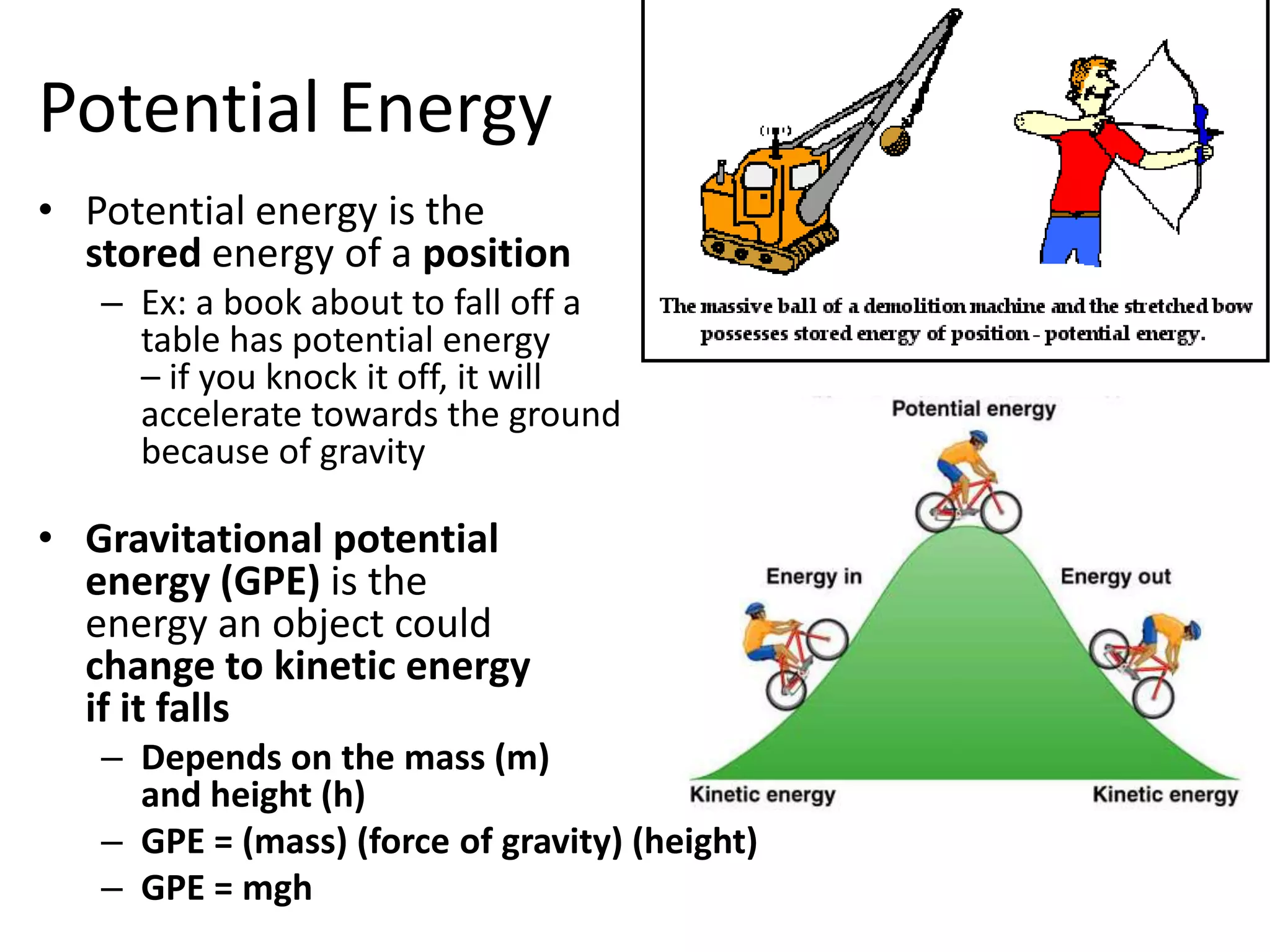
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion that an object possesses due to its mass and velocity. It can be transferred between objects through momentum or forces. The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or changed from one form to another, such as potential energy transforming to kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is calculated as one-half the mass times the velocity squared (KE=1/2mv^2), while potential energy depends on the mass and height of an object above the ground or another reference point and is calculated as mass times the force of gravity times height (PE=mgh).