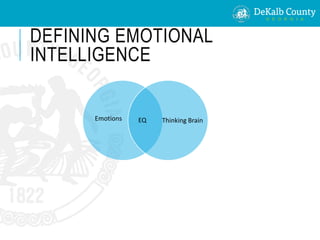
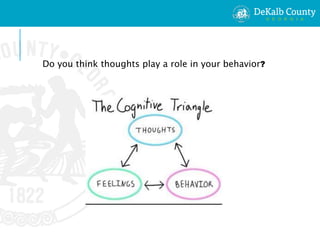
This document provides an overview of emotional intelligence for interns. It defines emotional intelligence as recognizing one's own and others' feelings, motivating oneself, and managing relationships. It identifies common emotions and negative thought patterns like "all-or-nothing thinking" and explains how to develop emotional intelligence through self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation, empathy, and social skills. Contact information is provided for the human resources department.