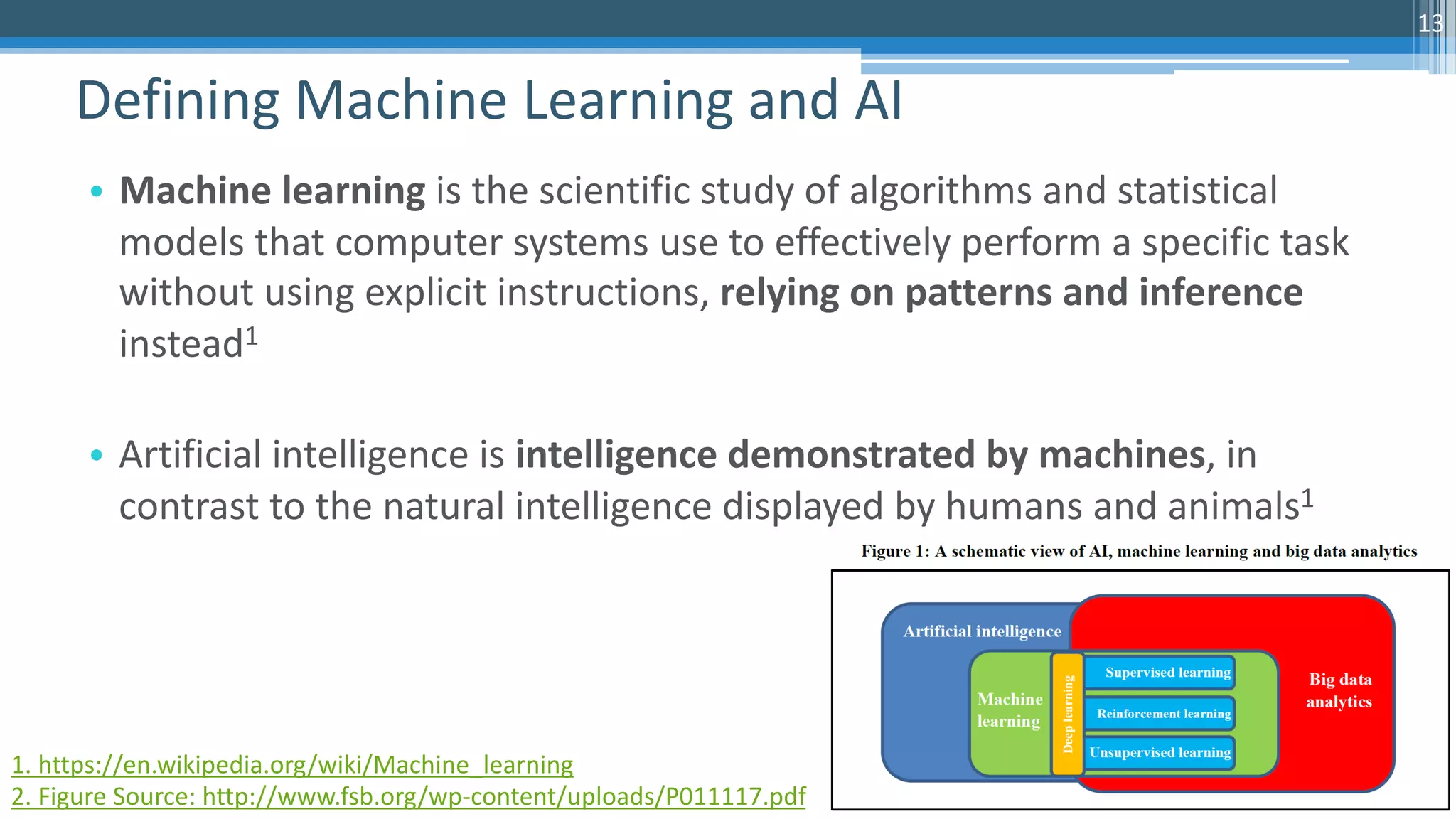
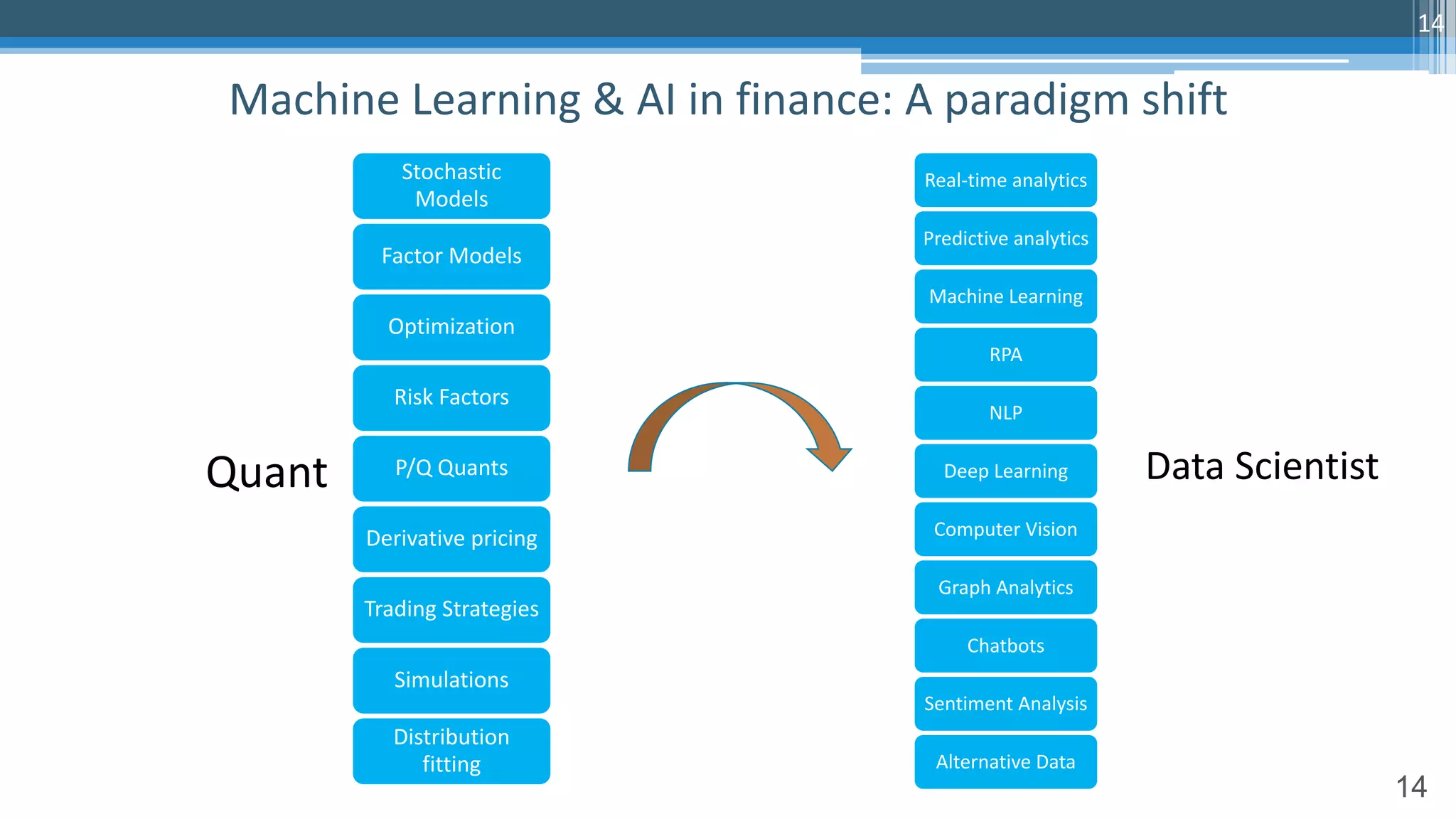
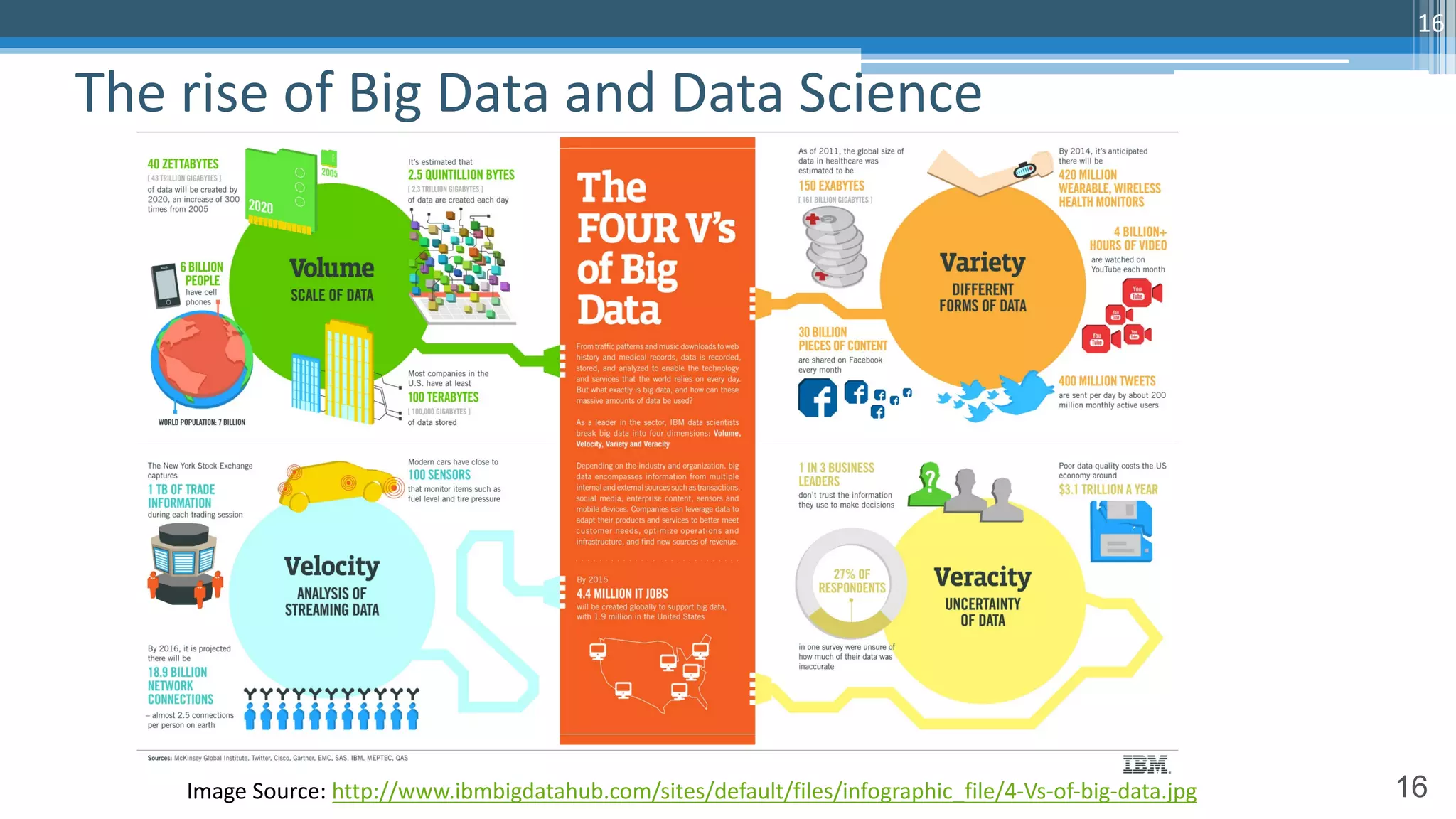
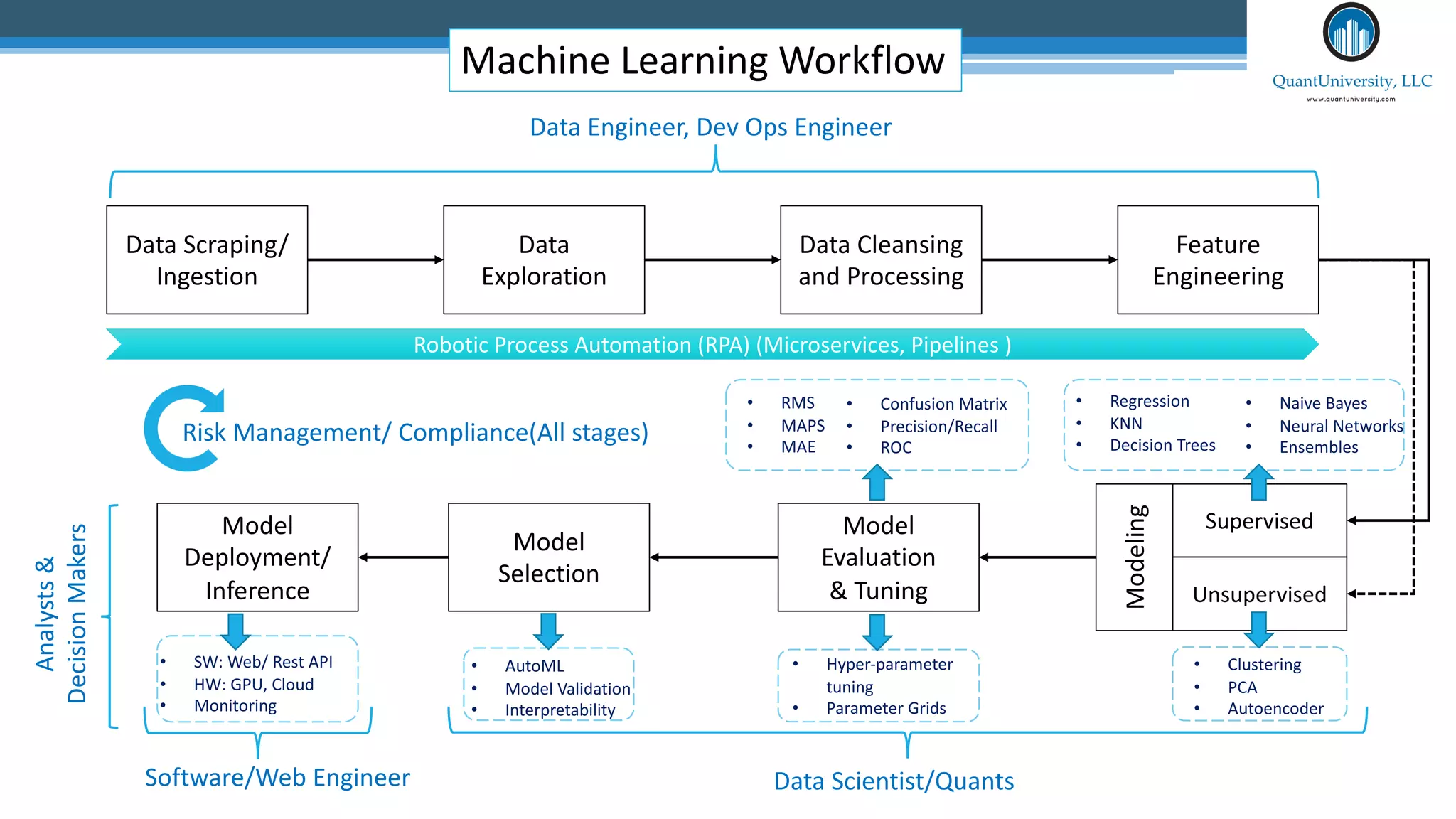
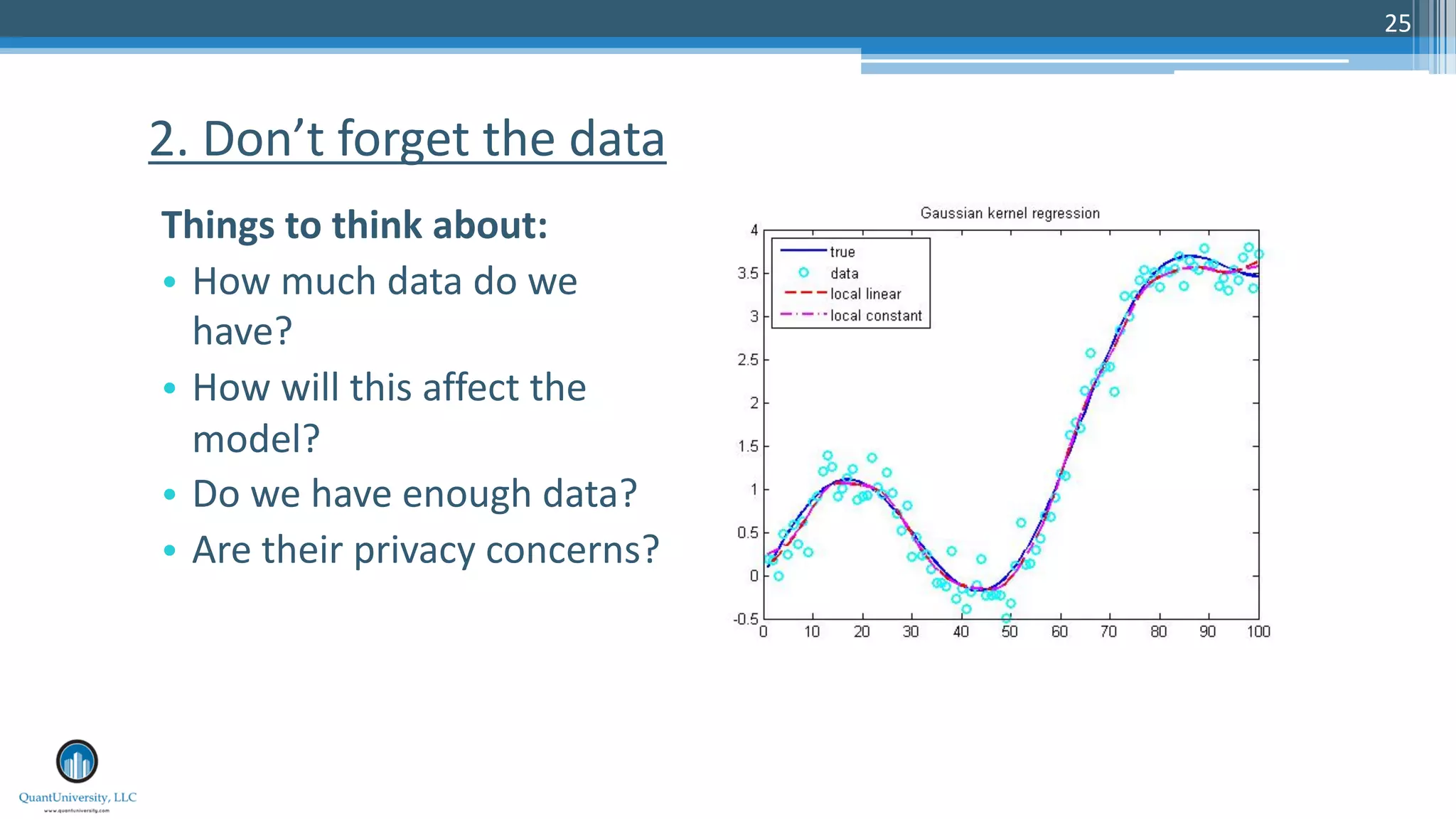
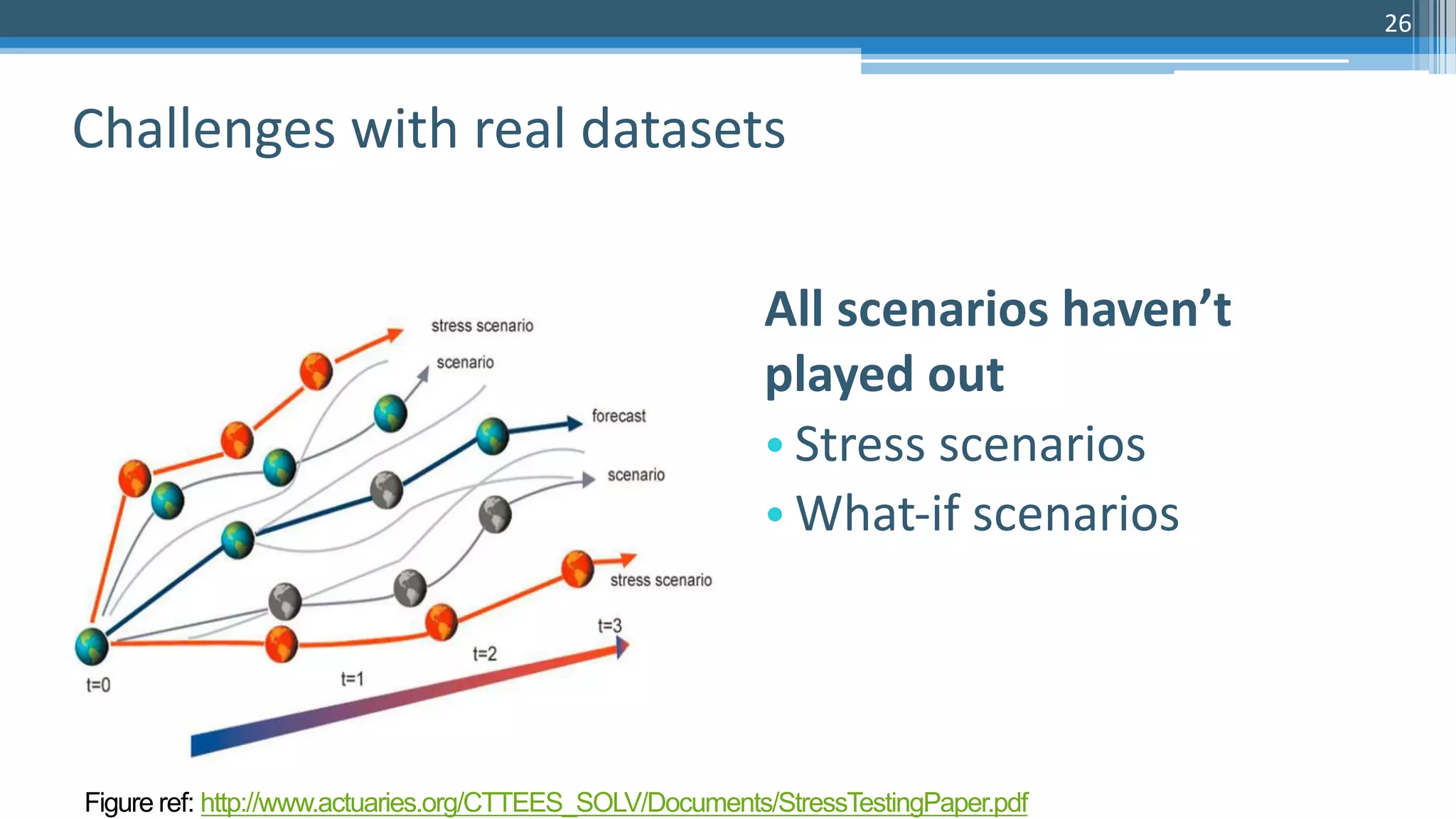
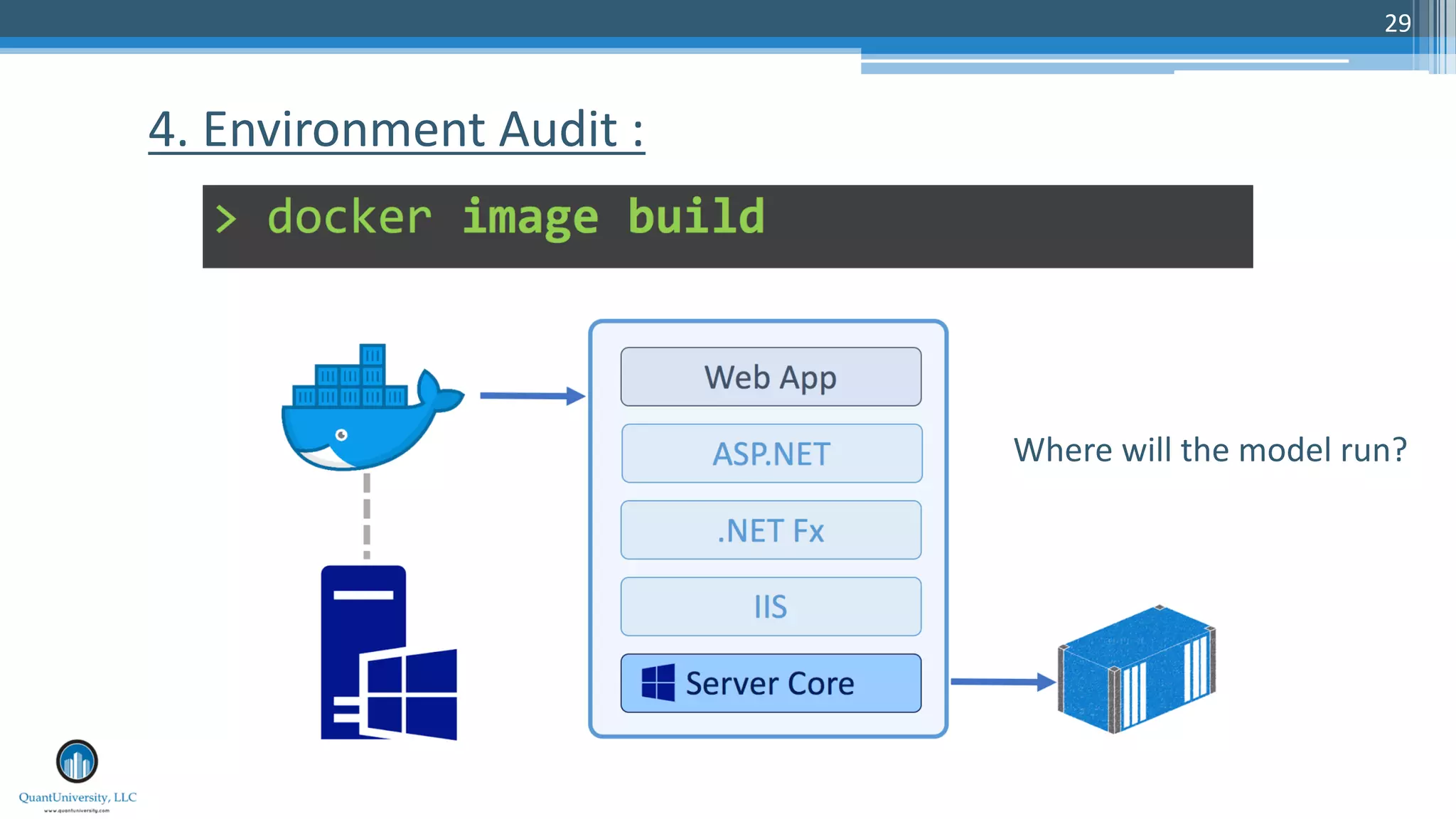
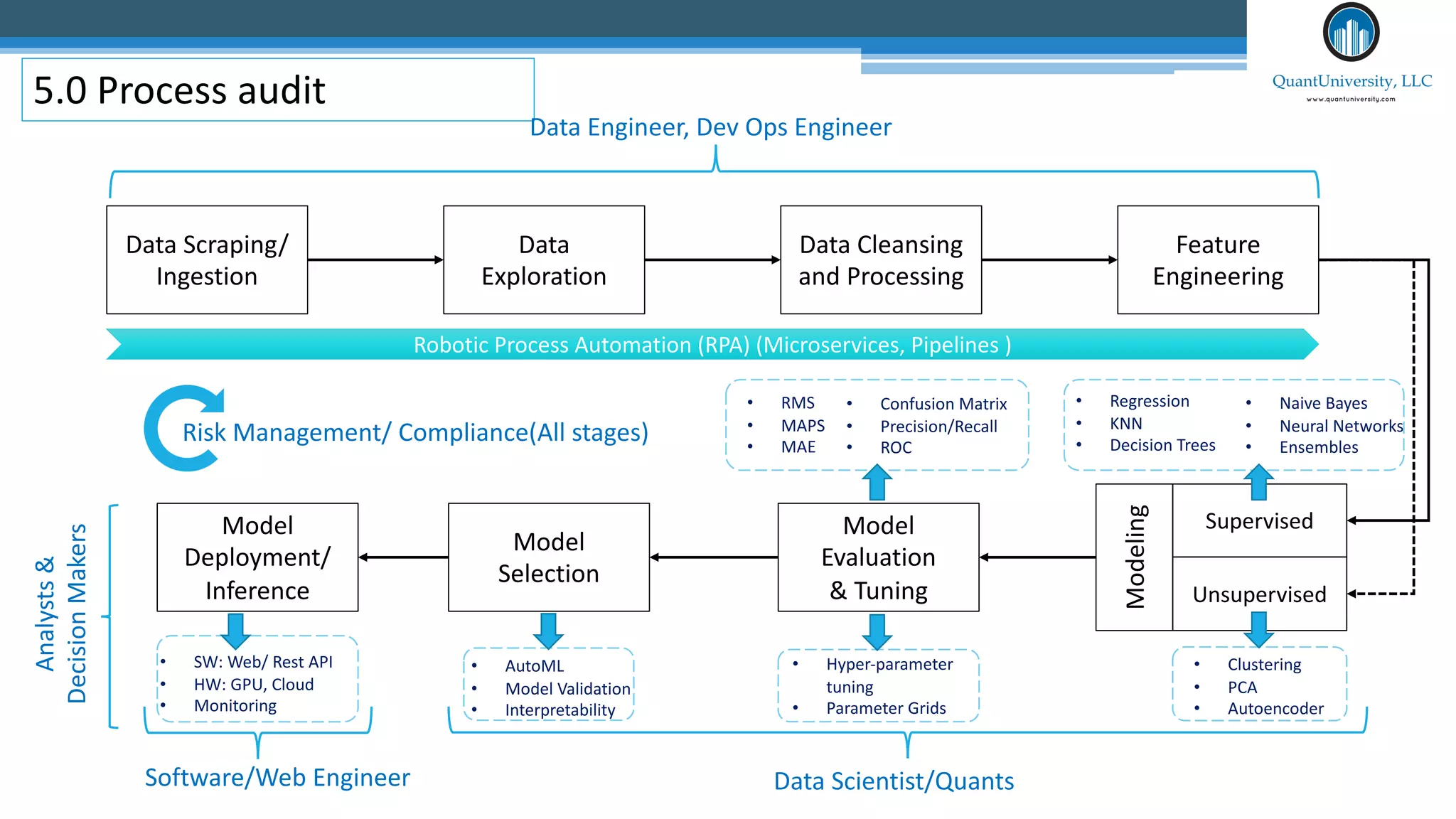
The document discusses algorithmic auditing within the context of AI and machine learning in finance, emphasizing the importance of validating algorithms, data, and processes for effective implementation. It outlines five key aspects to consider during auditing, including use cases, data quality, model evaluation, operational environment, and auditing processes. Sri Krishnamurthy, the presenter, highlights the relevance of algorithmic auditing in addressing biases, ensuring fairness, and enhancing interpretability in financial applications.