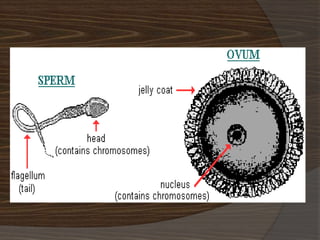
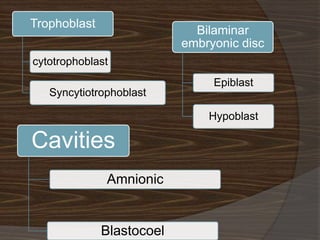
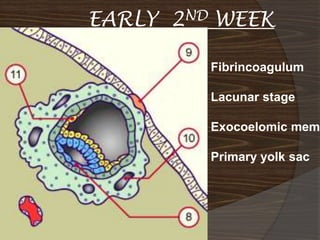
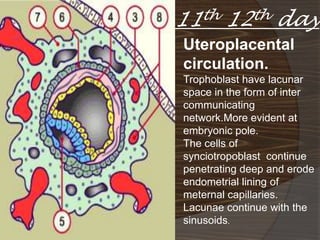
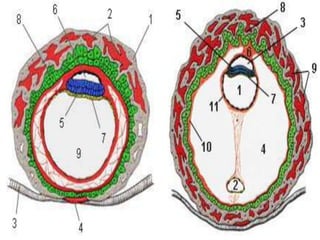
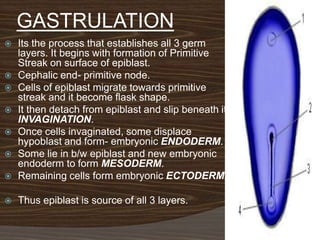
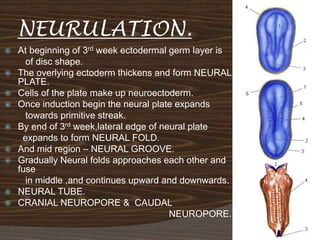
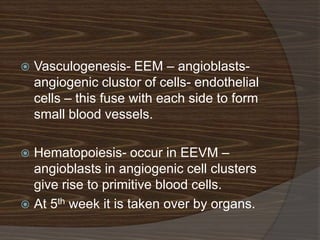
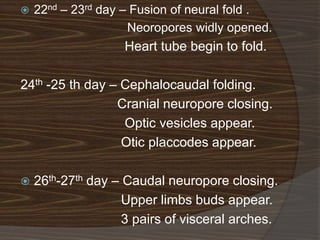
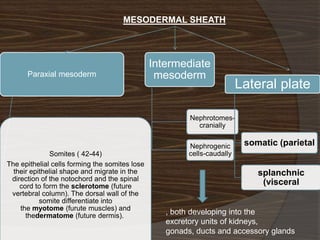
The document discusses the stages of early human development from fertilization through the 8th week. It describes the key events and changes that occur each week, including fertilization and cleavage of the zygote, formation of the blastocyst and implantation, gastrulation and formation of the three germ layers, development of the notochord and neural tube, somite formation, and the morphological changes that cause the embryo to fold from a disc to a cylinder as the major organs and body cavities begin to form. By the 8th week, the fetus is recognizably human-like and all major organs have developed.