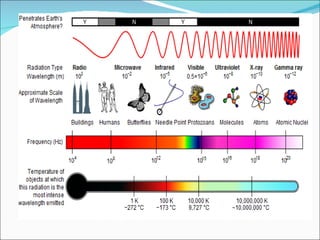
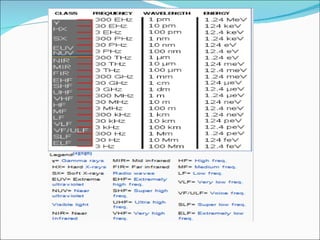
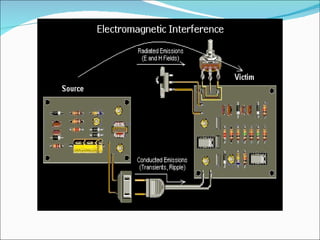
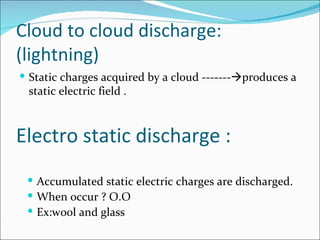
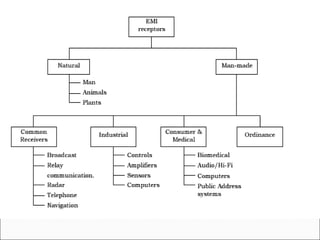
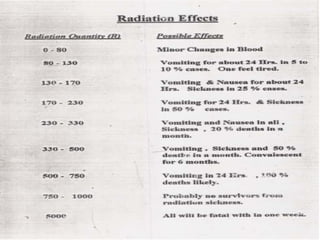
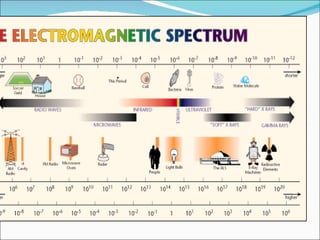
This document discusses electromagnetic interference (EMI), including definitions of key terms, sources of EMI, types of EMI, effects of EMI, and units used to specify EMI parameters. It addresses conducted and radiated EMI, natural and man-made sources of EMI, intra-system and inter-system EMI, and thermal and non-thermal biological effects of EMI. Measurement units covered include voltage, current, electric field strength, and magnetic field strength.