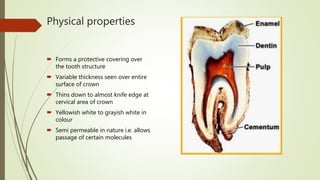
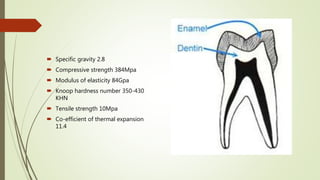
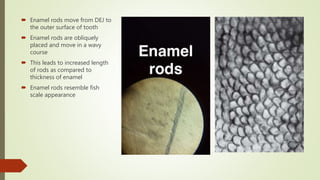
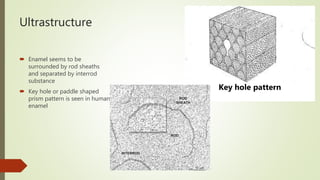
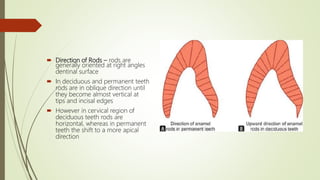
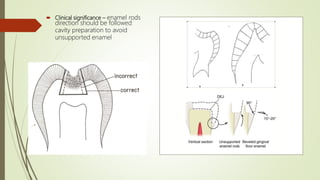
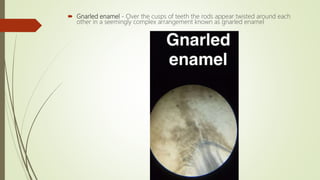
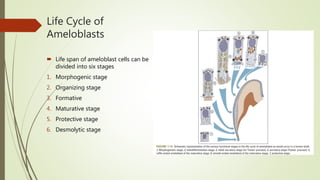
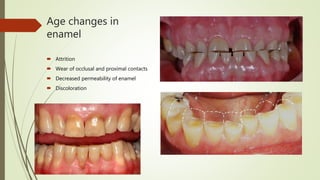
This document provides information on the physical, chemical, structural, and ultrastructural properties of enamel. It discusses how enamel forms a protective covering on the tooth and consists primarily of calcium hydroxyapatite. Enamel's structure includes enamel rods that run from the dentin-enamel junction to the outer surface. It also describes features like Hunter-Schreger bands, incremental lines of Retzius, and surface structures such as enamel tufts. The document outlines the life cycle of ameloblasts and process of amelogenesis, and discusses implications for clinical applications like fluoridation and acid etching.