Embed presentation
Downloaded 47 times
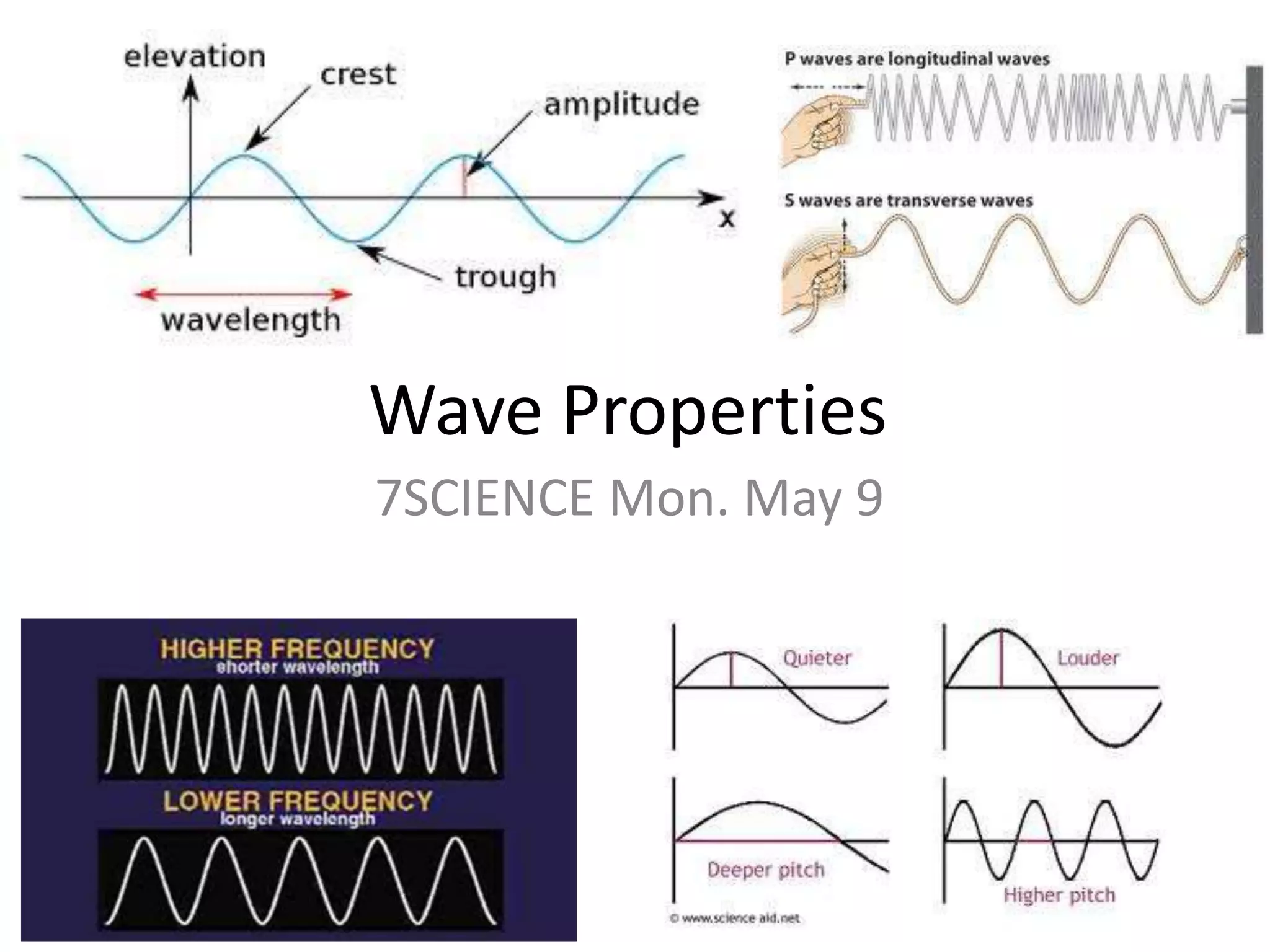

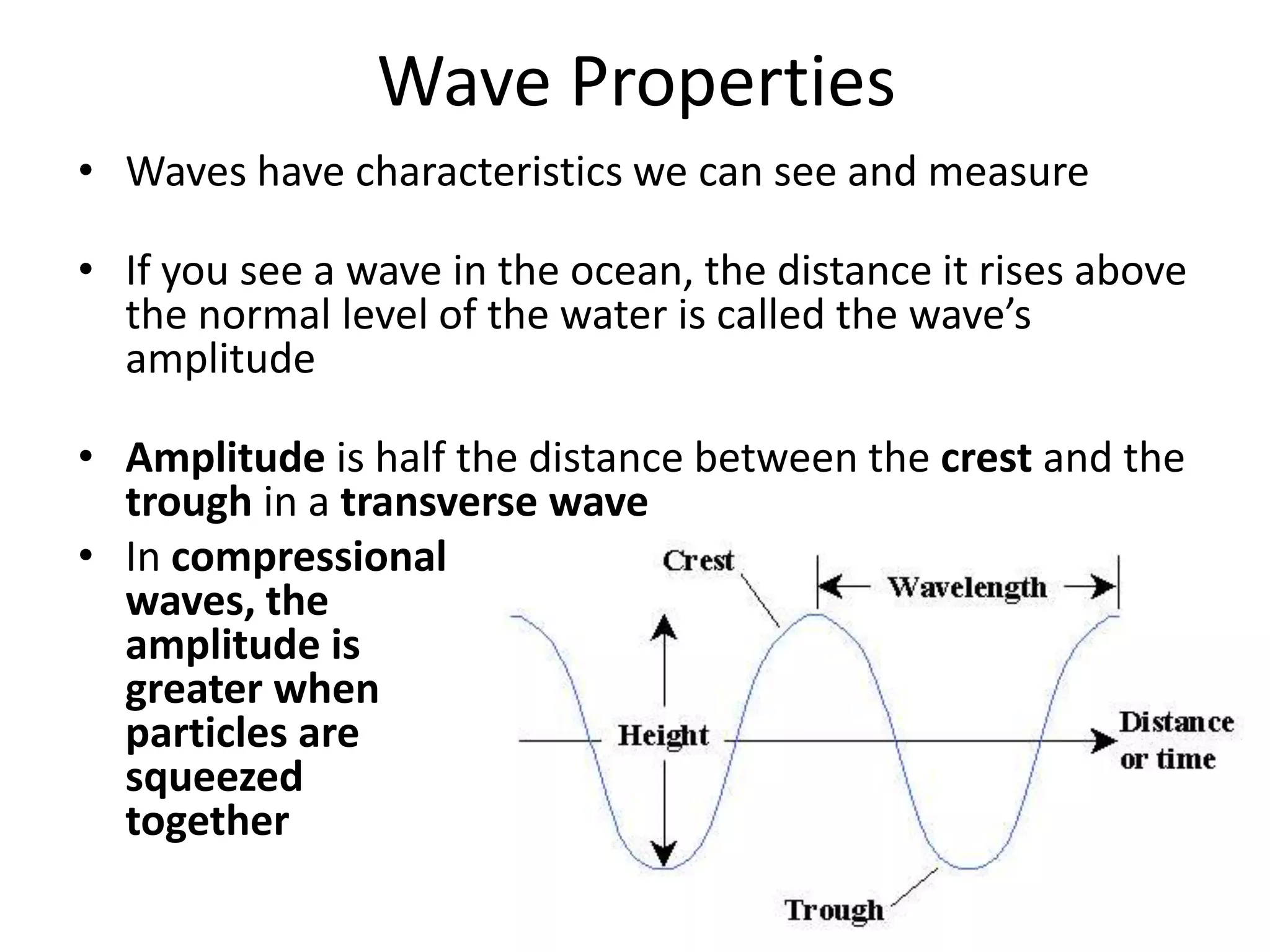

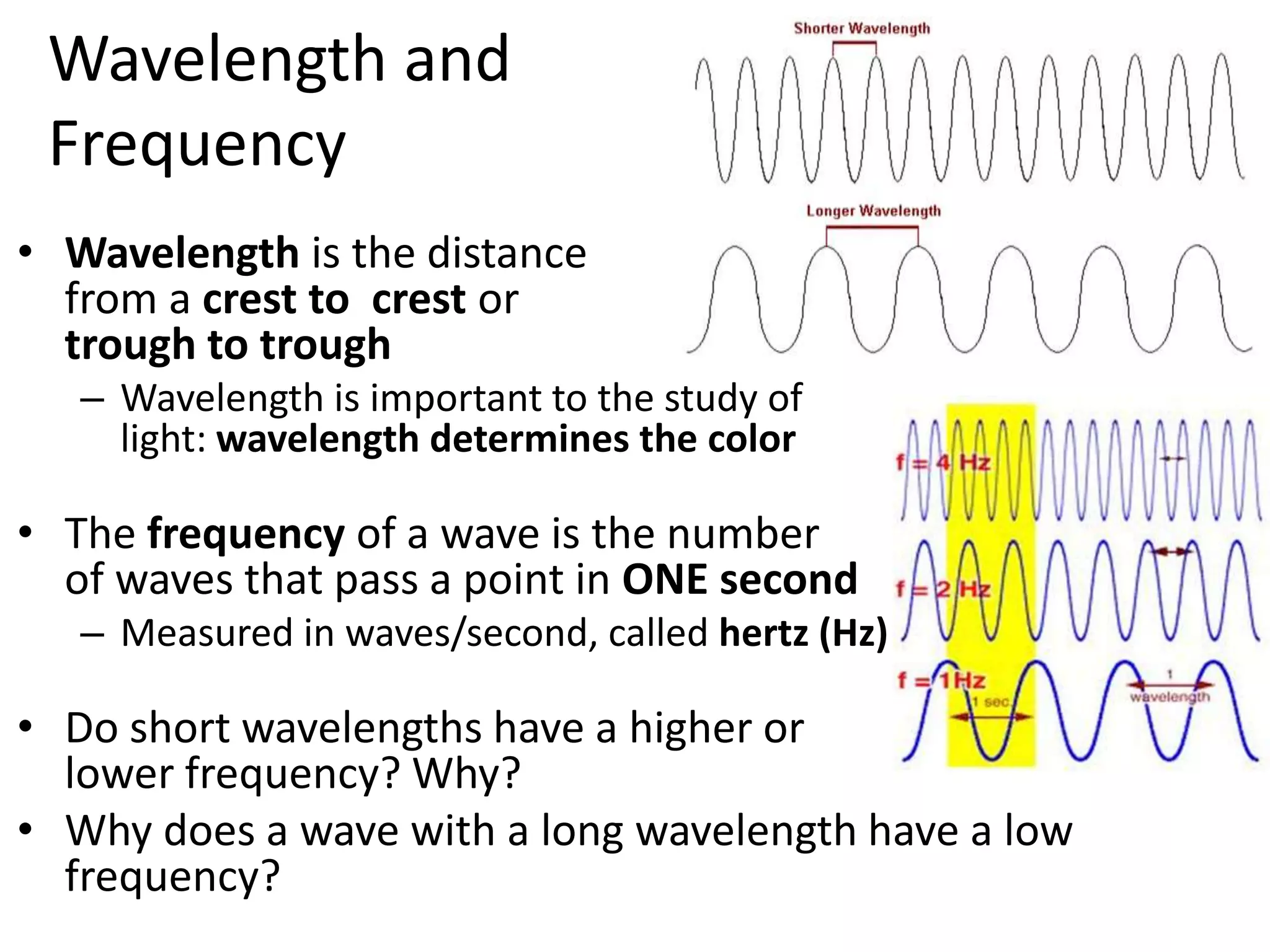
Waves have characteristics that can be observed and measured. The amplitude of a wave measures how far above or below the normal level it rises, and represents how much energy the wave carries. Amplitude is half the distance between the crest and trough of a transverse wave. Wavelength is the distance between two crests or troughs, and determines properties like a light wave's color. Frequency is the number of waves that pass a point in one second, measured in hertz, with higher frequencies associated with shorter wavelengths because more waves can fit in the same space.




