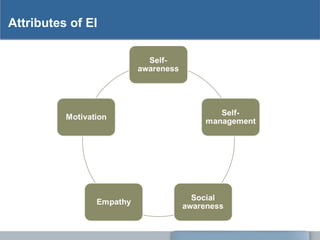
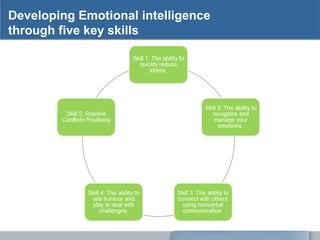
The document explains the nature of emotions, distinguishing between positive and negative emotions and outlining their functions, such as arousal and motivation. It discusses emotional intelligence (EQ), its attributes like self-awareness and empathy, and its importance in improving personal health, relationships, and workplace performance. The document also provides strategies for developing emotional intelligence and enhancing non-verbal communication.