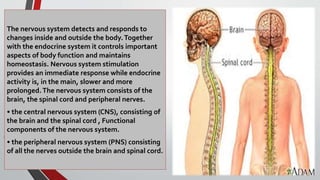
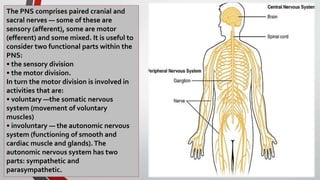
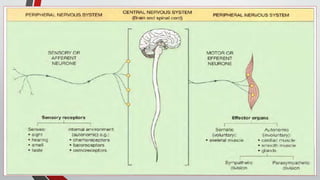
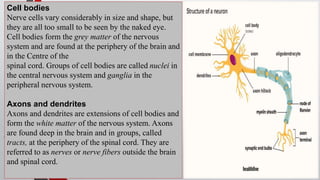
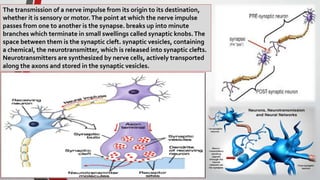
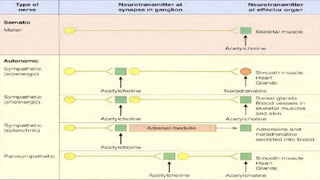
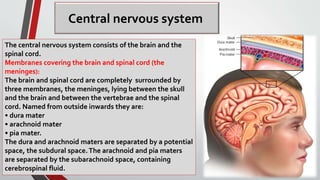
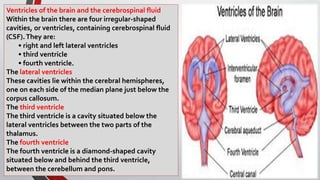
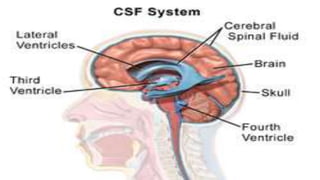
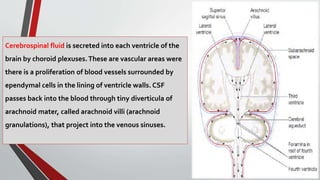
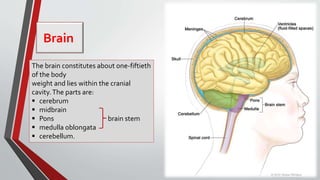
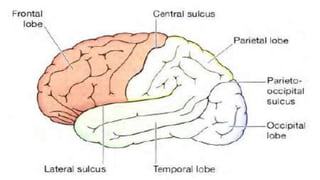
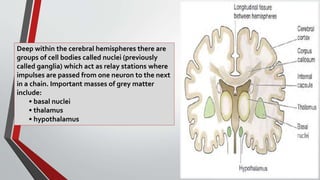
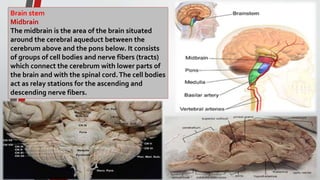
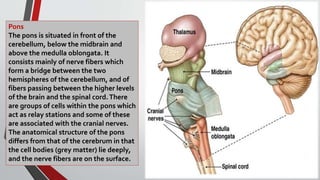
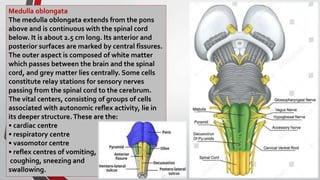
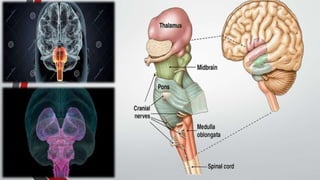
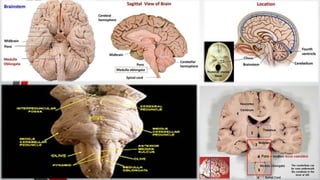
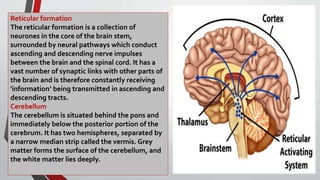
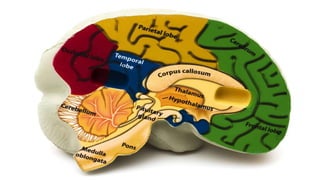
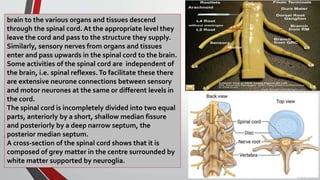
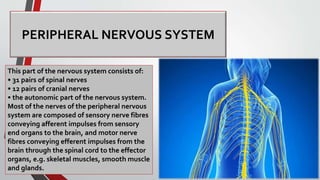
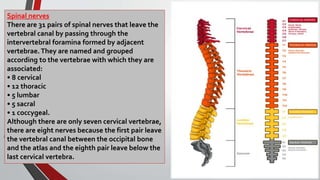
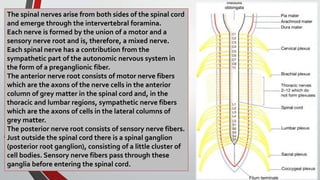
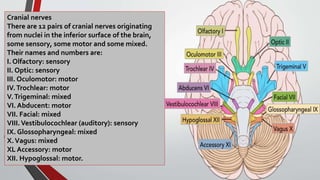
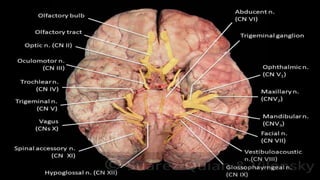
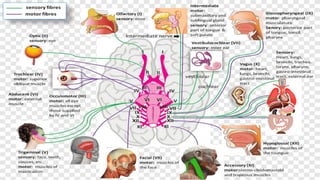
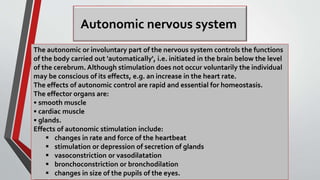
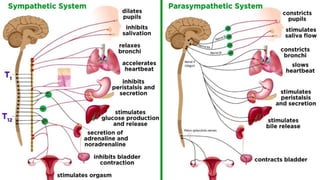
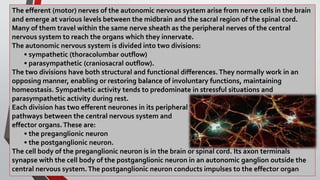
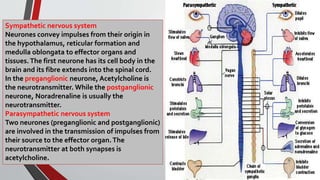
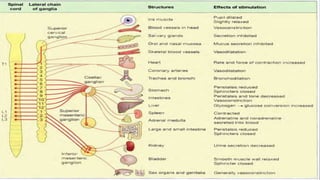
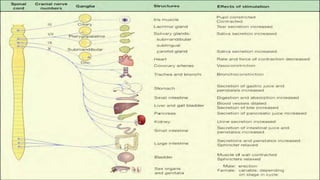
The nervous system, comprised of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS), detects and responds to body changes while maintaining homeostasis. The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, with the brain further divided into various parts such as the cerebrum, midbrain, and medulla oblongata, all interconnected by neurons that transmit impulses. The autonomic nervous system, a component of the PNS, manages involuntary functions and is divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions, each with distinct roles in regulating bodily functions.