The document covers forensic psychiatry, detailing its relevance in assessing mental illness within the legal system, including the role of forensic psychiatrists in determining competency and caring for mentally ill inmates. It provides an overview of various psychiatric conditions, terms, and delusions, as well as distinguishing between psychosis and neurosis while addressing legal implications of mental health issues. Additionally, it highlights classifications of mental disorders and the mental health act enacted in India in 1987.










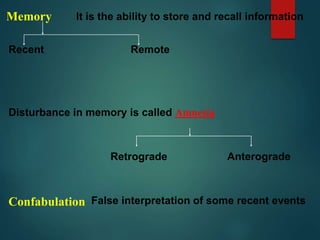










![Delusional Misidentification Syndromes
include four types of syndromes
Capgras syndrome (Delusion of doubles) -Person holds a
delusion that a friend, spouse, parent, or other close family
member has been replaced by an identical-looking
impostor [stranger].Familiar person is thus seen as a
stranger.
The syndrome of subjective doubles - The patient’s
own self is perceived as being replaced by a double.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-22-320.jpg)
![ The syndrome of intermetamorphosis - Familiar persons
are believed to have exchanged identities [no stranger is
involved]. A person misidentifies his wife as his deceased
mother and, later, as his living sister.
Fregoli syndrome -Delusional belief that one or more
familiar persons, usually persecutors following the
repeatedly change their appearance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-23-320.jpg)




















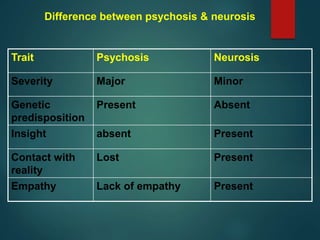








![ Mentally ill person is defined as a person who is in need of
treatment by reason of any mental disorder other than mental
retardation [S.2(l)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-55-320.jpg)
![ Establishment and maintenance of psychiatric hospitals or
psychiatric nursing homes can only be with license [S.6] which
has to be renewed every 5 years [S.94]
The license will be revoked if the hospital is not maintained
according to provisions of the Act [S.11]
If hospital is run without license, the penalty is imprisonment of
3 months and/or fine of `200 for first offence, 6 m and/or 1000
for second offence and if hospital is continued to run without
license even after that, a penalty of `100 per day [S.82]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-56-320.jpg)
![ Regular inspection of psychiatric hospitals by Inspecting
Officers
In order to know that psychiatric hospitals are working well and in
accordance with the Act, the State Government or licensing
authority will appoint an ‘Inspecting Officer’ who at any time can
enter and inspect any psychiatric hospital, inspect its records and
talk to patients in private. If working of hospital not found
satisfactory, he will report to the licensing authority who will take
appropriate action [S.13]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-57-320.jpg)
![Appointment of visitors and monthly inspection by them
For every psychiatric hospital, the Govt shall appoint 5 or
more visitors (of these at least one should be a medical
officer, preferably a psychiatrist, two should be social
workers and two others) [S.37]
Every month three or more visitors will make a joint
inspection of every part of the psychiatric hospital and
examine every minor admitted as a voluntary patient, and
preferably every other mentally ill person admitted [S.38]
Regular visits by inspecting officers and visitors ensure that
psychiatric hospitals are run smoothly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-58-320.jpg)

![[A] Immediate restraint means taking a mentally unsound
person into immediate control whose illness has exacerbated
acutely, or who has suddenly become violent.
There is no specific provision in MHA 1987 for immediate
restraint. It is done U/s 81, IPC [act done to prevent other
harm]
Prerequisites – informed consent of guardian must be obtained.
If consent not obtainable for any reason, person can be restrained
without consent, but only as long as danger exists.
Method – by safely locking up in a room under immediate
personal care of attendants.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-60-320.jpg)
![[B] Admission in a Psychiatric Hospital
Procedures for admission in a psychiatric hospital have been
made so no person may exploit the law.
If a person is aggrieved over an unfavorable will made by a
relative, he may try to prove him mentally ill by getting him
admitted to a psychiatric hospital.
A criminal may himself get admitted in order to claim benefit
of S.84, IPC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-61-320.jpg)
![[1] Admission on a voluntary basis
Any person >18 y who considers himself a mentally ill person
and desires to be admitted to any psychiatric nursing home for
treatment, may request the doctor in charge for being admitted as
a voluntary patient [S.15].
In case of persons <18 y, request is made by guardian [S.16].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-62-320.jpg)
![Procedure
The doctor in-charge shall make such inquiry [examination etc]as
he may deem fit within 24 h and if satisfied that the applicant or
minor requires treatment he may admit him [S.17]
Comments
A straightforward procedure. The possibility of patient
malingering illness is prevented by doctor himself examining
such person.
Very few patients are admitted under this law.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-63-320.jpg)
![[2] Admission under special circumstances [application by
relative or friend]
If mentally ill person is unable to express his willingness for
admission
(i) Patient may be admitted for up to 90 days on an application
by relative or friend [S.19(1)]
(ii) Application should be on prescribed form
(iii) It should be accompanied by certificates from 2 medical
practitioners [allopath, homeopath, or ayurveda (S.2k)], one
of whom should be a Govt doctor
(iv) Each doctor should have examined the MIP separately within
10 days prior to application[S.30]
(v) If above certificates are not attached, the doctor in charge
may appoint 2 doctors working in the hospital to examine
him [S.19(2)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-64-320.jpg)
![[3] Reception order on application
Reception order [RO]– means a magisterial order for MIP to be
“received”, admitted and kept in hospital.
Application by doctor in charge
If doctor thinks that treatment is needed for >6 m or detention is
needed for patient’s own safety and that of others, he would make
an application to magistrate for a reception order [S.20(2)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-65-320.jpg)
![Application by husband, wife or relative
Husband or wife of patient can make an application to
magistrate.
If there is no husband or wife or if they are ill or absent or can
not make an application for whatever reason, any relative of
patient can make an application [S.20(3)].
He must state why the husband or wife is not making the
application. He should also indicate his relationship with the
patient, and the circumstances under which the application is
being made [S.20(4)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-66-320.jpg)
![ All persons making application under this provision [husband,
wife, relative] must be >18 y and must have seen the patient
within 14 days of making application [S.20(5)].
The application must be in prescribed form and must be
accompanied by certificates from 2 medical practitioners, one
of whom must be a Govt doctor [S.20(6)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-67-320.jpg)
![ Each medical practitioner should examine the patient
independently [S.21(a)]
The certificate should state that the MIP is suffering from
mental disorder of such a nature and degree that his treatment in
the psychiatric hospital is required and that such detention is
necessary in the interests of the health and personal safety of
patient or for the protection of others [S.21(b) ].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-68-320.jpg)
![[4] Reception order on production of mentally ill
person before Magistrate
[a] Wandering or dangerous mentally ill person
A police officer in charge of a police station may detain any
wandering mentally ill person (WMIP) [who is wandering
aimlessly] or dangerous mentally ill person (DMIP) [who is
dangerous to himself or others due to his violent
behavior][S.23(1)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-69-320.jpg)
![ The Police officer would immediately inform him why he is
being detained. If WMIP or DMIP is incapable of
understanding, their relatives or friends must be informed
[S.23(2)].
Such WMIP or DMIP must be produced before a magistrate
within 24 h of detention. The period of journey is not included
[S.23(3)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-70-320.jpg)
![ In respect of examination - Magistrate shall
(a) examine the person personally
(b) cause him to be examined by a doctor
(c) make any other relevant enquiries [S.24(1)].
In respect of admission – Doctor must certify the person to be
mentally ill.
If he feels that patient may be malingering and needs sustained
observation or there is some other difficulty in on-the-spot
diagnosis, he may ask the magistrate to pass a temporary order
for detention for observation of a period of up to 10 days
[S.28(1)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-71-320.jpg)
![ If diagnosis cannot be made during that period, two more such
orders can be passed
The doctor must make a diagnosis within 30 days [S.28(2)]
If after medical certificate from doctor the magistrate is
satisfied of the need of his treatment or for protection of
himself or others (a) he may make a RO.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-72-320.jpg)
![ If any relative or friend wants him to be admitted to a
particular licensed psychiatric hospital and agrees to bear cost,
and doctor in-charge of that hospital consents, an RO for that
particular hospital is made.
If relative or friends furnishes a bond ensuring that WMIP or
DMIP would neither injure himself nor others, and agrees to
keep him, the magistrate, instead of making an RO, would
hand over such person to the relative or friend [S.24(2)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-73-320.jpg)
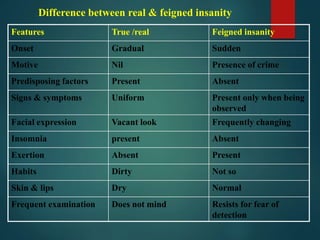
![[b] Cruelly treated mentally ill person
Police officer – may inform magistrate if a MIP is in the
custody of relative or guardian, and is being cruelly treated by
him [cruelly treated mentally ill person, CTMIP] [S.25(1)].
Any private person – can similarly inform magistrate
[S.25(2)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-75-320.jpg)
![ The magistrate would call CTMIP, relative who is cruelly
treating him and person who is legally bound to maintain such
CTMIP [S.25(3)].
Magistrate would order the person who is legally bound to
maintain such CTMIP to take his proper care. If he willfully
neglects to comply with the order, he can be fined up to `2,000
[S.25(4)].
If it appears to magistrate that despite fine etc, the CTMIP
would not be properly looked after, he would make an RO,
under same procedural guidelines as with WMIP and DMIP
above [S.25(5)].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-76-320.jpg)
![[5] Discharge of a mental ill person in asylum
1. A voluntary patient must be discharged within 24 hrs
of receipt of request for discharge made by the patient
himself or by the guardian
2. Admission by application can be discharged by
request but it must first be made certain that the
patient is fit to be discharged.
3. The O.I.C of psychiatric hospital can order the discharge of
any patient, on the recommendation of two medical practitioner
one of whom should be a psychiatrist.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/forensicpsychiatry-201124082442/85/Forensic-psychiatry-77-320.jpg)




















