1. The document discusses the two-stroke cycle gasoline engine, describing its basic parts and principle of operation. It has several key advantages over the four-stroke engine, including higher power density and simpler design.
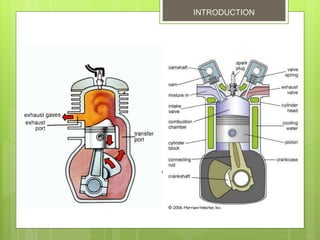
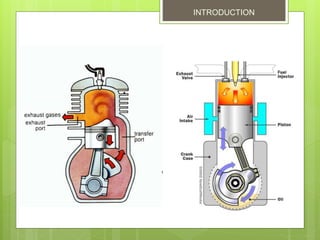
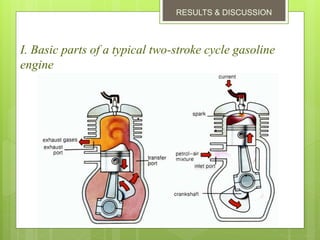
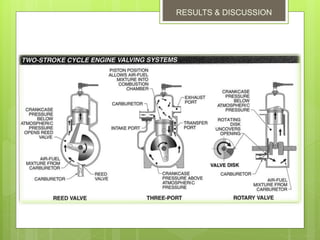
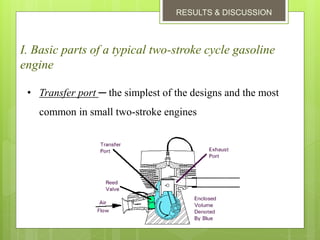
2. The basic parts are the piston, cylinder block, crankshaft, connecting rod, flywheel, spark plug, inlet port, exhaust port, and transfer port. Each downward piston stroke is a power stroke, and each upward stroke is a compression stroke.
3. It intakes and exhausts on the same stroke, achieving two cycles per revolution compared to one cycle per two revolutions for a four-stroke. However, its scavenging is less efficient, resulting in lower thermal