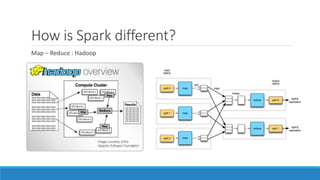
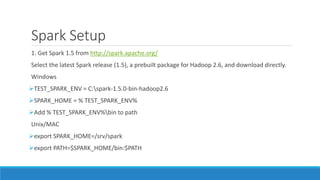
The document discusses energy analytics and the use of Apache Spark for large-scale data processing in the energy sector, focusing on customer segmentation and load forecasting use cases. It outlines the capabilities of Spark, highlighting its speed, ease of use, and integration with various data sources. The material also provides setup instructions for using Spark and discusses relevant algorithms such as k-means for clustering and regression for forecasting.