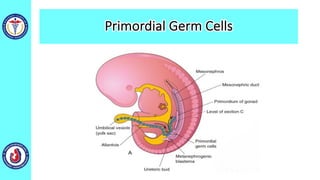
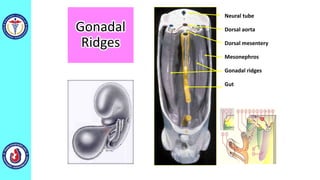
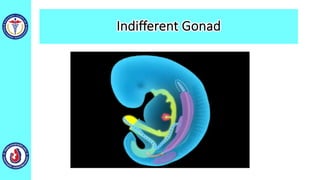
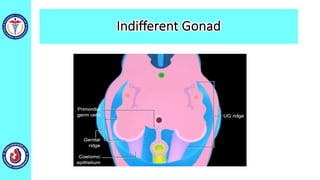
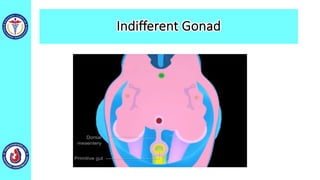
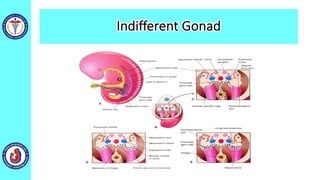
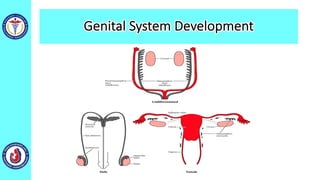
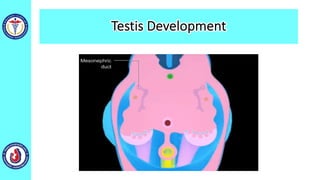
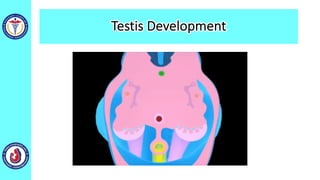
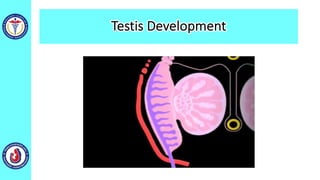
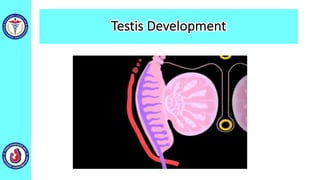
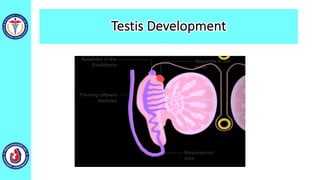
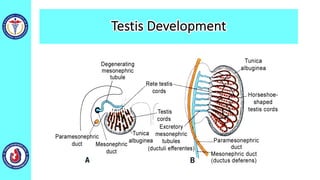
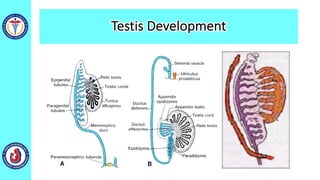
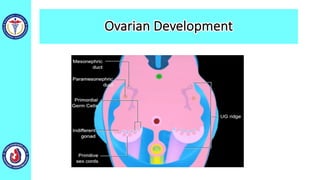
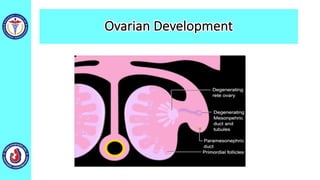
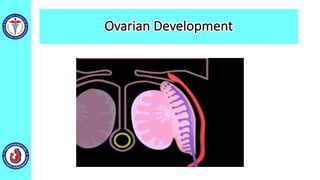
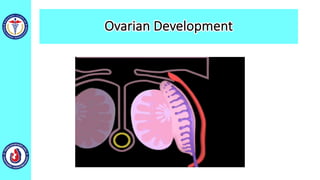
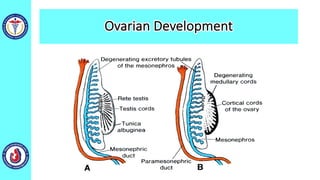
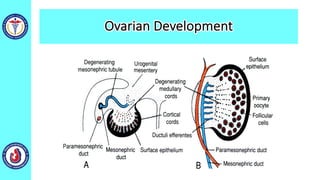
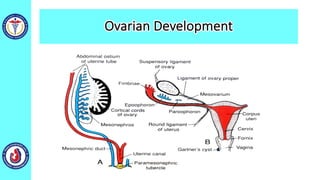
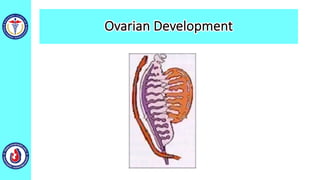
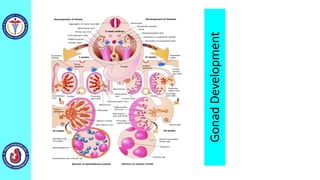
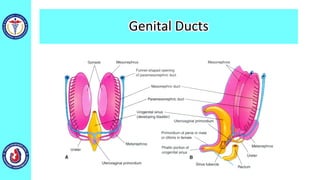
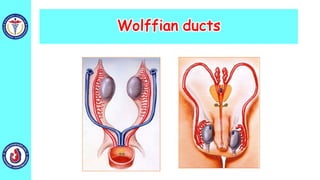
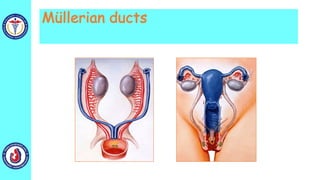
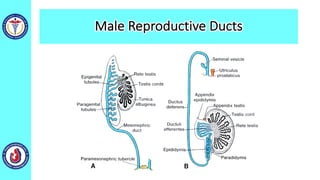
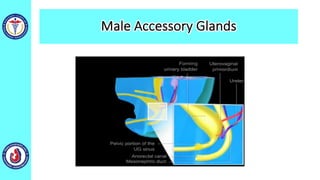
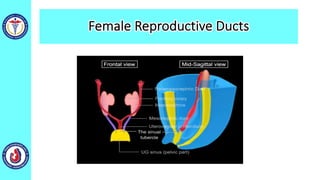
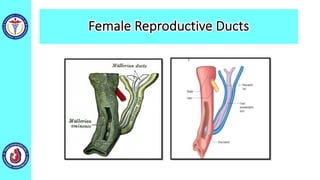
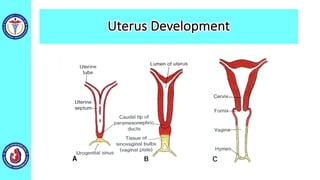
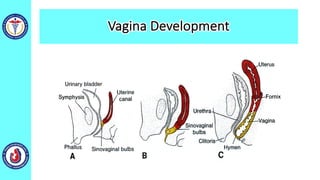
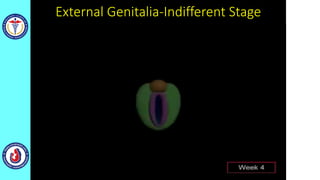
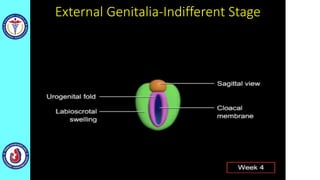
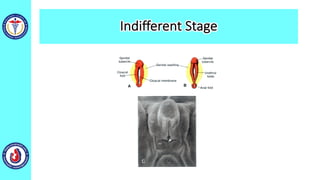
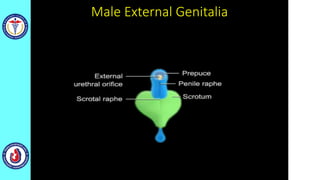
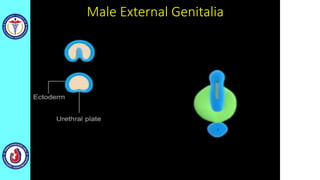
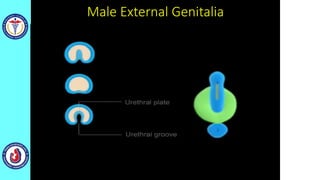
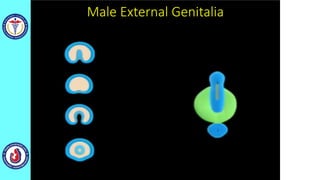
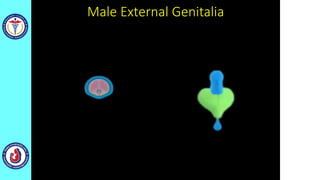
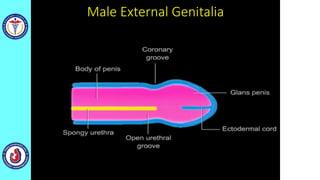
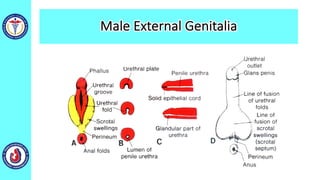
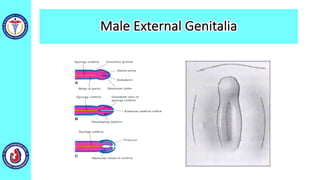
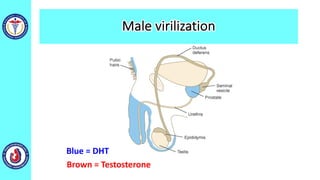
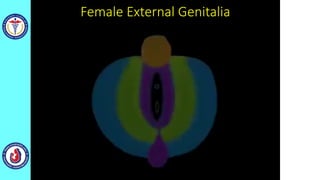
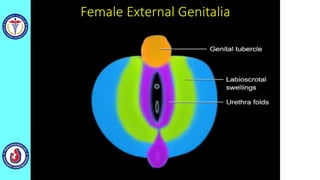
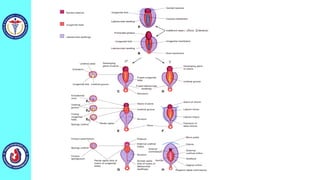
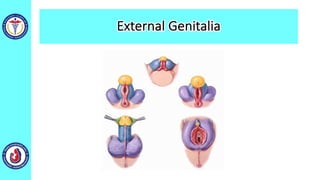
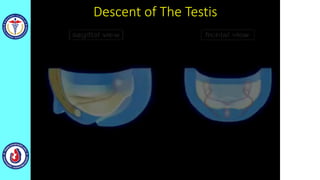
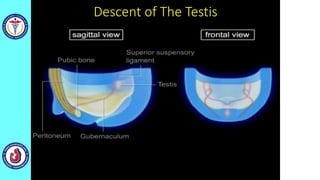
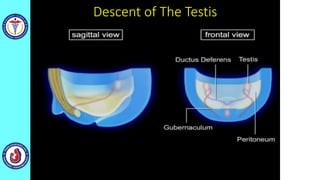
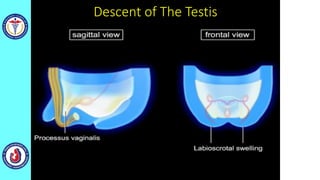
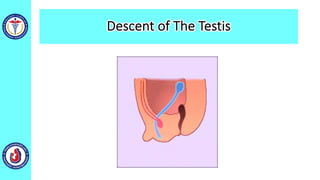
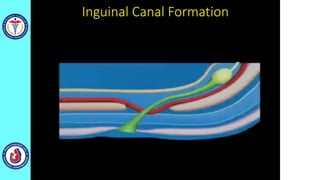
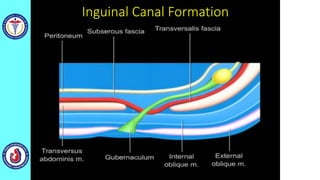
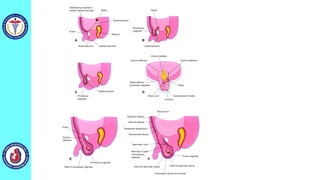
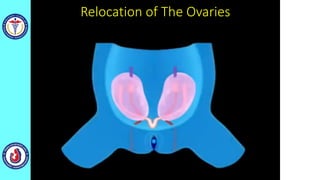
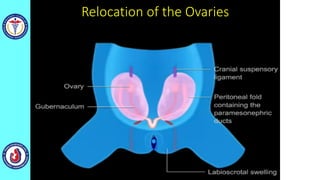
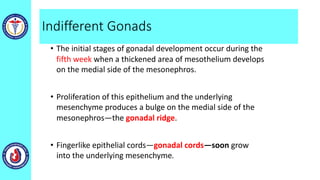
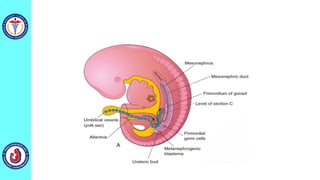
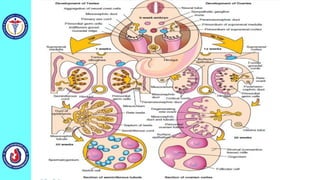
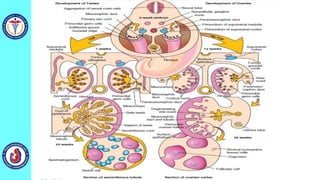
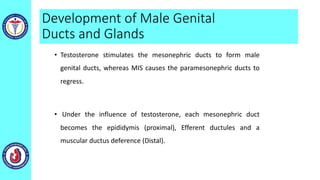
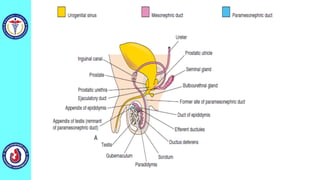
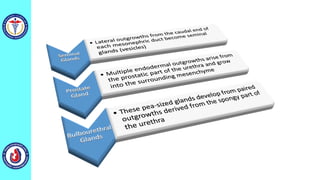
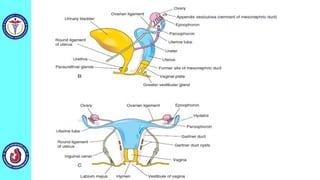
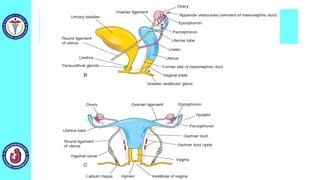
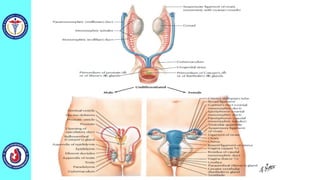
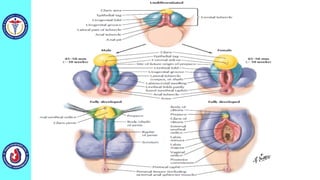
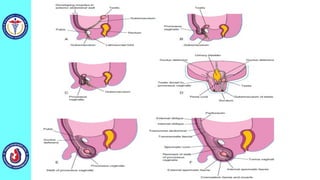
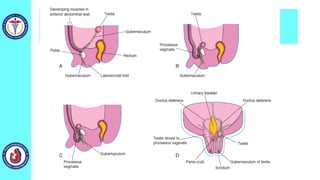
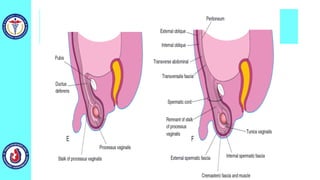
The genital system develops from three main sources: the primordial germ cells, the indifferent gonads that develop into either ovaries or testes, and the genital ducts including the Müllerian and Wolffian ducts. In males, testosterone causes the Wolffian ducts to form the epididymis, vas deferens and seminal vesicles while regressing the Müllerian ducts. In females, the lack of testosterone causes the Müllerian ducts to form the fallopian tubes, uterus and upper vagina while regressing the Wolffian ducts. The external genitalia initially develop in an indifferent state before differentiating into either male or female forms based on hormone levels.