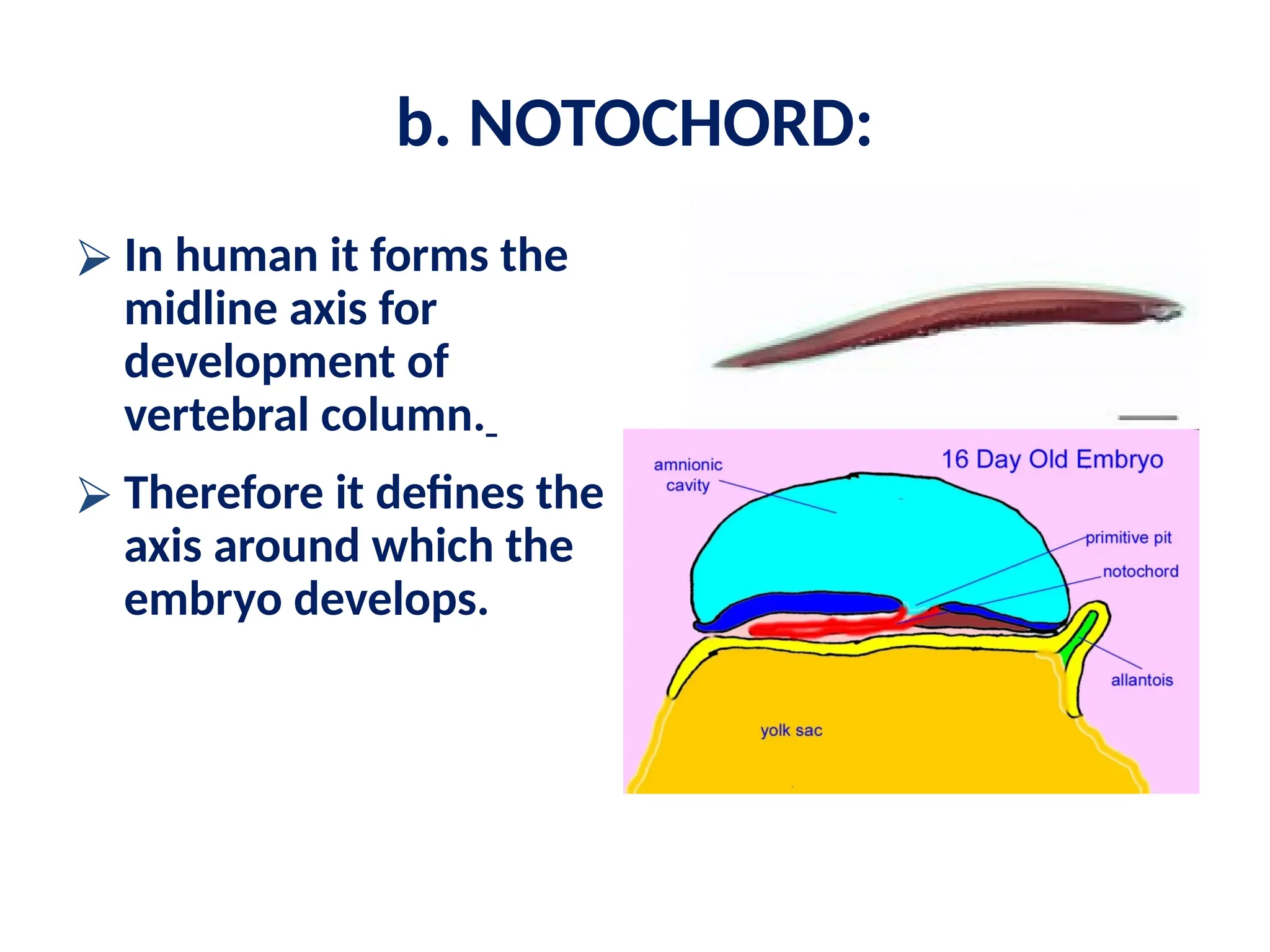
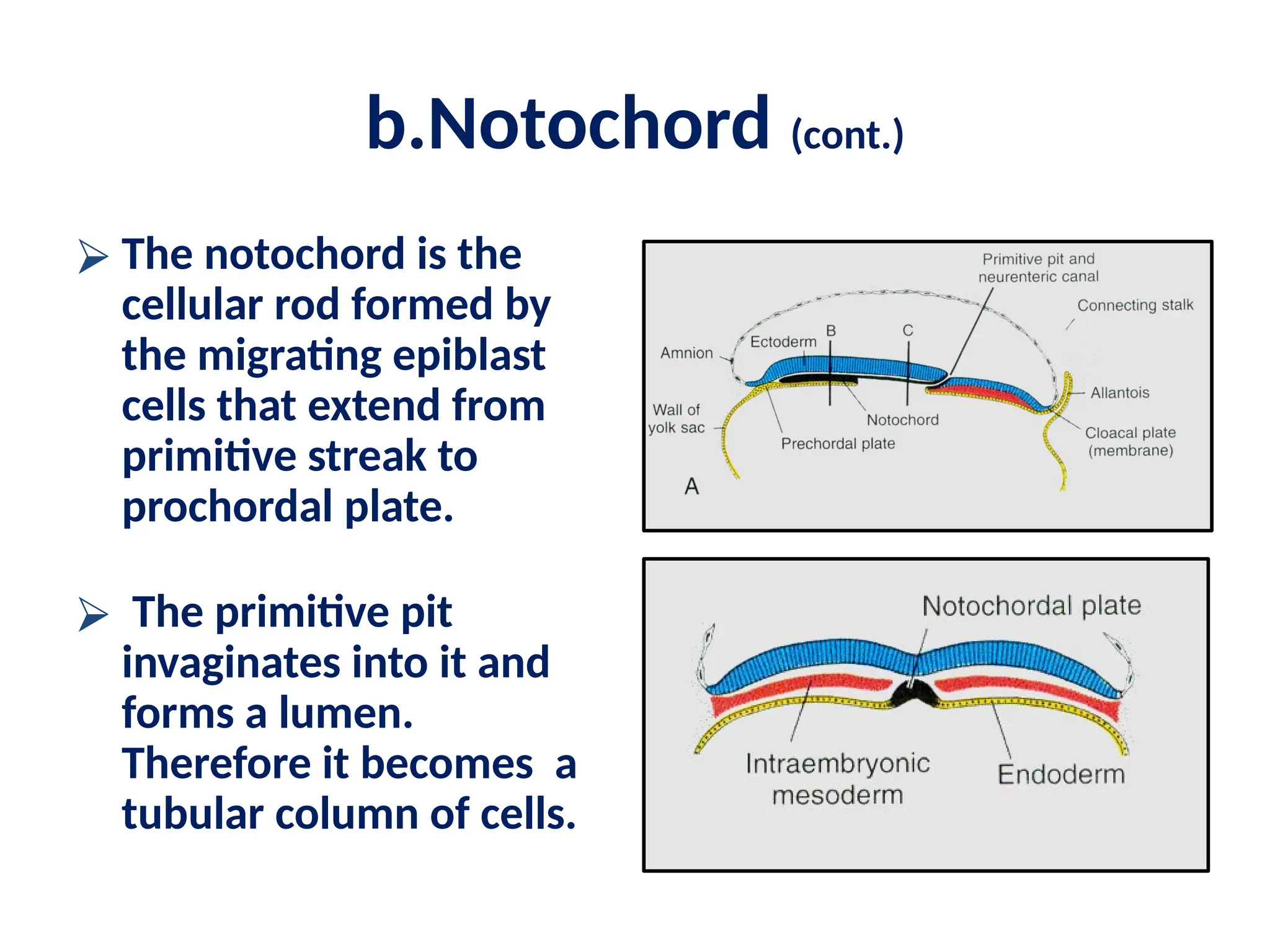
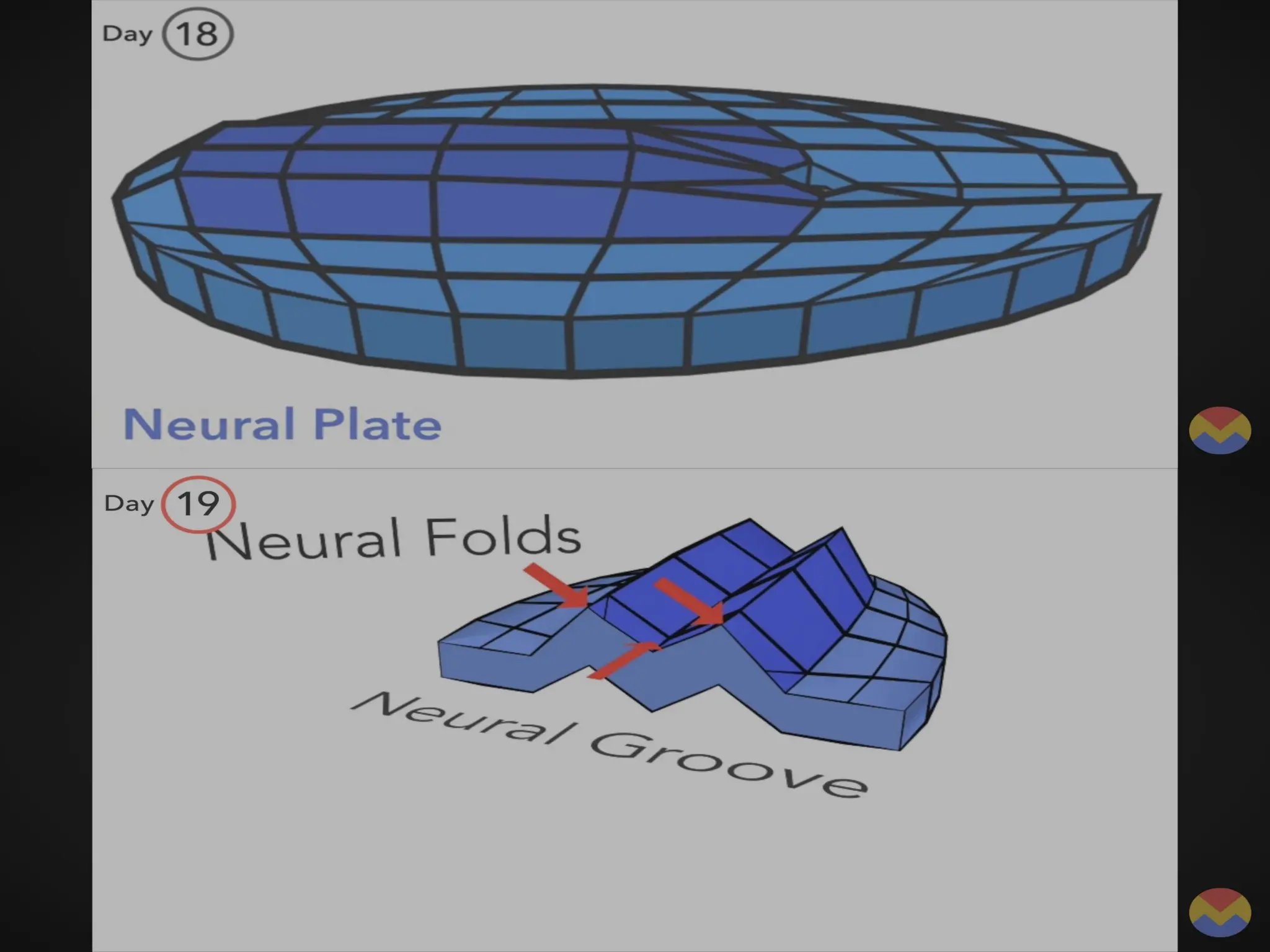
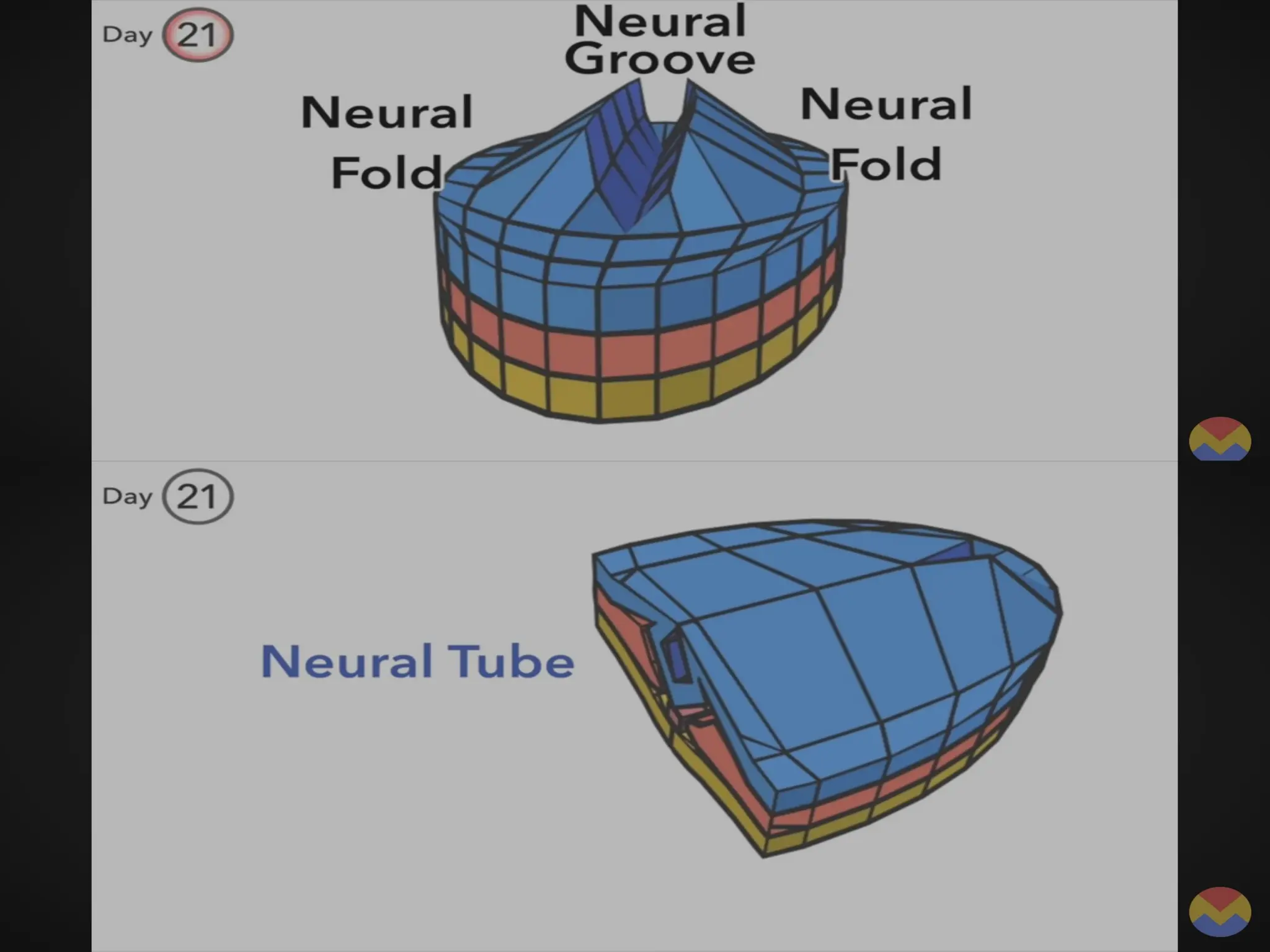
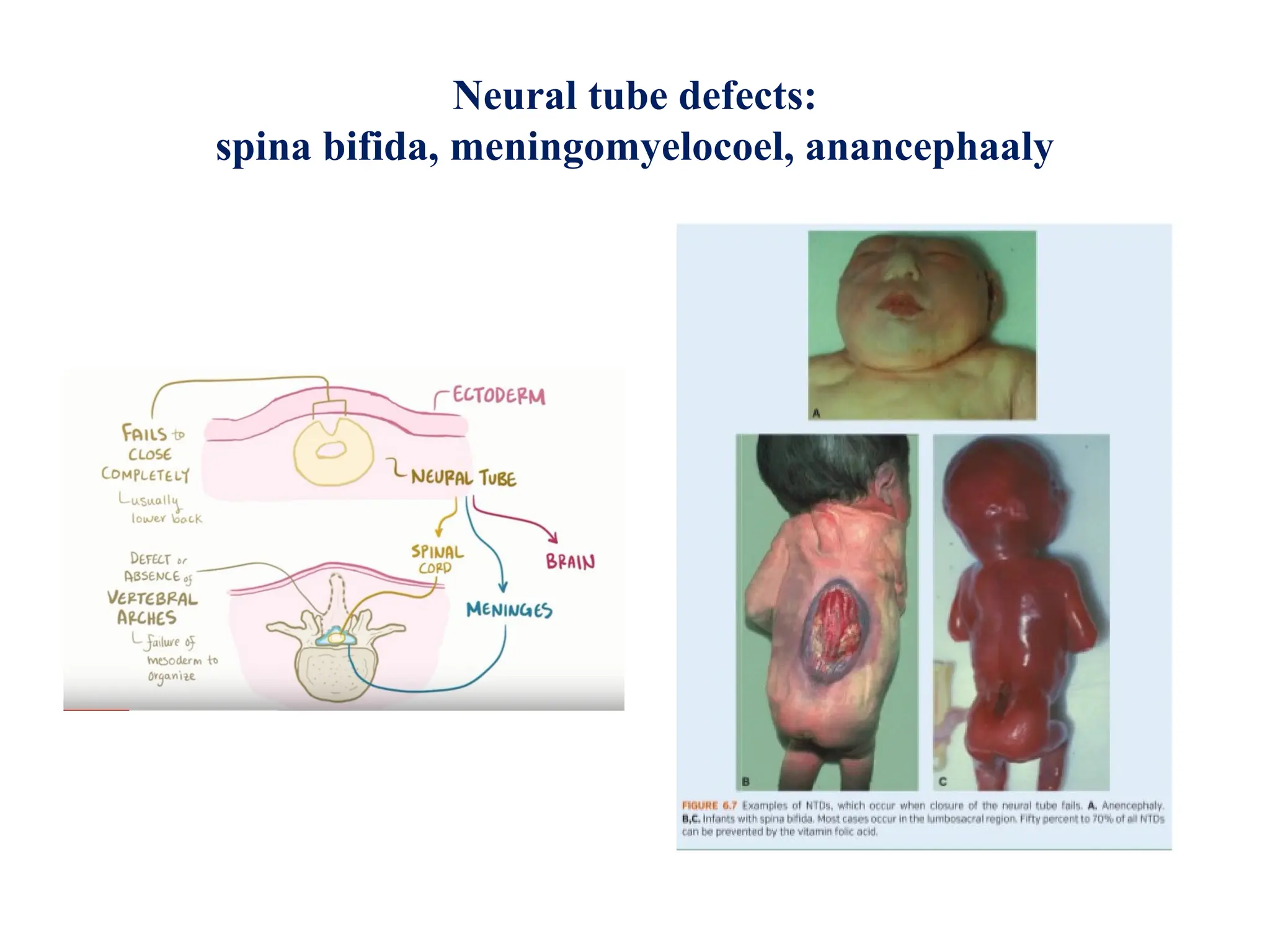
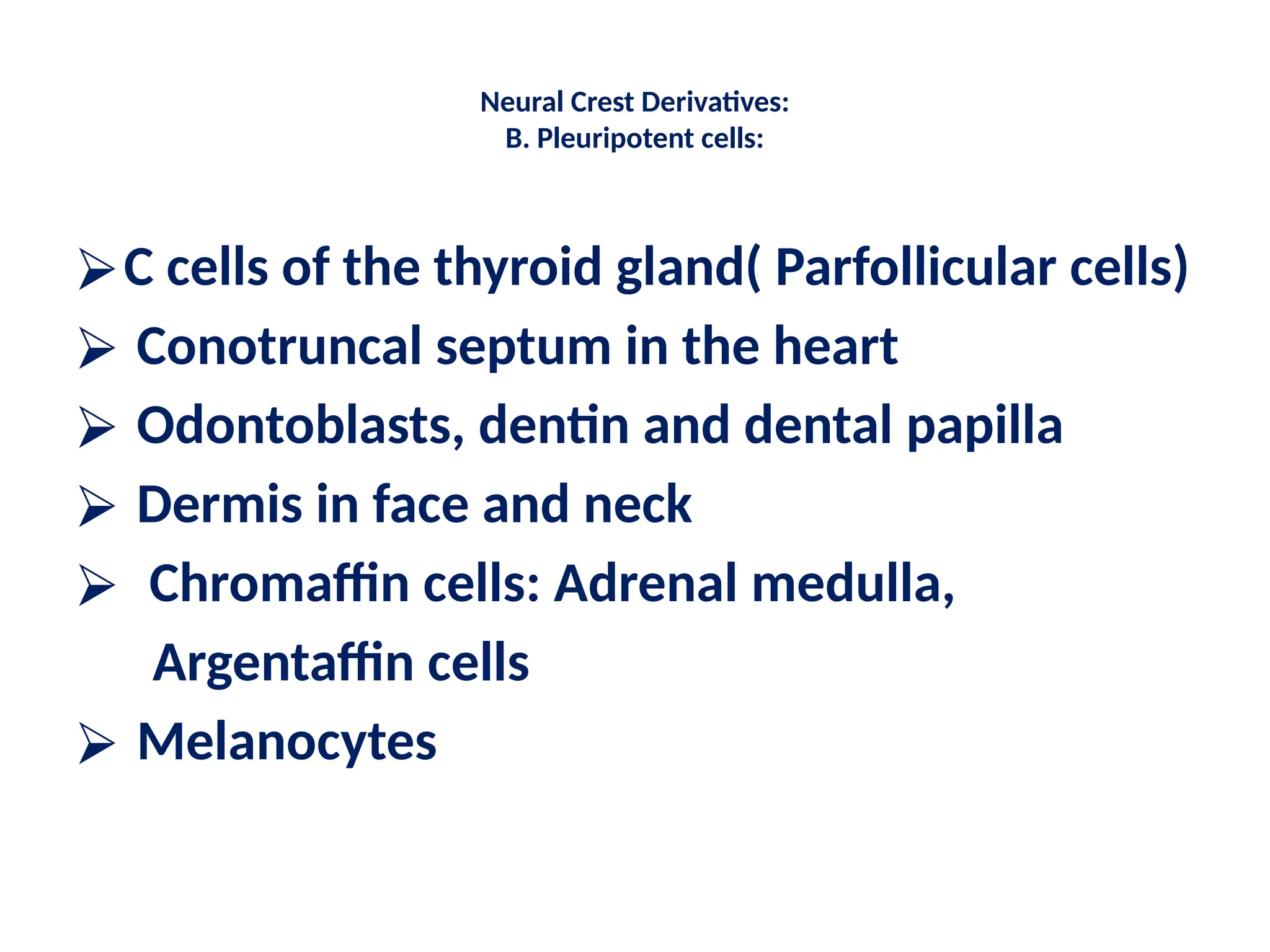
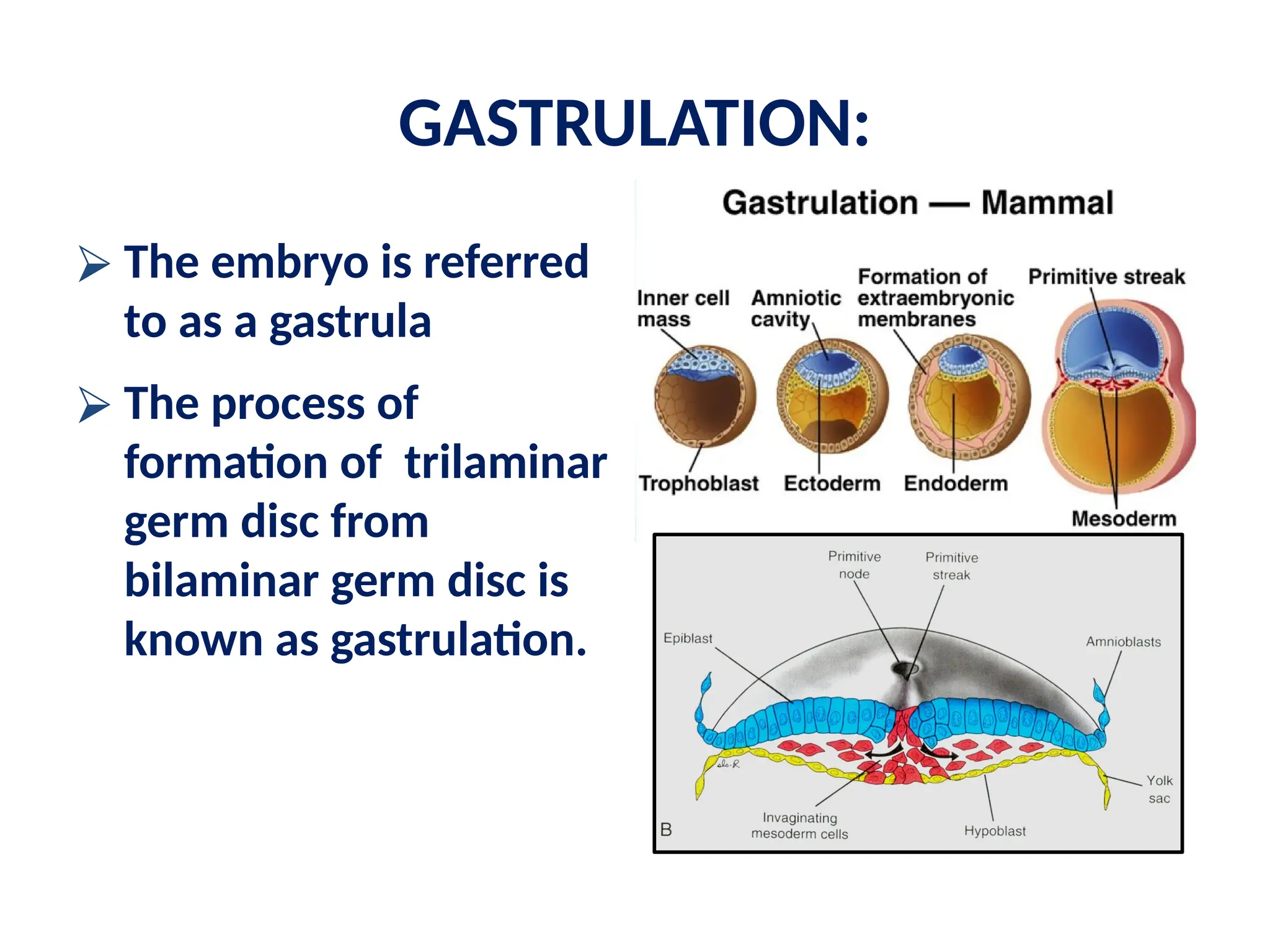
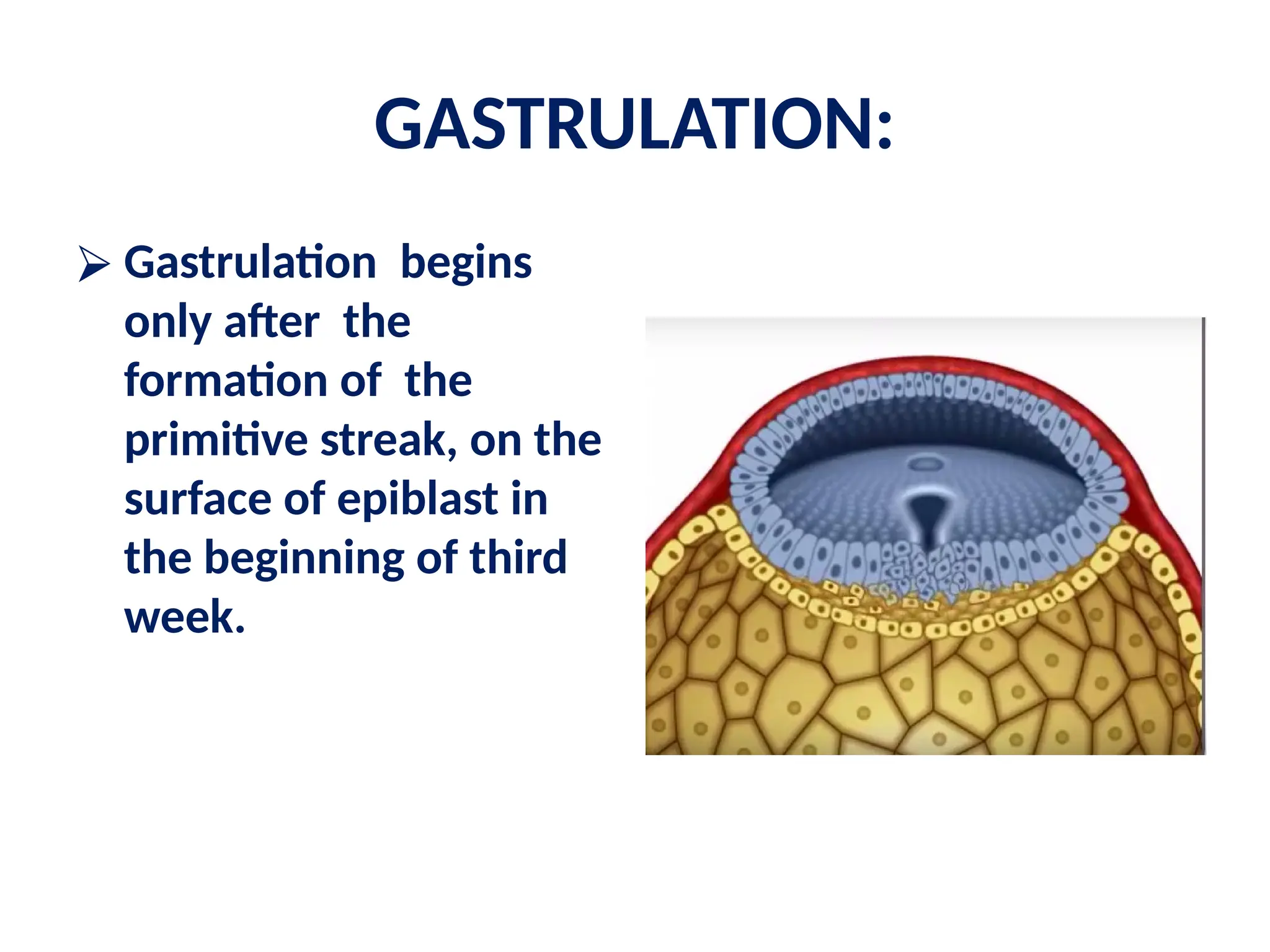
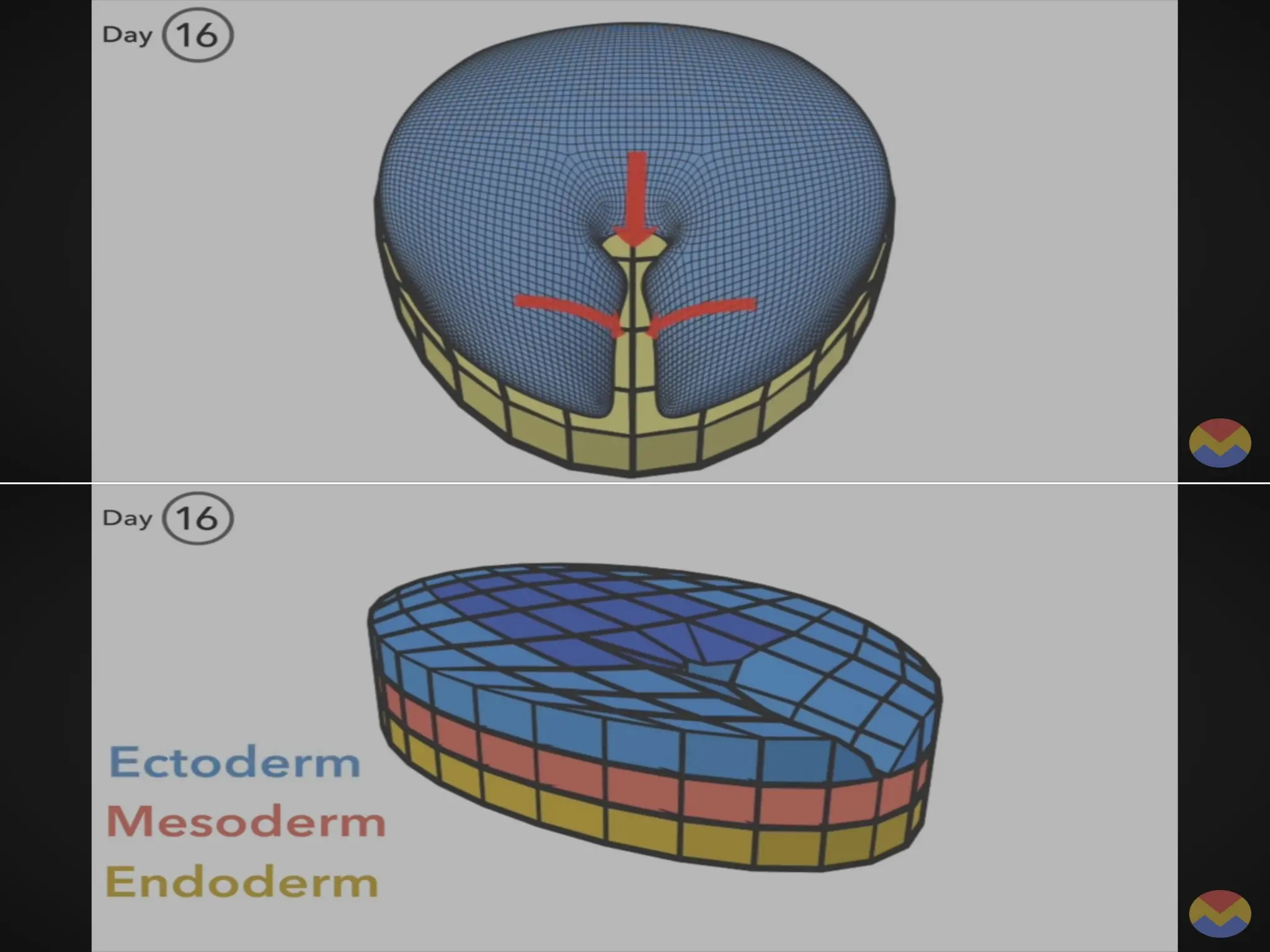
The document describes the process of gastrulation and neurulation during human embryonic development, emphasizing the formation of the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm), the primitive streak, notochord, and neural tube. Key events occur between days 15 and 27, including the invagination of epiblast cells to create the definitive endoderm and the neural tube's formation, which will develop into the brain and spinal cord. Additionally, it outlines the derivatives of neural crest cells and potential neural tube defects.




![Primitive Streak:
⮚ it defines the major body
axis with cranial and
caudal ends and left and
right sides.
⮚ At its anterior end
( cephalic end) - a knob-like
thickening - primitive node
[Hensen’s node] appear
whose centre has a pit
“primitive pit”.
⮚ This continue caudally as
primitive groove.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neurulation-250212163657-09b00c00/75/Neurulation-pptxvvvbbbbhbbbbvffghhjjjjjh-8-2048.jpg)