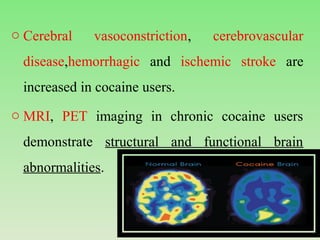
Cocaine is derived from the coca plant and can be administered via smoking, insufflation, or injection. It acts by inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine. Initial effects include euphoria and increased energy, but overdose can cause seizures, cardiac issues, and death. Regular use is associated with nasal damage, weight loss, dependence, and psychological issues. Treatment focuses on managing the acute effects of overdose and providing therapies for addiction.