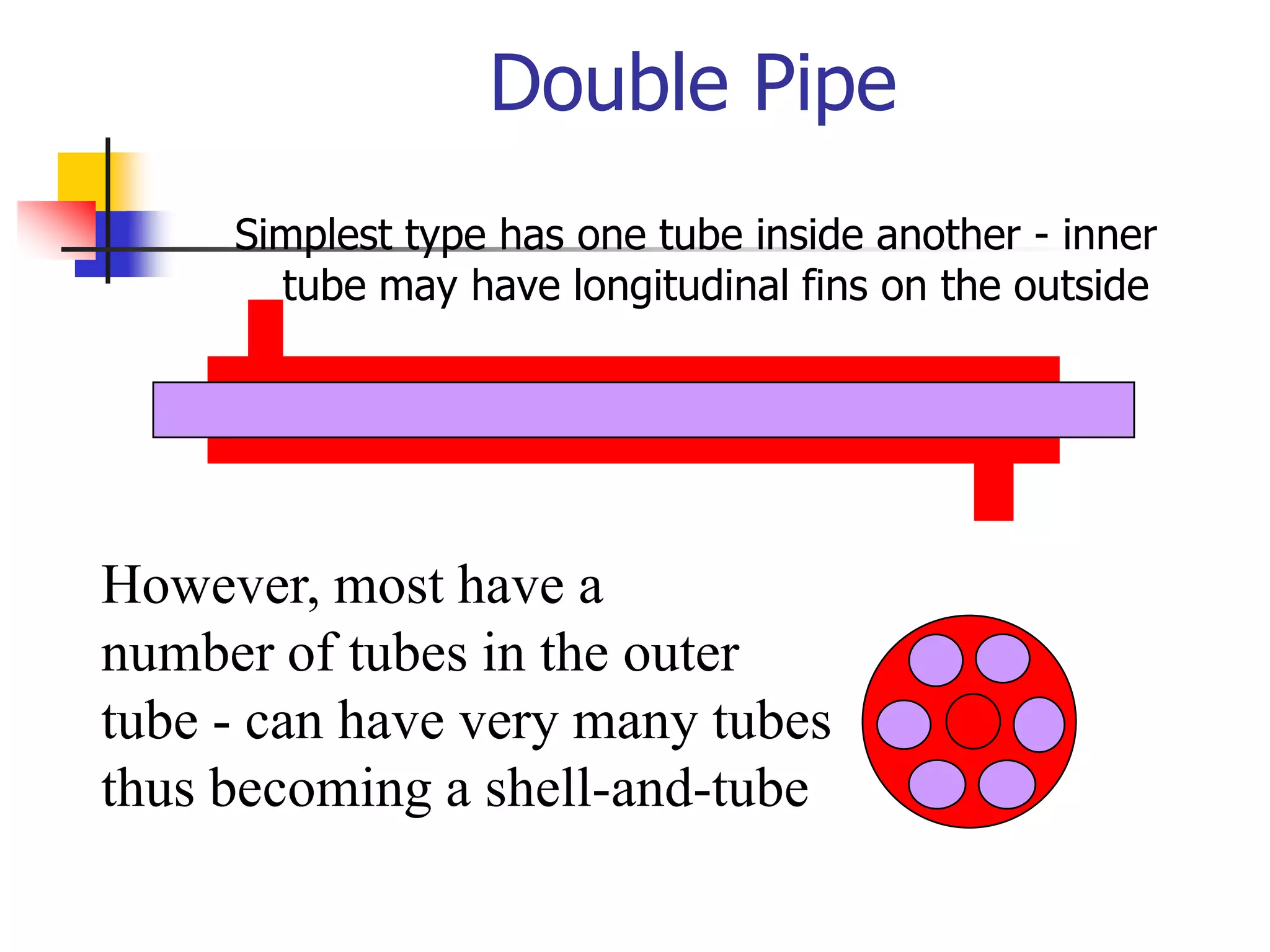
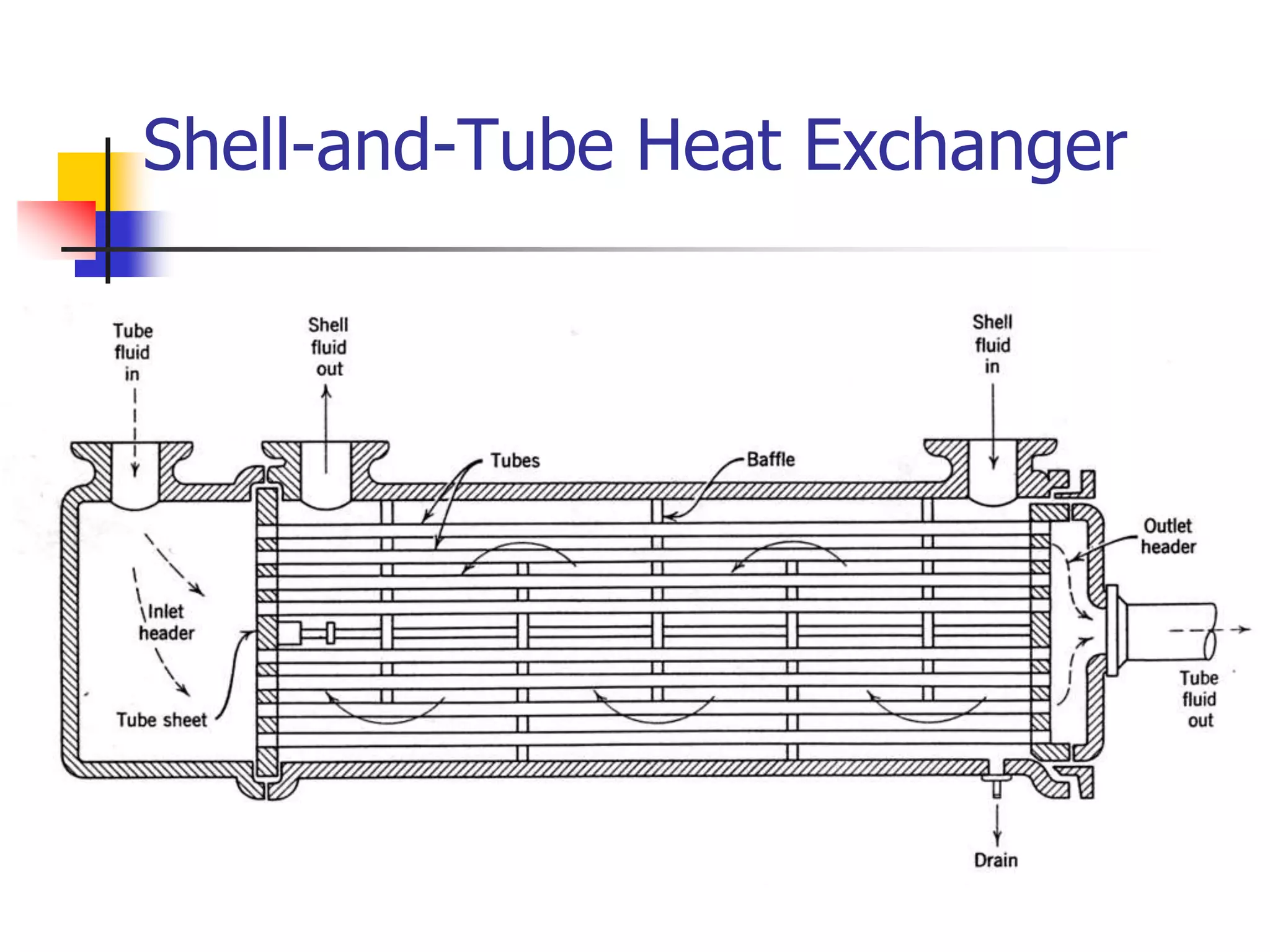
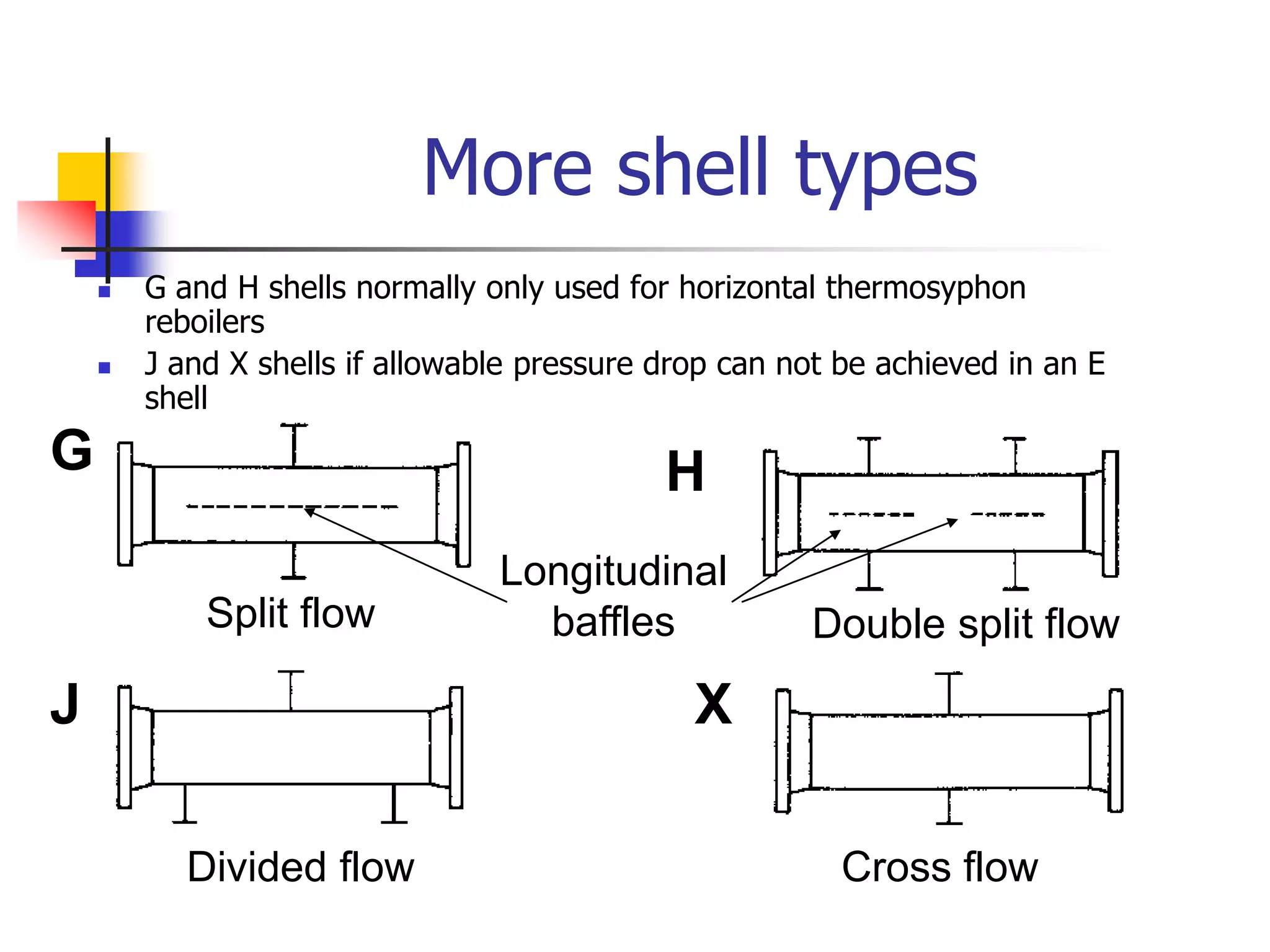
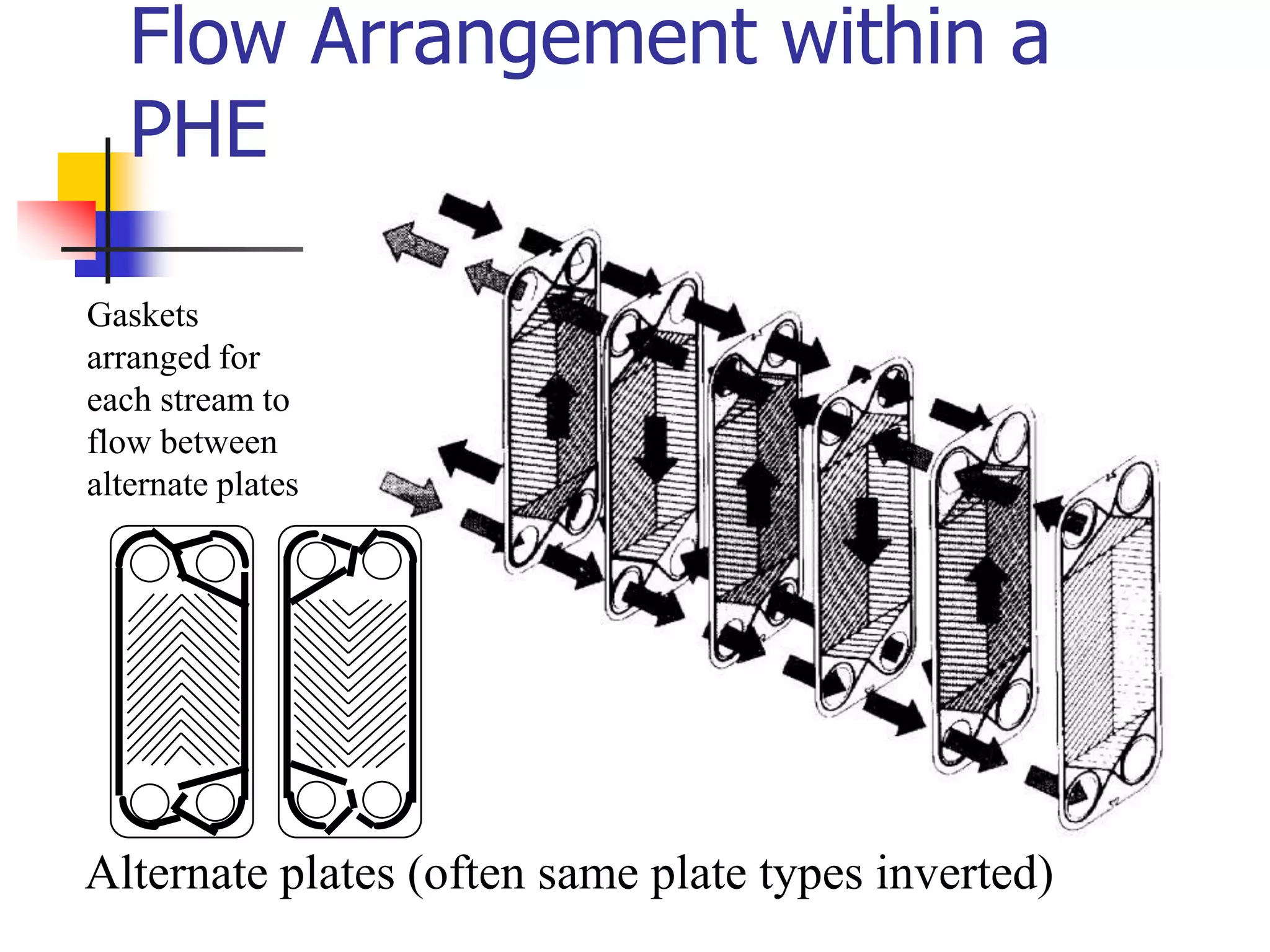
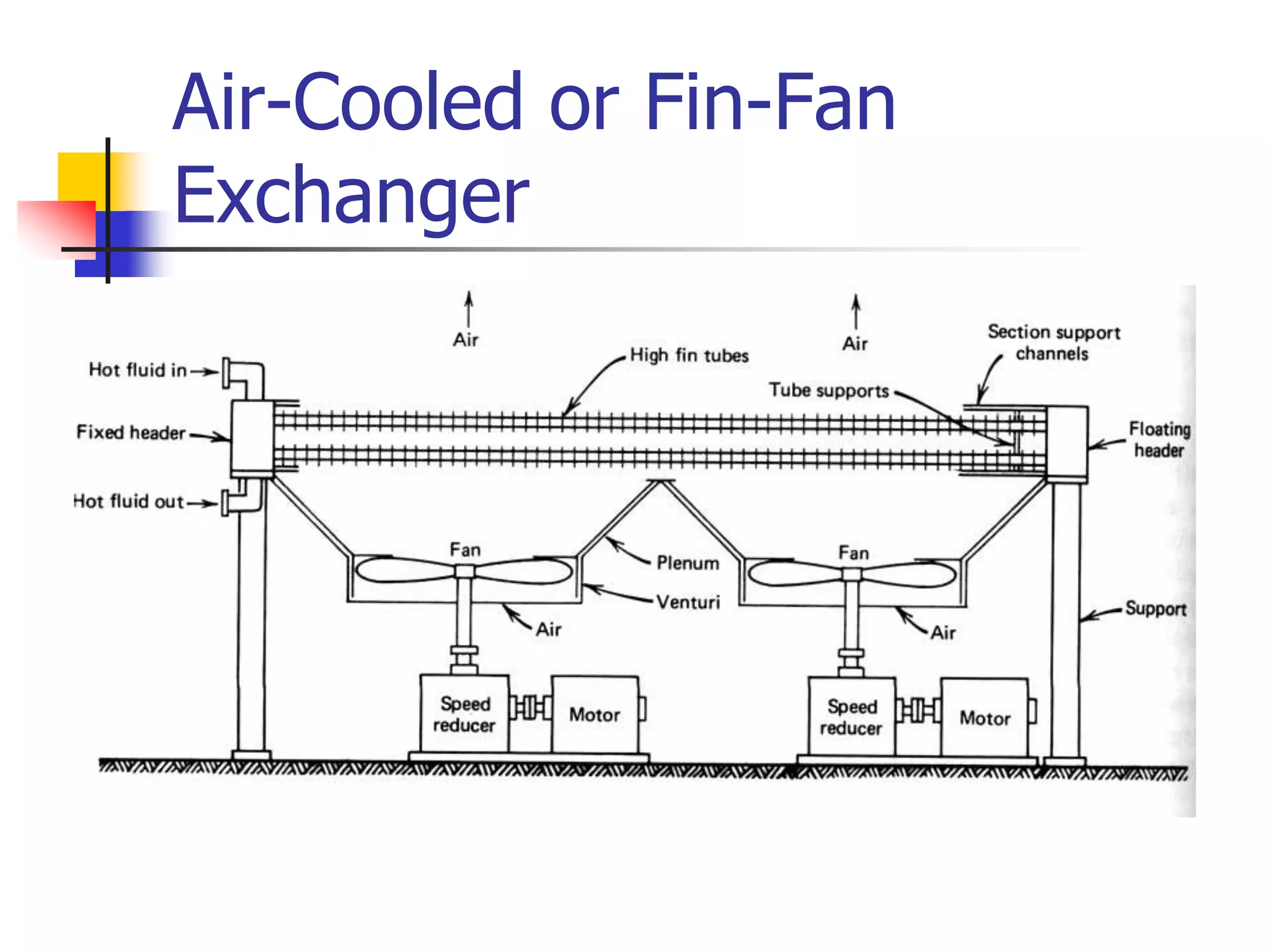
Heat exchangers allow the transfer of heat between two fluids without direct contact. The main types are shell-and-tube, plate, air-cooled, and spiral. Shell-and-tube exchangers consist of tubes in a shell and are the most common, used across many industries. Plate exchangers use corrugated plates clamped together with gaskets to direct fluid flow. Spiral and air-cooled exchangers provide alternatives for applications where fouling is a problem.