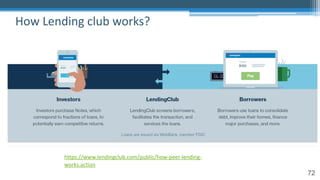
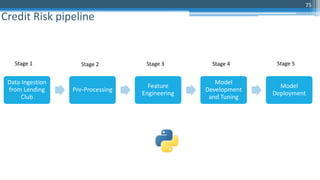
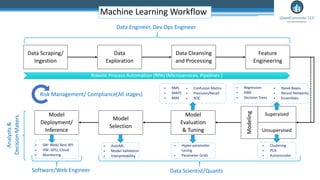
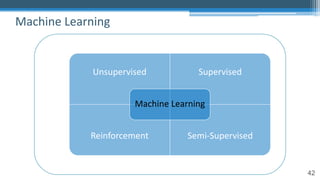
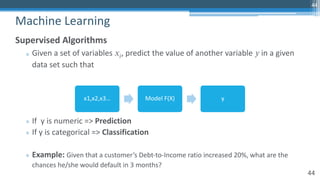
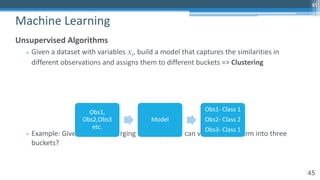
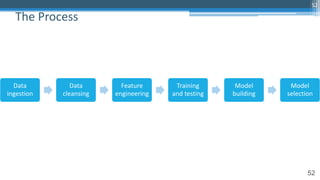
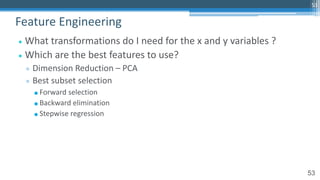
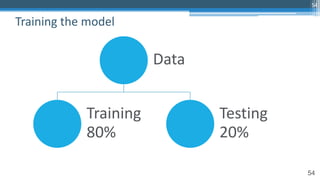
The document provides an overview of machine learning and artificial intelligence applications in finance, emphasizing its role in transforming investment strategies and risk management. It discusses key trends, case studies, and the importance of data science in enhancing financial analytics. Additionally, the speaker, Sri Krishnamurthy, highlights educational initiatives to train professionals in these technologies at QuantUniversity.






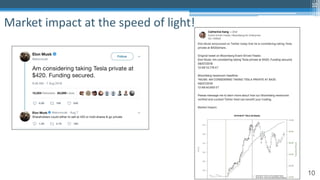
















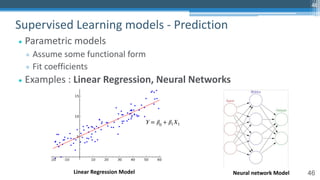
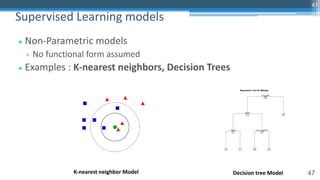
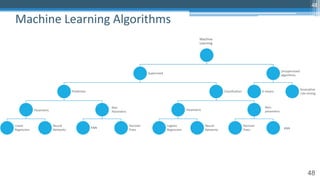
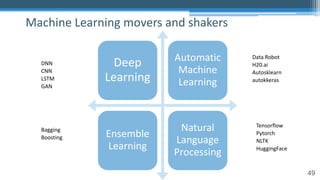
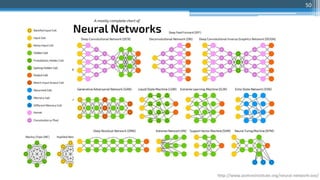




![65
AI and Machine Learning in Production
https://www.itnews.com.au/news/hsbc-societe-generale-run-
into-ais-production-problems-477966
Kristy Roth from HSBC:
“It’s been somewhat easy - in a funny way -
to get going using sample data, [but] then
you hit the real problems,” Roth said.
“I think our early track record on PoCs or
pilots hides a little bit the underlying issues.
Matt Davey from Societe Generale:
“We’ve done quite a bit of work with RPA
recently and I have to say we’ve been a bit
disillusioned with that experience,”
“the PoC is the easy bit: it’s how you get that
into production and shift the balance”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quforindia-210607002555/85/Qu-for-India-QuantUniversity-FundRaiser-65-320.jpg)