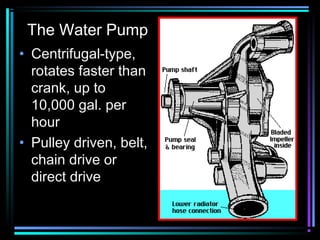
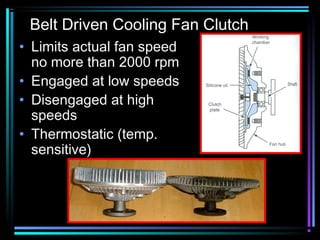
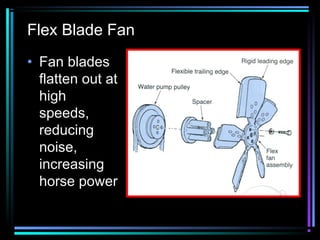
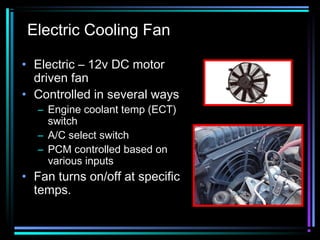
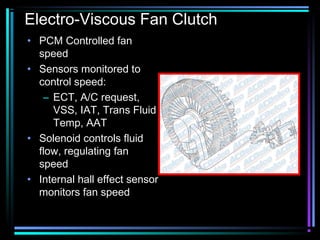
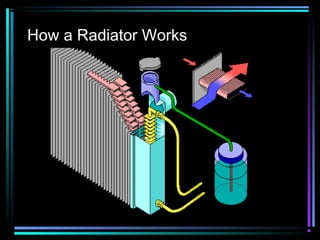
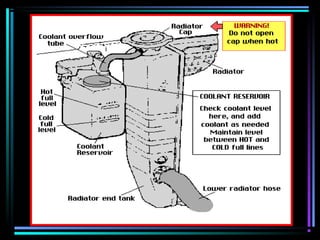
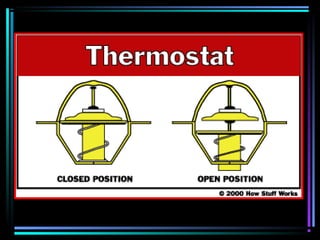
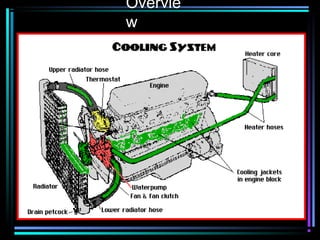
This document summarizes the key components of an automobile cooling system and how they work together. The main components are the water pump, cooling fan, radiator, thermostat, coolant, and heater core. The water pump circulates coolant throughout the system at high volumes to regulate the engine's temperature. The cooling fan provides airflow through the radiator to dissipate heat into the atmosphere. Sensors and the engine control module monitor temperatures and control electric cooling fans and fan clutches to maintain optimal operating temperatures.