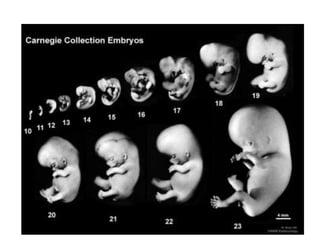
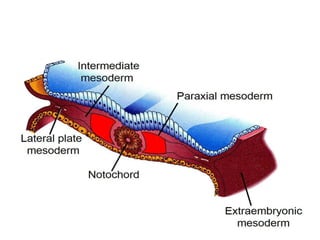
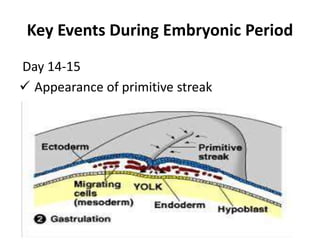
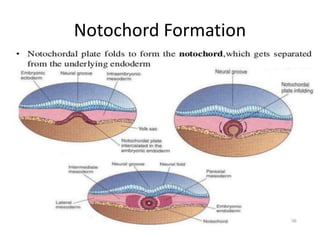
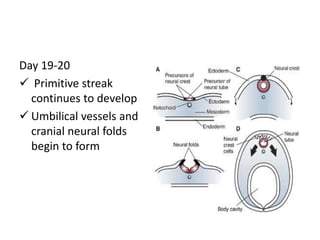
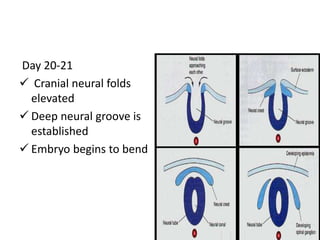
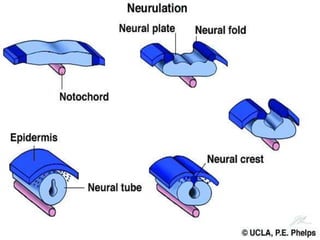
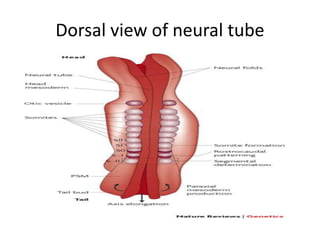
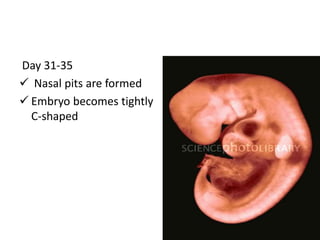
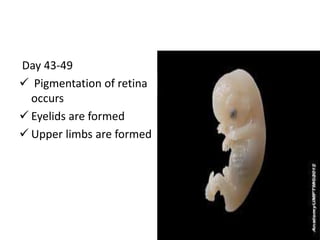
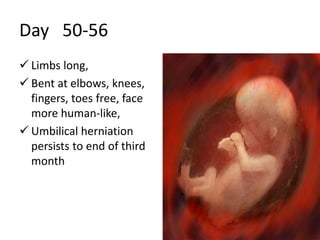
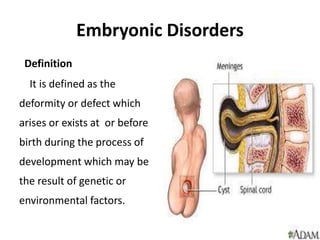
The document summarizes key aspects of embryonic development from weeks 3-8. It defines the embryonic period as the time of organogenesis from the three germ layers. Ectoderm forms skin and nervous system. Mesoderm forms muscles, bones, blood vessels and urogenital systems. Endoderm lines the gut and forms organs like liver and pancreas. It describes events like neural tube formation and development of limbs. The fetal period follows from week 9 to birth involving further growth and maturation. Common embryonic disorders are also listed.