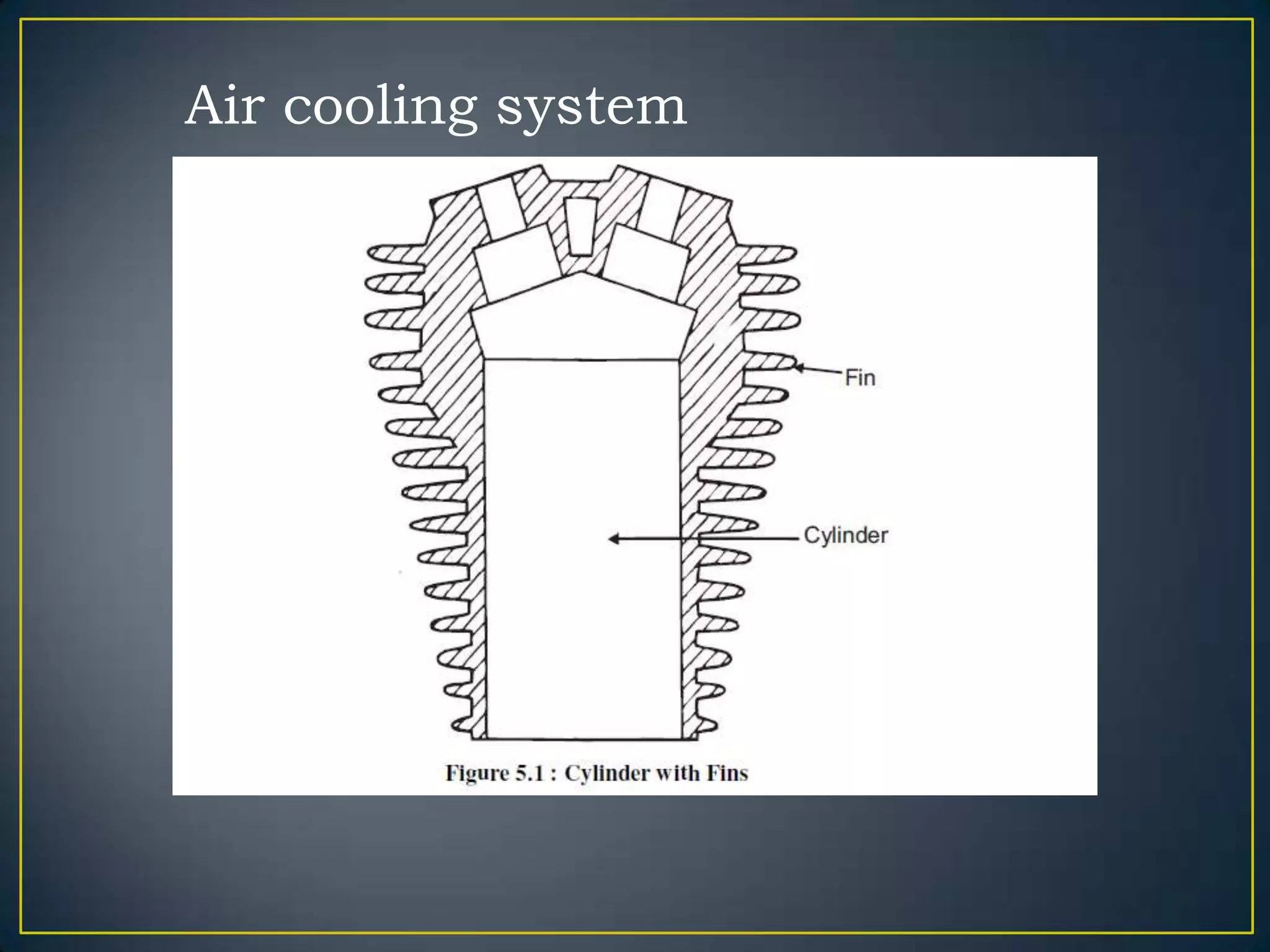
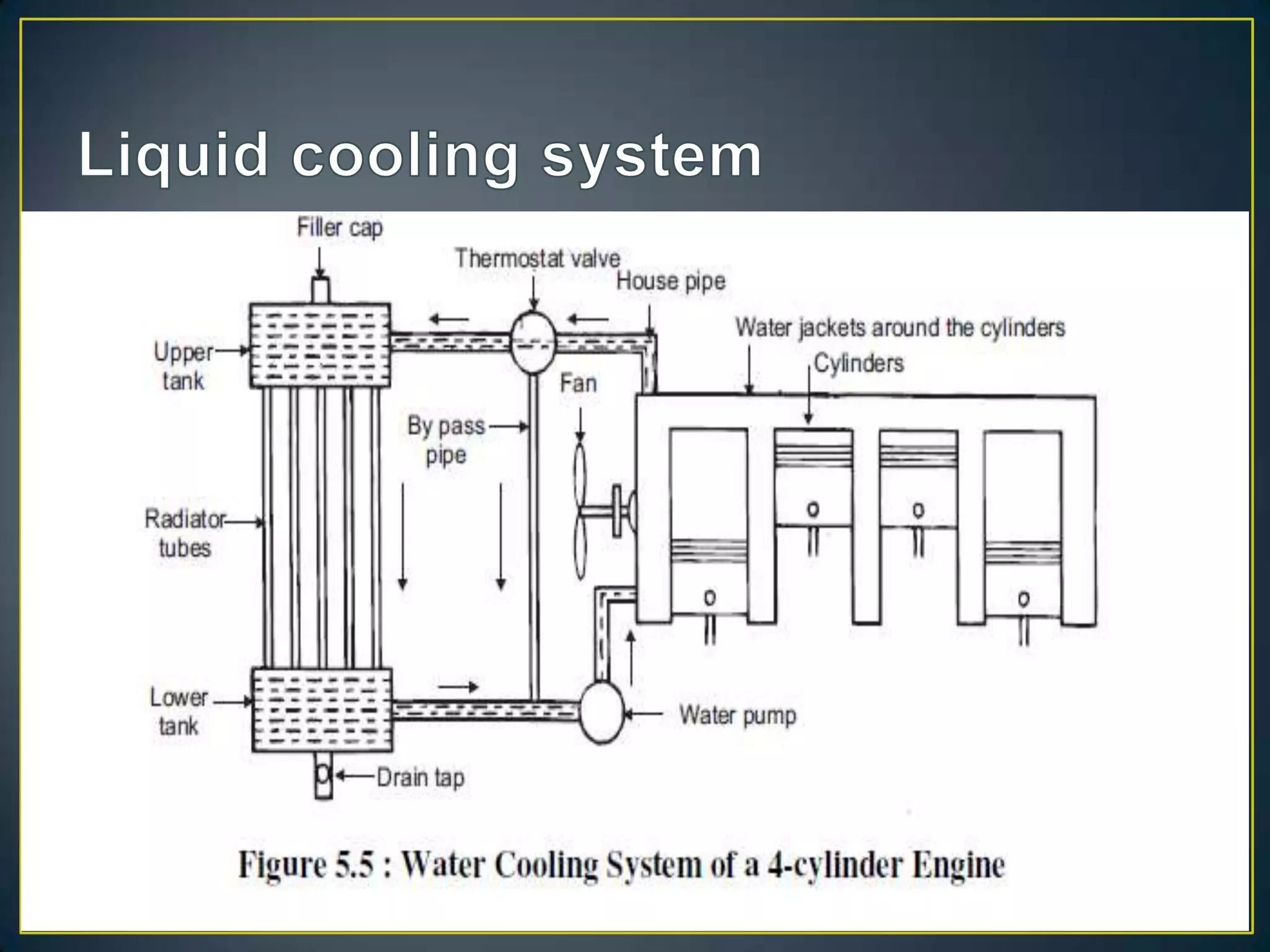
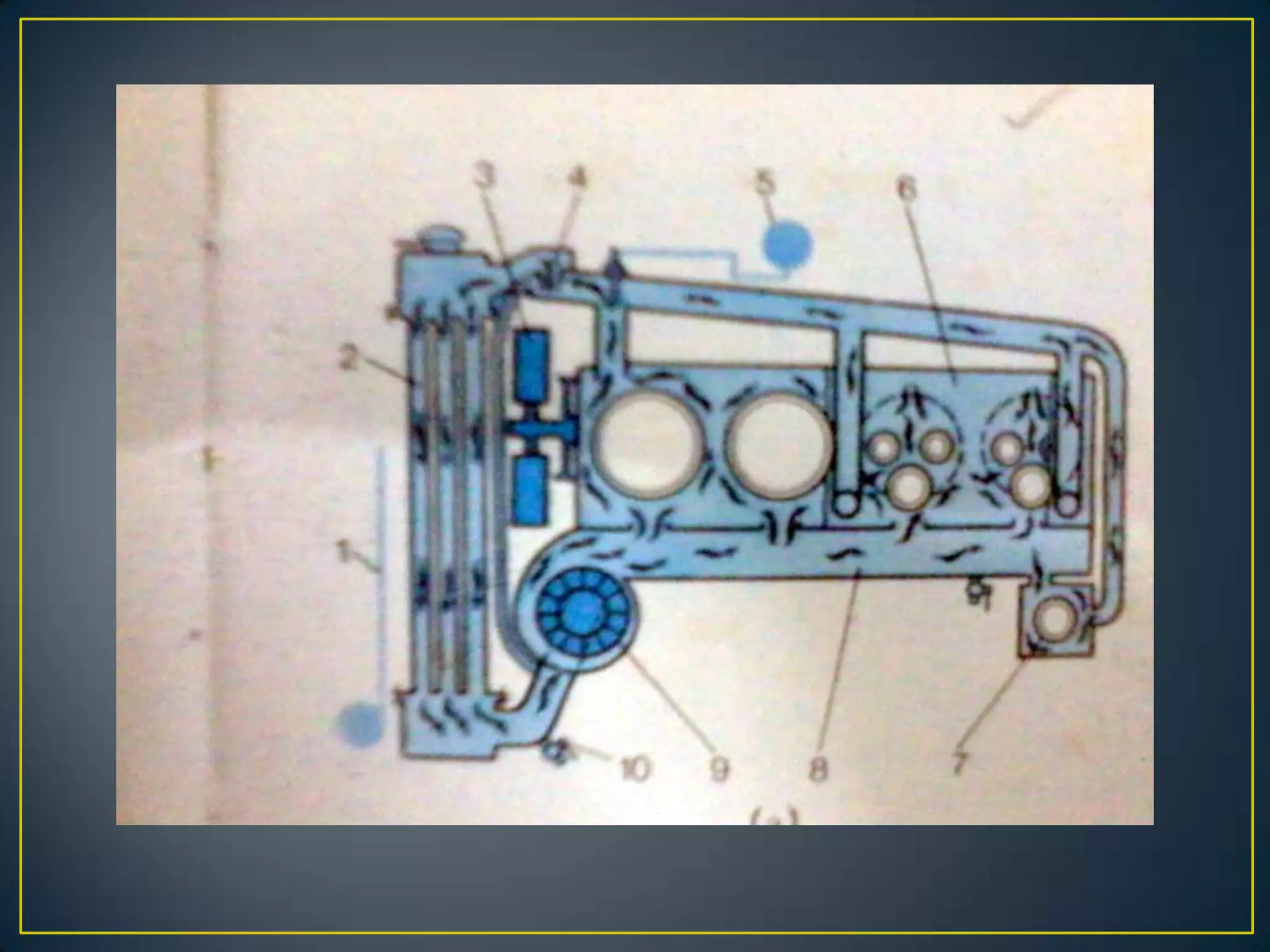
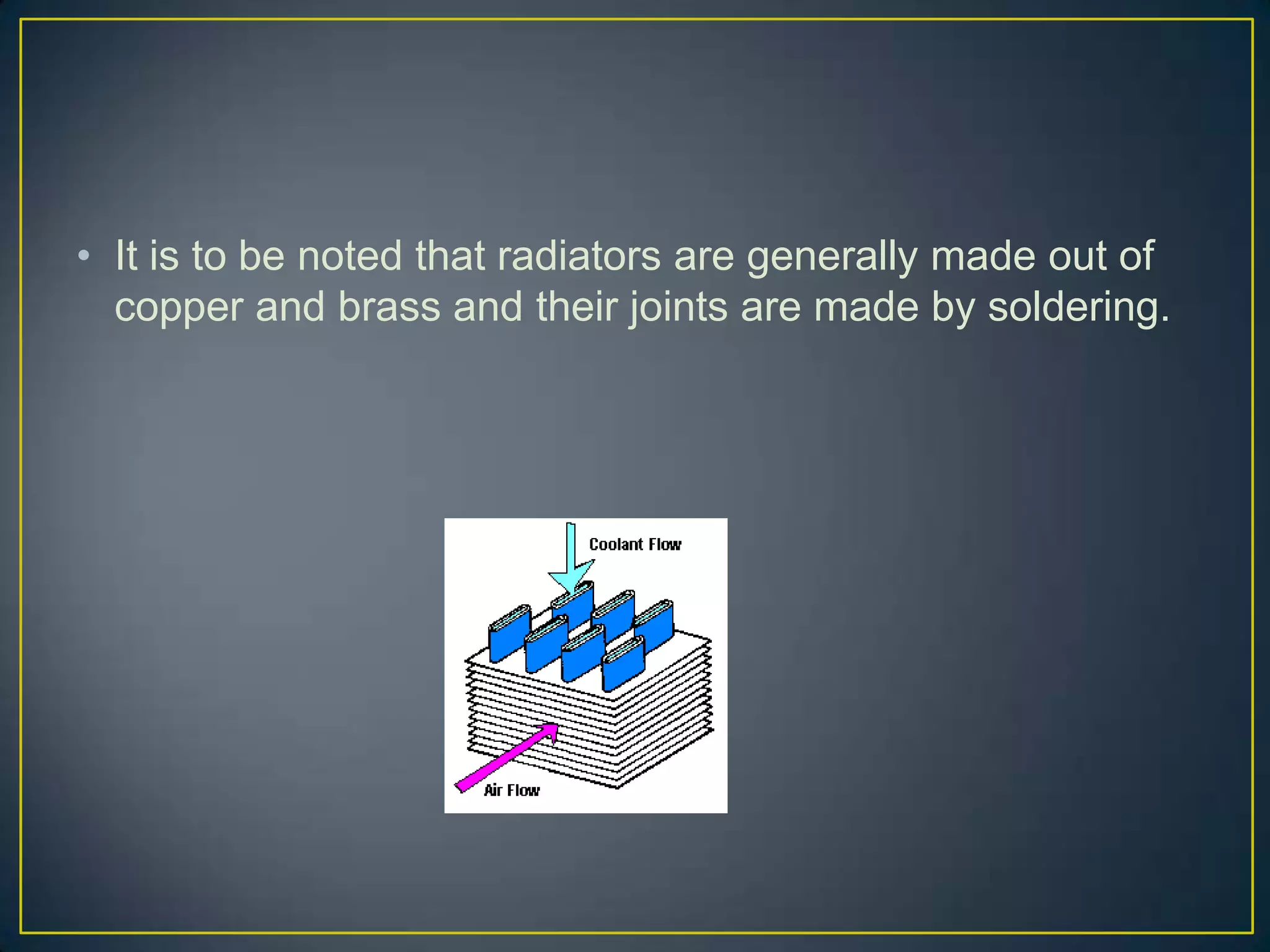
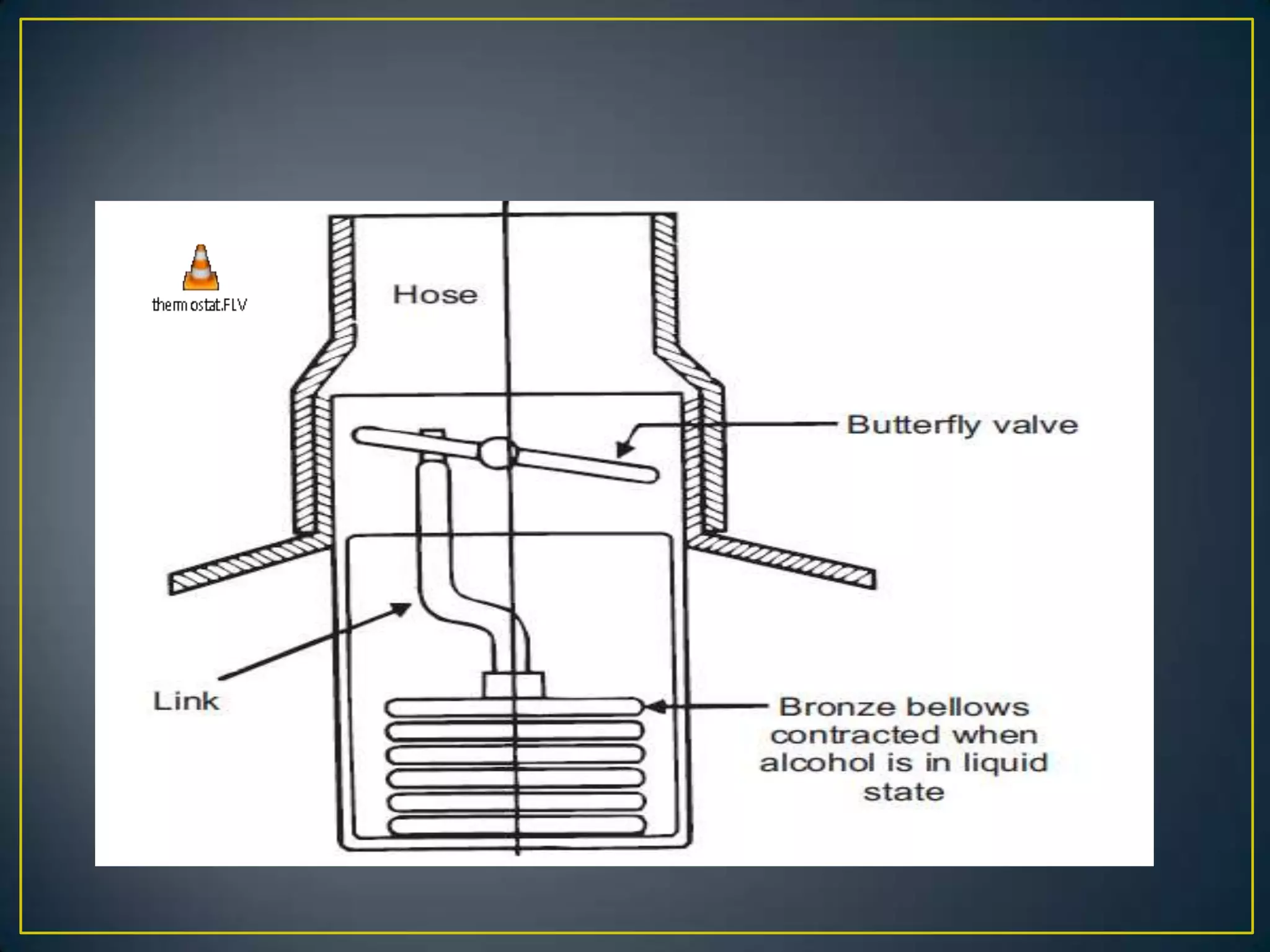
The document summarizes the components and functioning of liquid cooling systems for engines. It discusses that liquid cooling systems use water jackets and a circulating coolant to absorb heat from the engine. The main components are the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and hoses. The radiator cools the hot coolant, while the water pump circulates the coolant and the thermostat regulates the coolant temperature. The cooling system works to maintain a stable engine temperature during operation.