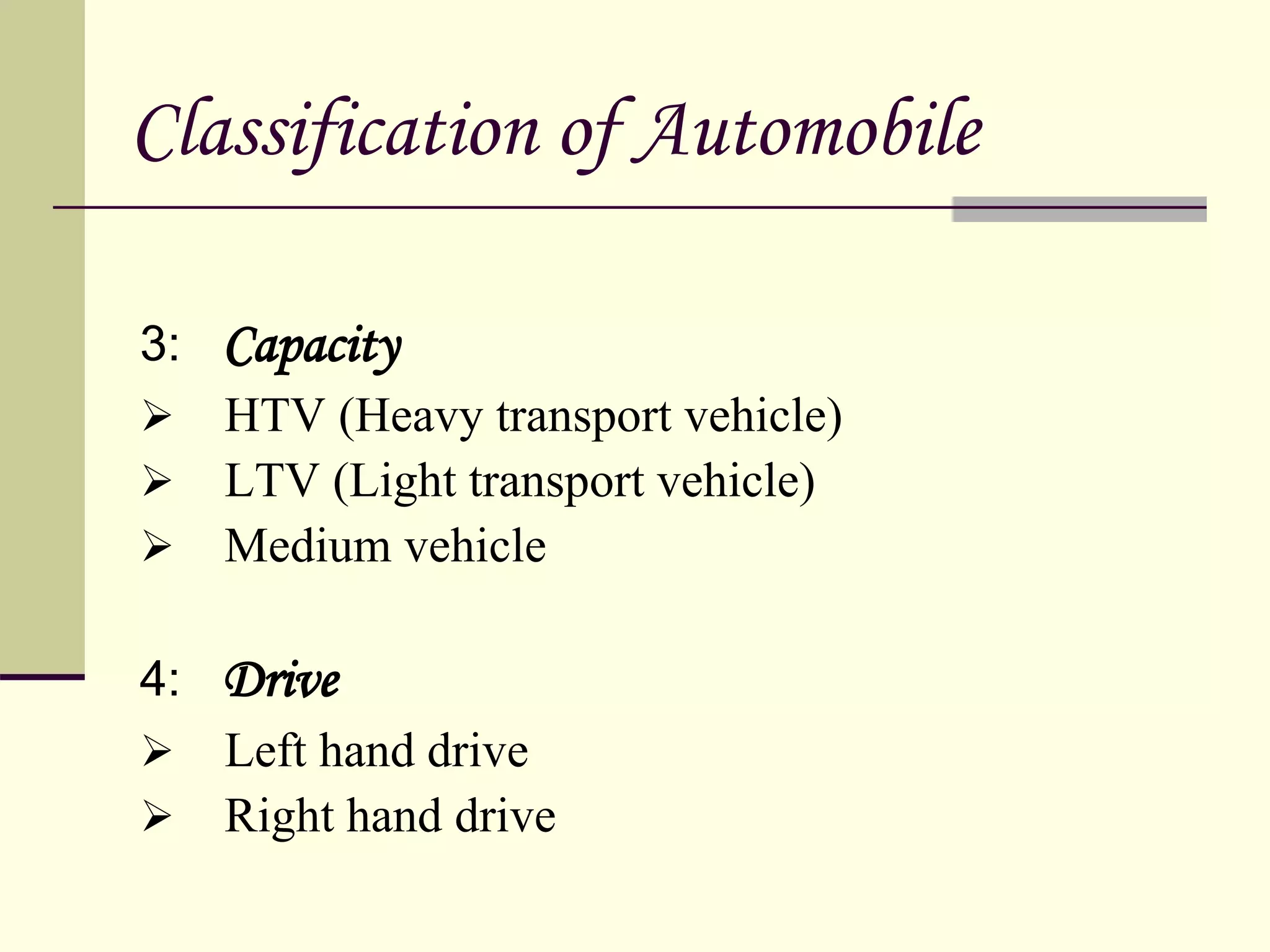
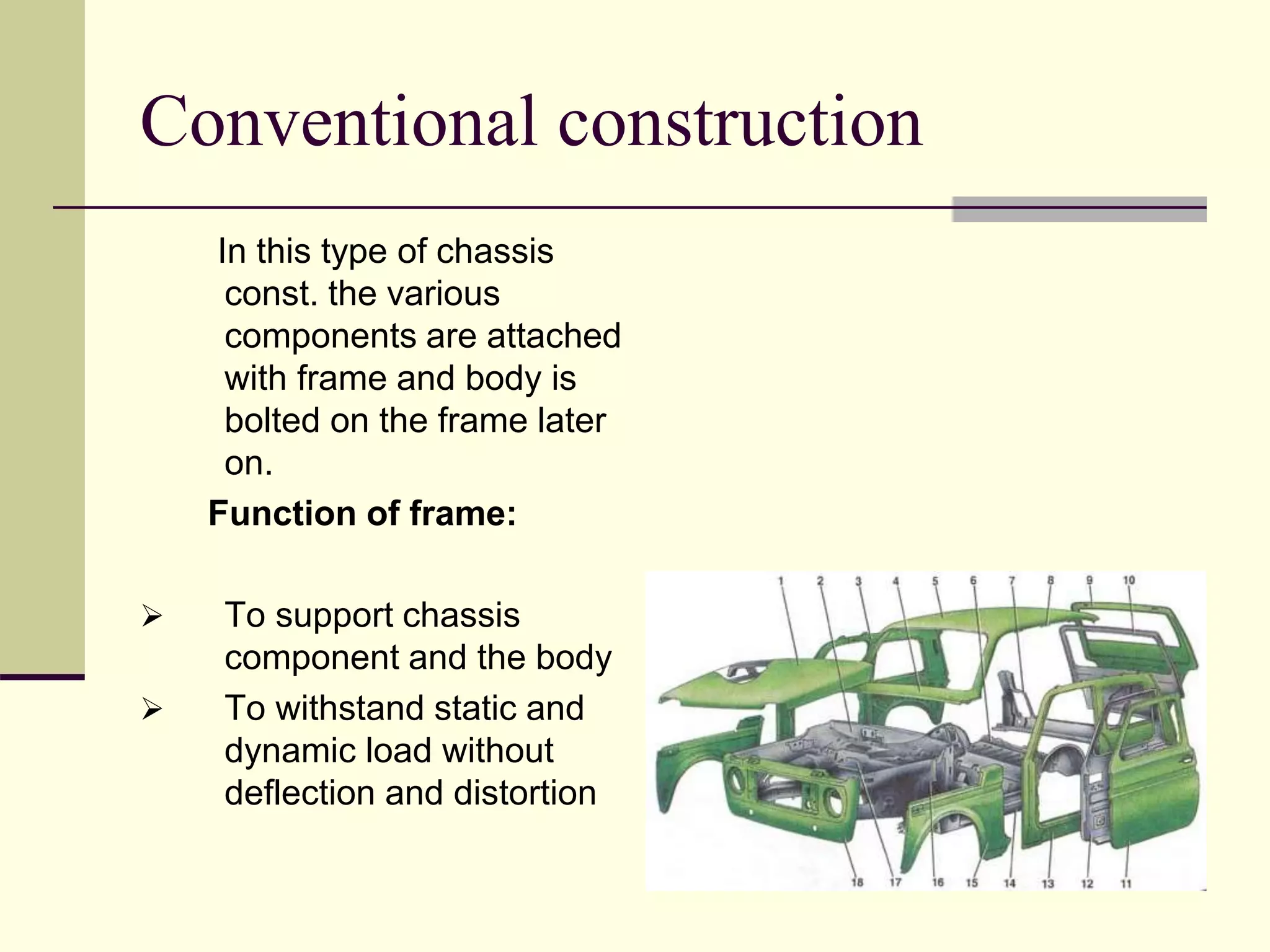
The document discusses the components and classification of automobiles. It describes how an automobile is a self-propelled vehicle powered by an internal combustion engine that transports passengers and goods. The key components include the power plant (engine), transmission system, auxiliaries (electric system), controls (steering and brakes), and suspension. Automobiles are classified based on their purpose, fuel type, capacity, drive, wheels/axles, suspension system, transmission, and body style. The document also discusses the different positions of the engine, including at the front, crosswise at the front, in the center, and at the back.