Embed presentation
Downloaded 217 times





The spinal cord arises from the neural tube which forms when the neural plate folds and fuses. The neural tube is made of neuroepithelial cells that migrate and differentiate to form the gray matter of the spinal cord, consisting of the alar plate and basal plate. Axons from cells in the mantle layer collect in the marginal layer to form the white matter. Neural crest cells originate between the neural tube and ectoderm, migrate, and give rise to many structures including ganglion cells, meninges, melanocytes, and Schwann cells.











An introduction to the topic of embryology presented by Raza Rehman, Maria Ilyas, and Isfandyar.
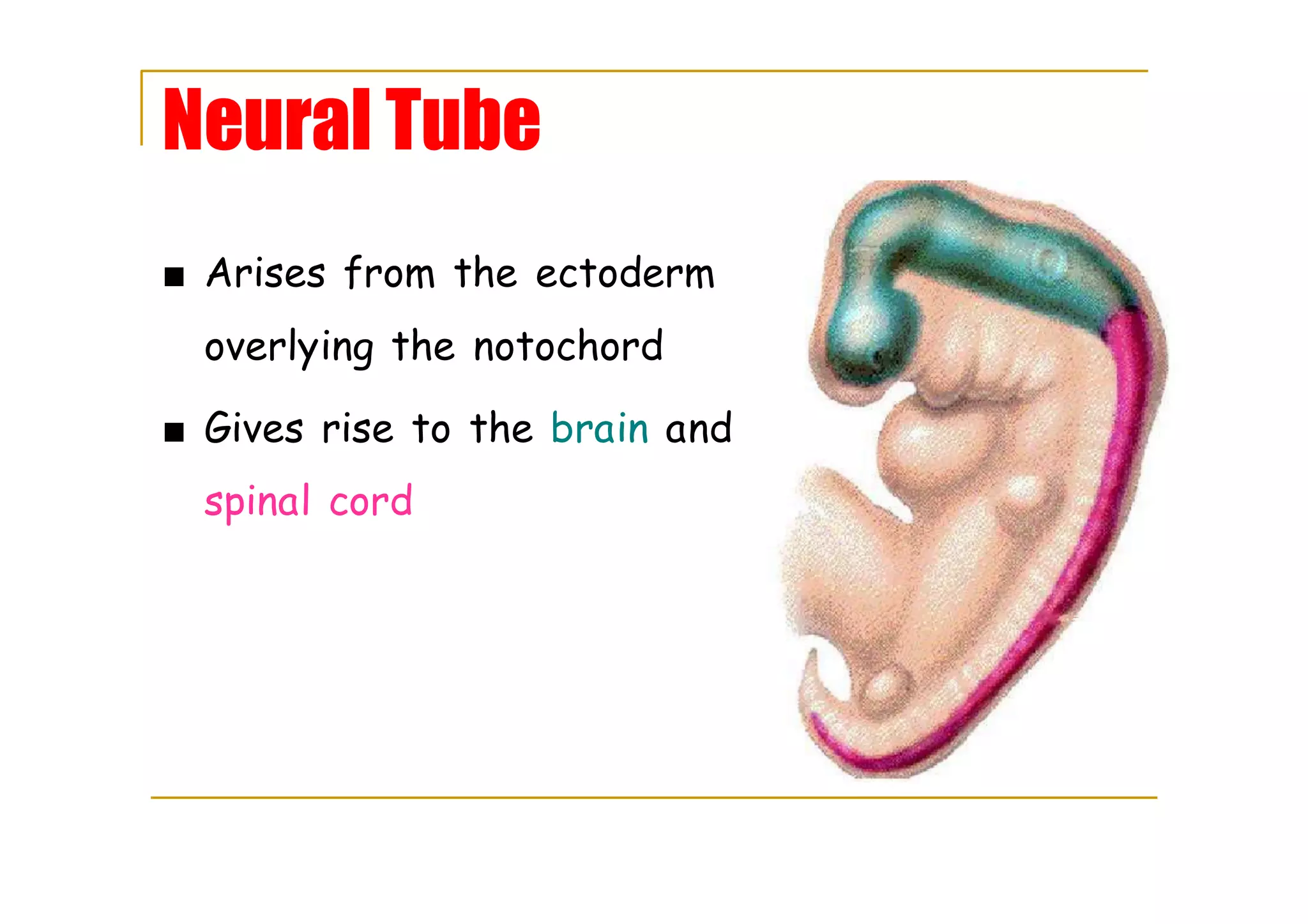
The neural tube arises from ectoderm and is crucial for developing the brain and spinal cord.
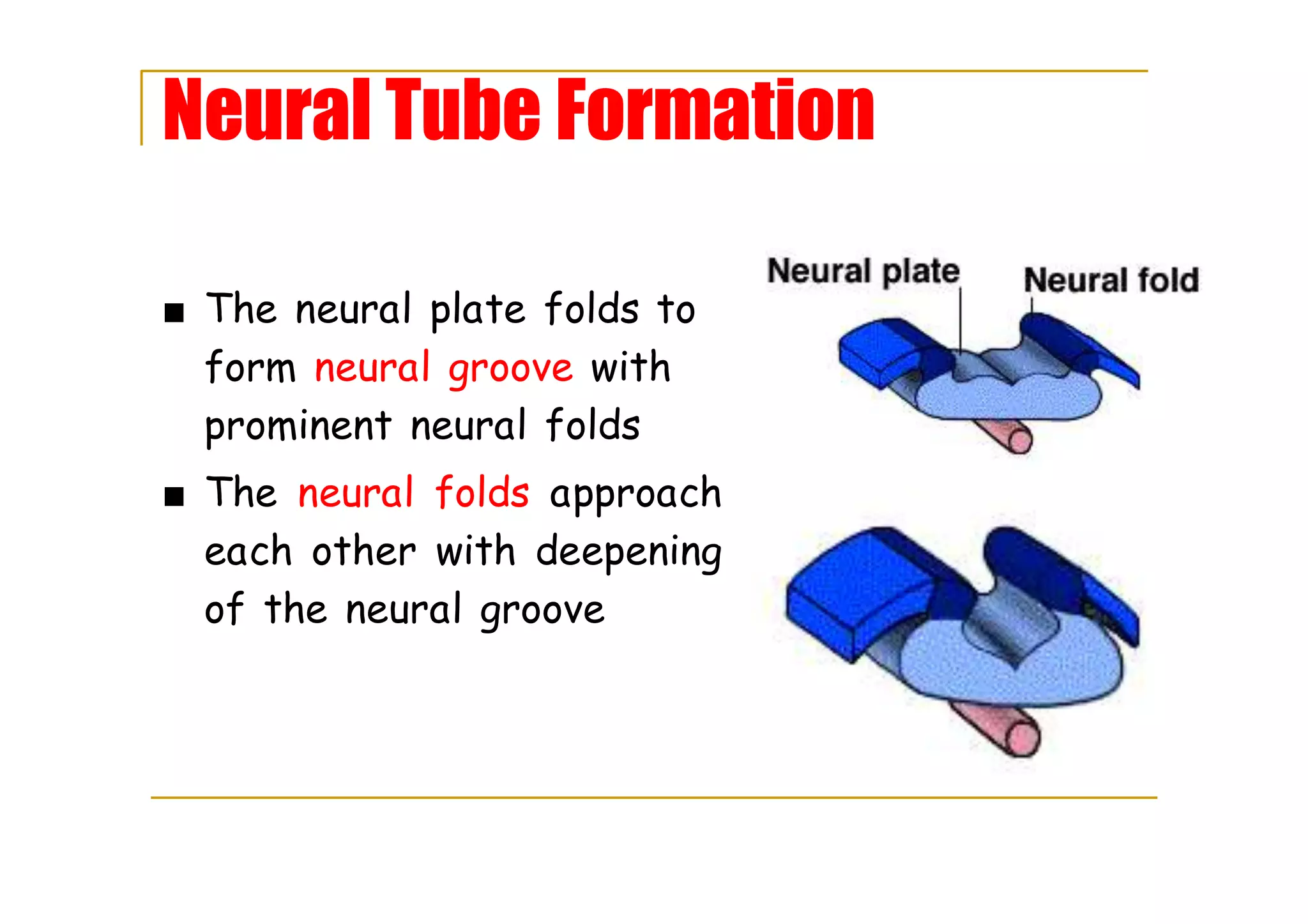
The process involves the folding of the neural plate to create the neural groove and folds.
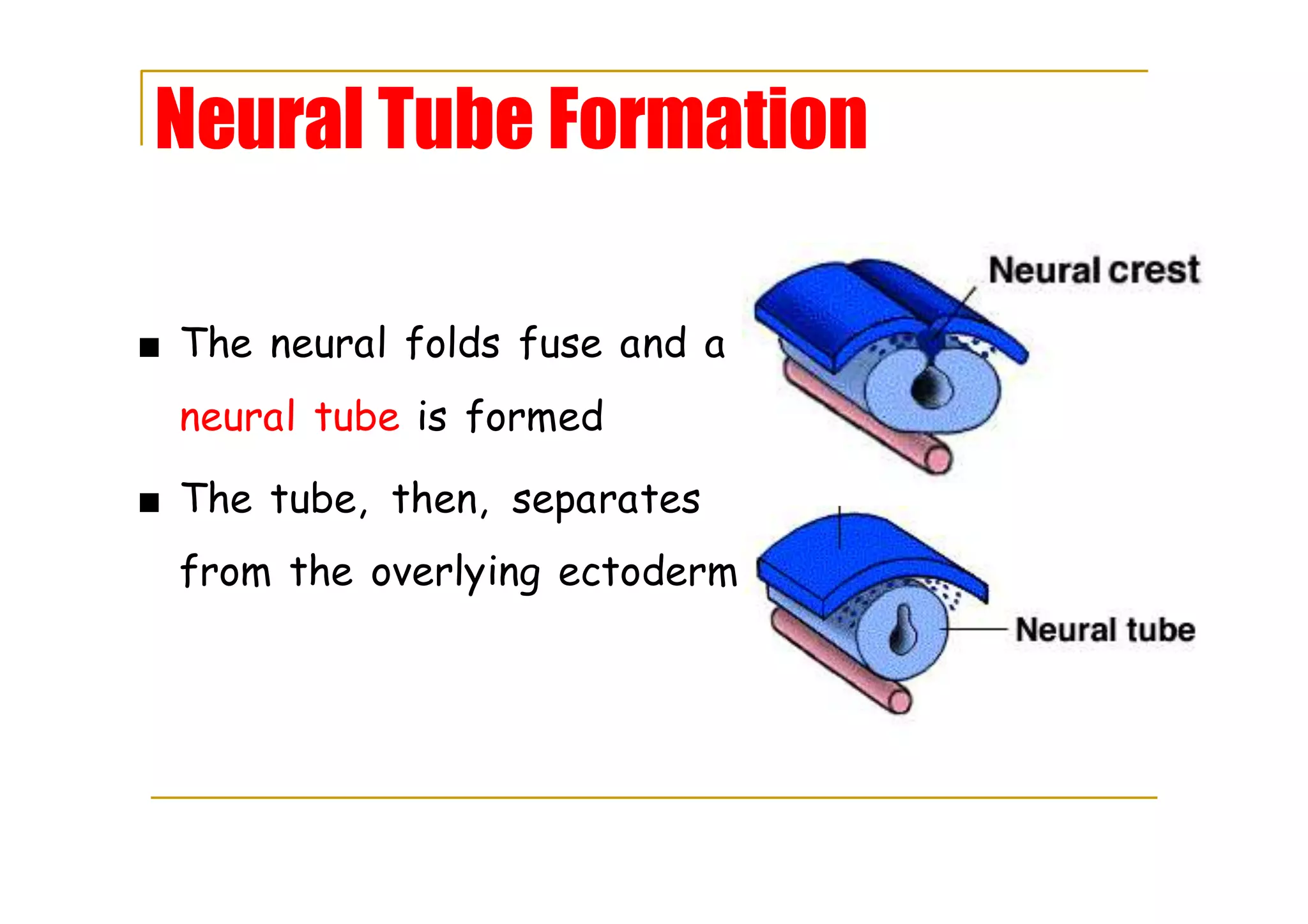
The neural folds fuse to form the neural tube, which later separates from the ectoderm.
Neuroepithelial cells create three zones in the developing spinal cord: ventricular, intermediate, and marginal.
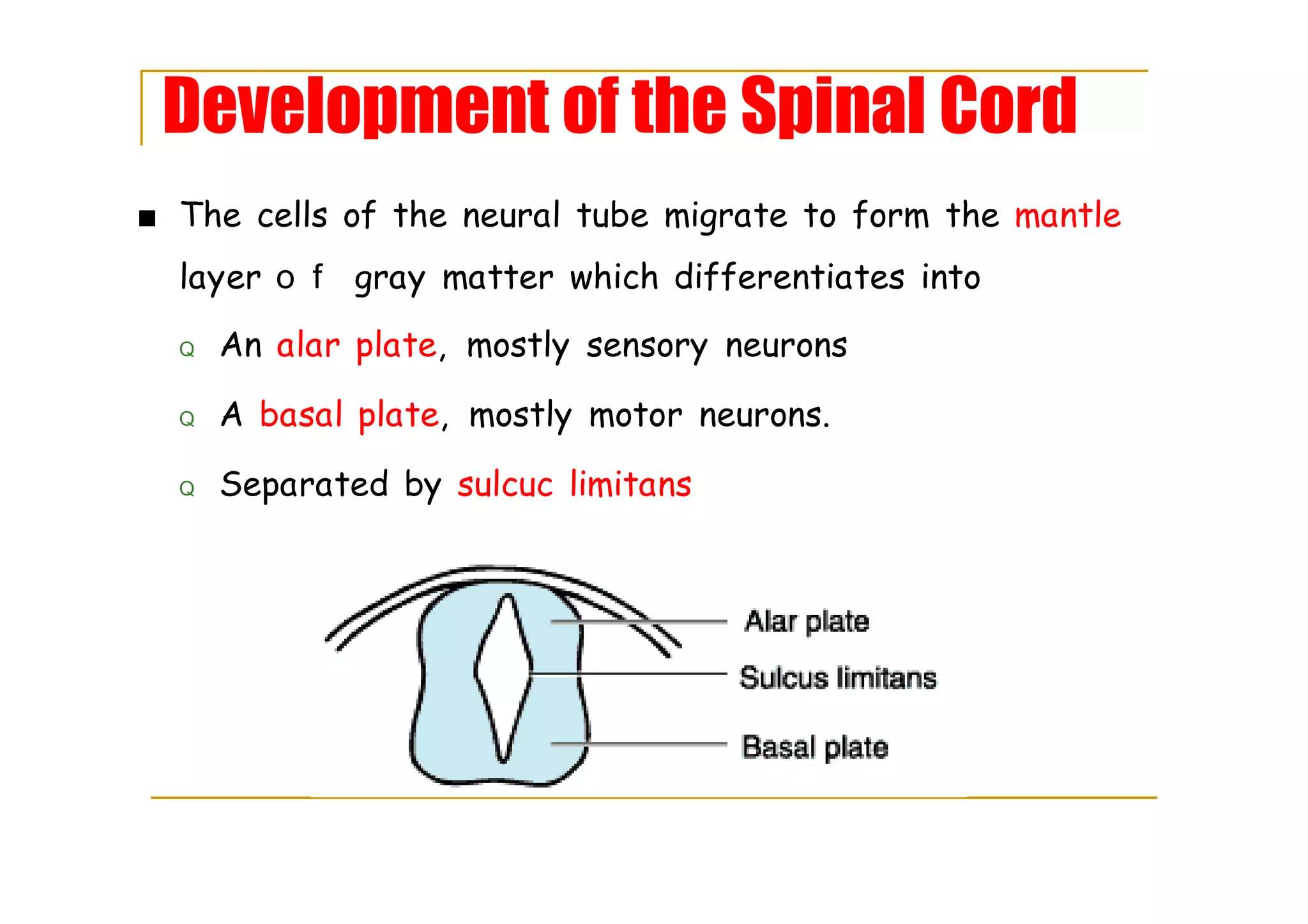
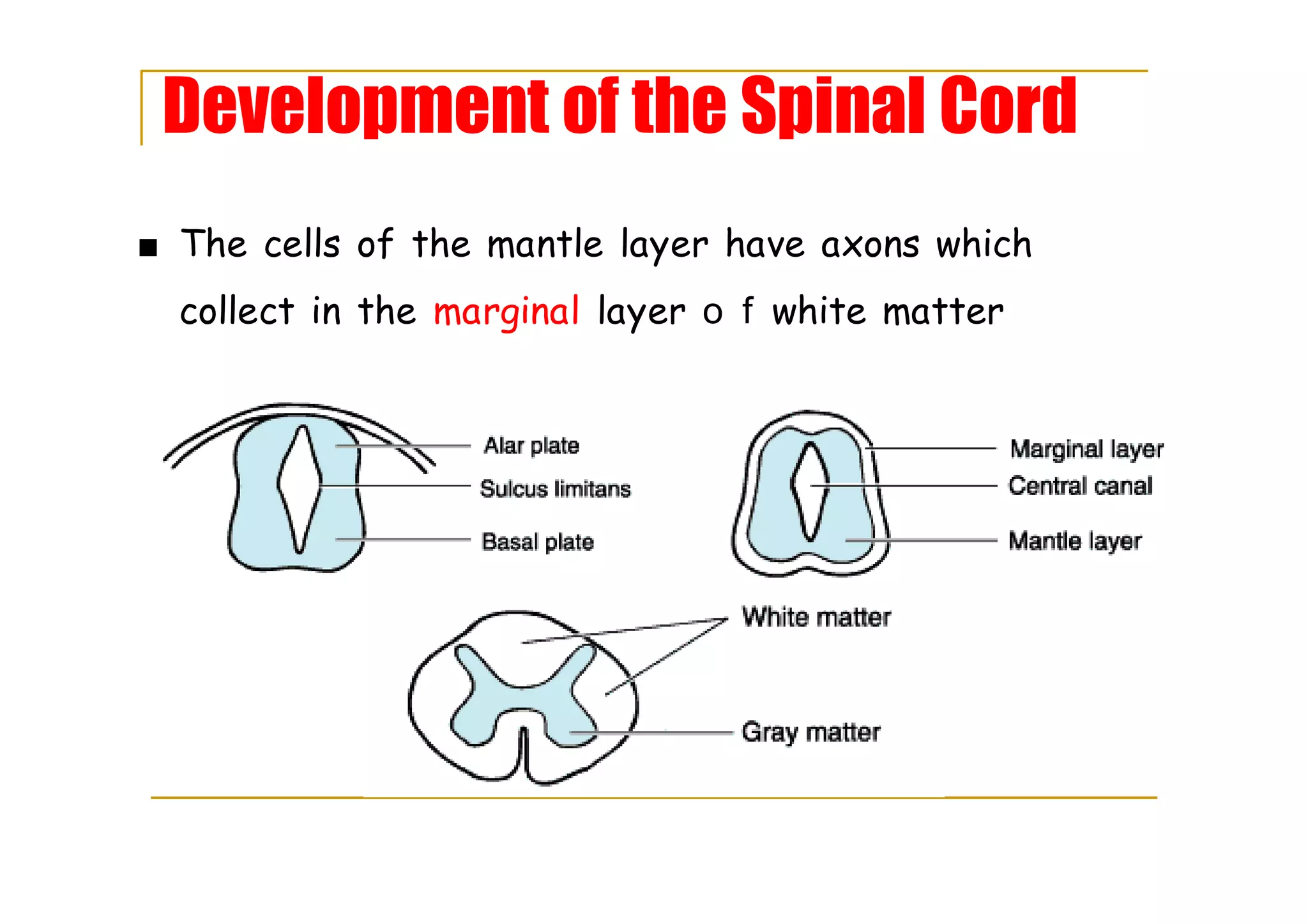
The mantle layer forms gray matter with alar and basal plates, separated by sulcus limitans.
Axons from the mantle layer converge in the marginal layer, contributing to the spinal cord's white matter.
Meninges consist of dura mater (external) and pia arachnoid layers, developing from neural crest cells.
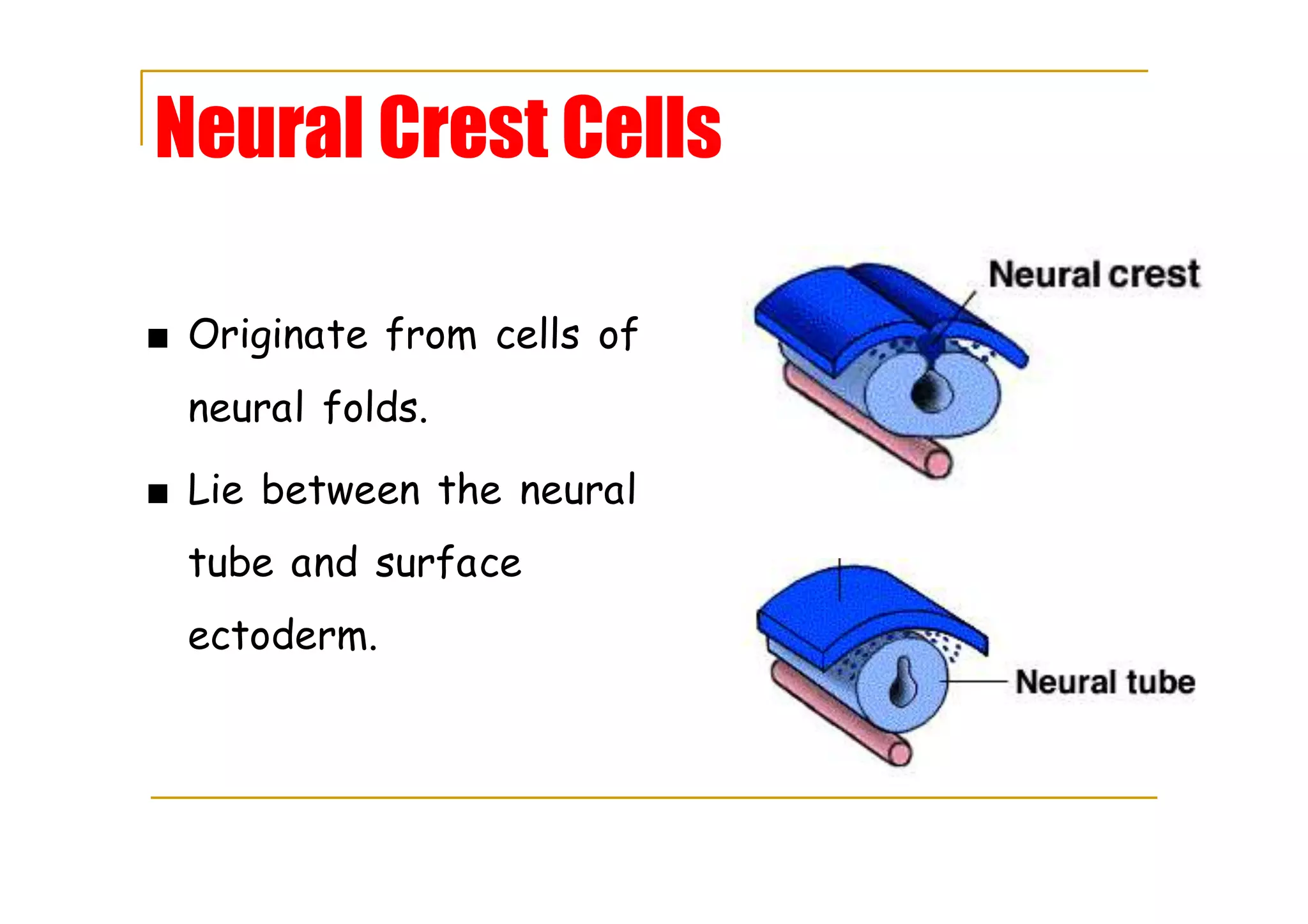
Neural crest cells form from neural folds and lie between the neural tube and ectoderm.
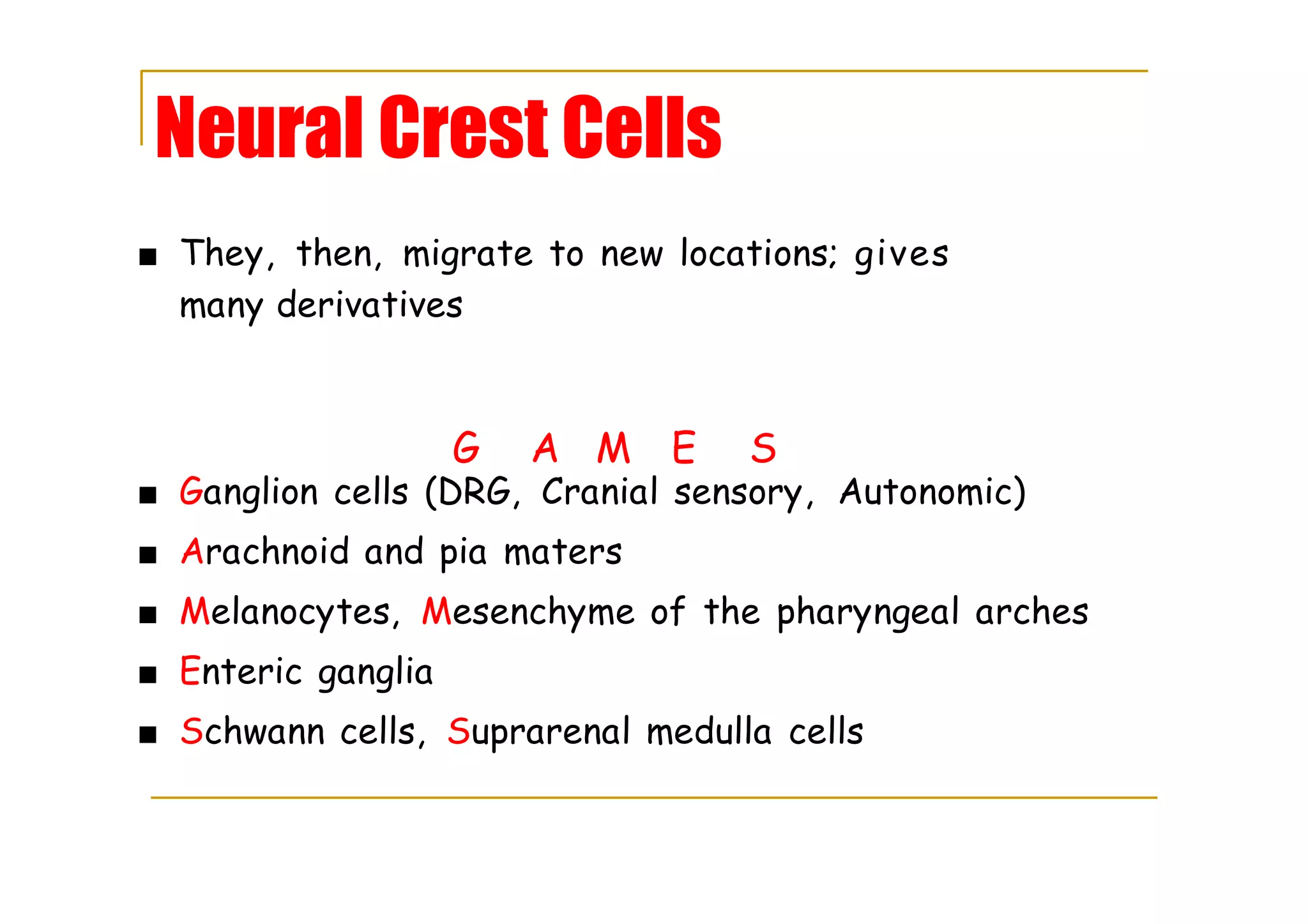
Neural crest cells migrate and differentiate into various types of cells, including ganglion and melanocytes.