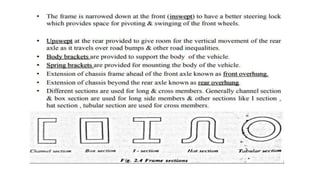
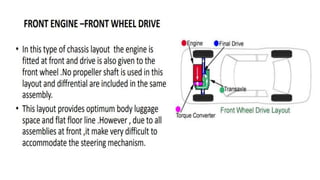
The document provides an overview of automobile engineering, including the classification and components of engines, engine systems, and types of vehicles such as four-wheel drive and multi-cylinder engines. It details the functions and structures of essential engine parts like the crankshaft, camshaft, and piston, as well as the significance of balanced firing orders for optimal performance. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of different engine settings and outlines the core engine systems necessary for operation.