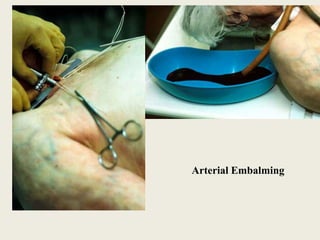
The document discusses different methods of embalming a dead body, including arterial embalming, cavity embalming, and surface embalming. It describes the composition of embalming fluids and the process of injecting the fluids into the body. Embalming preserves the body and prevents decomposition by coagulating proteins, fixing tissues, and bleaching and hardening organs. It must be done within 6 hours of death for best results. Embalming has medical, legal, and transportation purposes but can complicate autopsy and toxicology analyses.