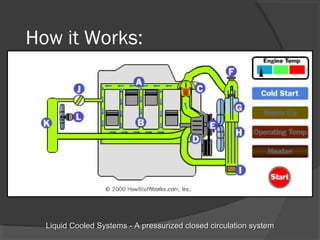
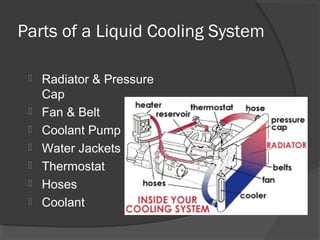
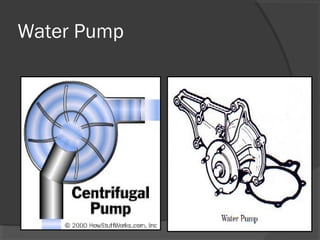
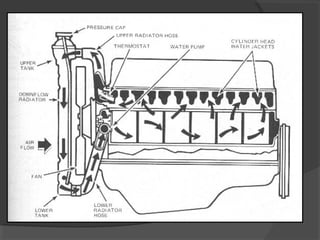
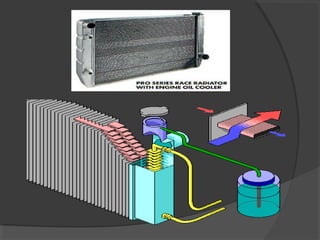
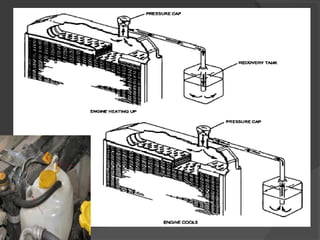
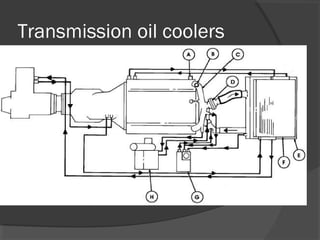
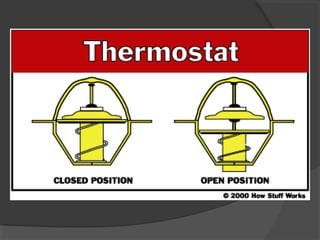
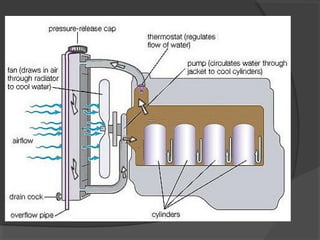
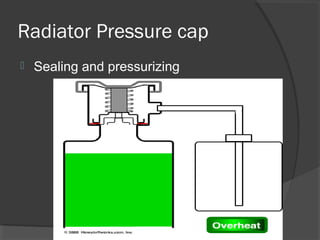
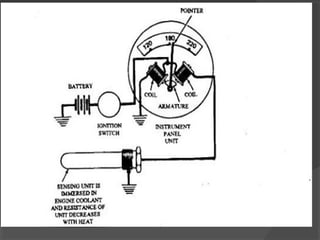
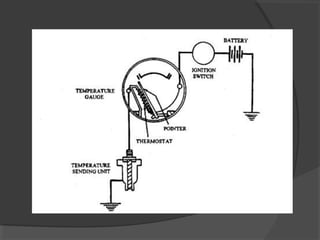
The engine cooling system works to maintain an efficient operating temperature for the engine. It uses either air or liquid cooling methods. Liquid cooling uses a pressurized closed system to circulate a coolant mixture of water and antifreeze through water jackets in the engine and back to a radiator, where a fan helps dissipate heat to the air. Key components include the water pump, radiator, thermostat, hoses, and pressure cap. The cooling system works to absorb up to 35% of the engine's heat and reject it to keep components within their optimal temperature range.