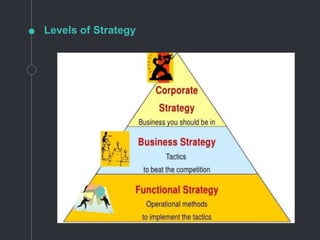
Strategic management involves managerial decisions and actions that shape a corporation's long-term performance, including environmental scanning, strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation. It operates at three levels: corporate-level strategy focuses on organization-wide policies, business-level strategy addresses competition within markets, and functional-level strategy pertains to specific functional areas. The importance of strategic management lies in enhancing organizational performance, adapting to environmental changes, and enabling proactive decision-making to capitalize on opportunities.