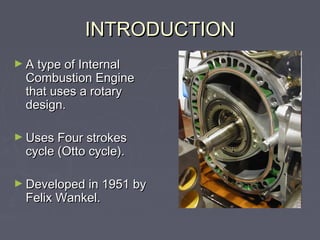
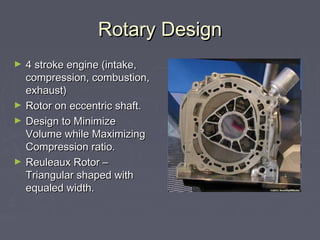
The Wankel engine is a type of internal combustion engine that uses a rotary design instead of pistons. It was developed in 1951 by Felix Wankel and uses a four-stroke combustion cycle. The key components are a triangular rotor that rotates inside an oval-shaped housing, with the rotor acting like a piston in a traditional engine. The rotor spins on an eccentric output shaft, turning three times for every one revolution to power the vehicle. Benefits include simplicity, high power-to-weight ratio, and smooth operation, though fuel efficiency is reduced compared to piston engines. It has seen limited automotive use primarily in Mazda vehicles.