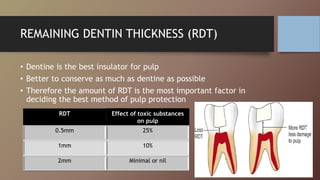
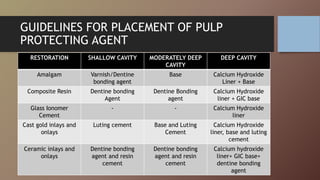
This document discusses pulp protection in restorative dentistry. It outlines the goals of preserving pulp health and various irritants that can harm the pulp. The amount of remaining dentin thickness is an important factor in determining the appropriate protection method. Various protective agents are described, including cavity sealants, liners, and bases made of materials like varnish, resin bonding agents, calcium hydroxide, and glass ionomer cement. Guidelines are provided for selecting the proper agent based on restoration type and cavity depth. Indirect and direct pulp capping procedures are also summarized.