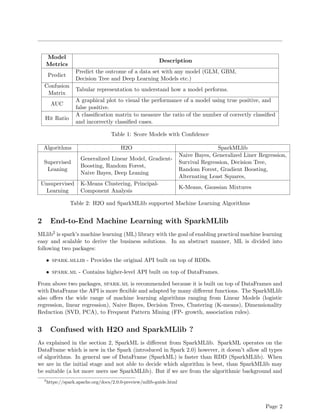
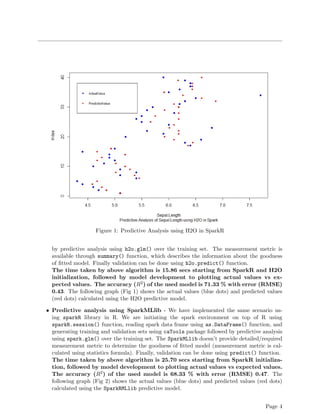
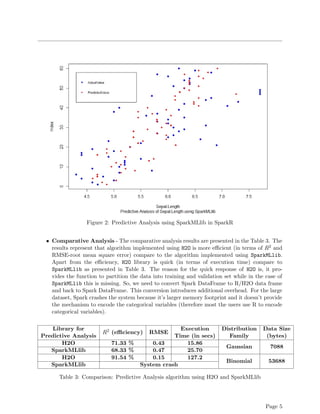
This technical report compares the machine learning libraries H2O and SparkMLlib. It finds that H2O offers more advanced machine learning algorithms and faster performance for tasks like linear modeling and random forests. Experiments show predictive analysis using H2O's GLM took 15.86 seconds and achieved 71.33% accuracy on iris data, while SparkMLlib's GLM took 25.70 seconds and had lower 68.33% accuracy. The report concludes H2O provides more efficient algorithms and integration with Spark for machine learning on big data.