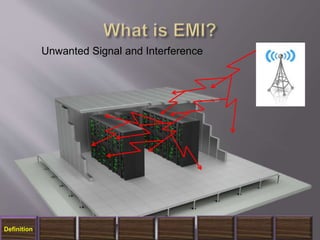
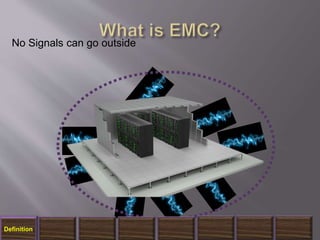
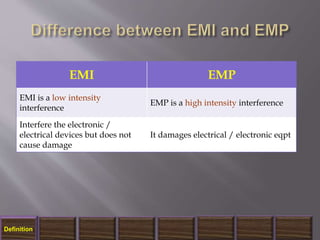
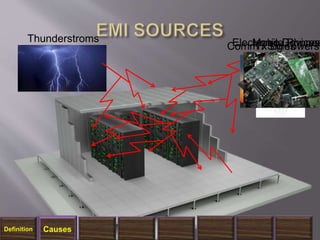
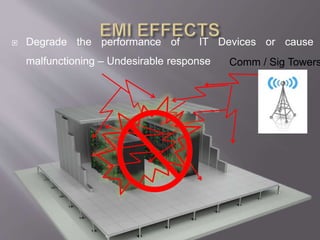
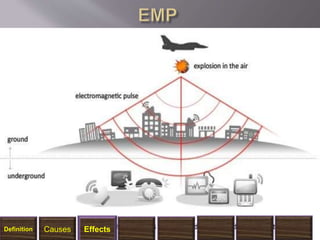
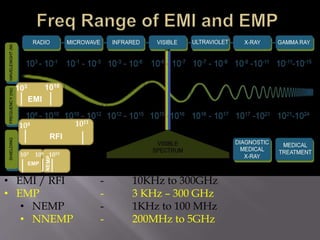
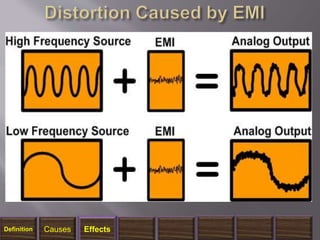
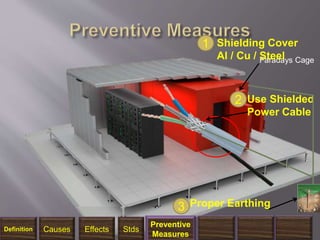
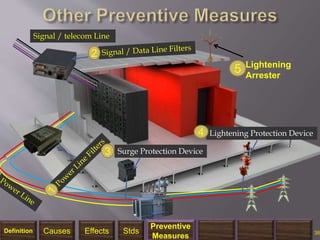
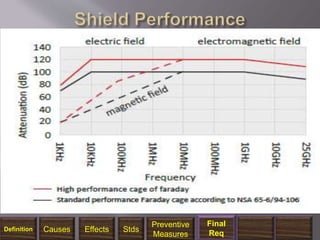
The document discusses electromagnetic interference (EMI), electromagnetic pulse (EMP), and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), detailing their definitions, sources, effects on electronic equipment, and applicable military standards for protection. It outlines preventive measures, including shielding techniques, surge protection, and specific military standards for C4I facilities. The document provides various options for shielding and power supply integrity during such electromagnetic events and the associated advantages and disadvantages of each method.