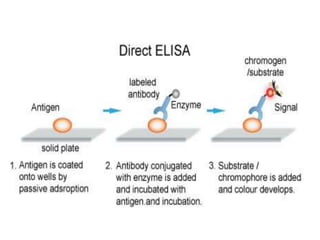
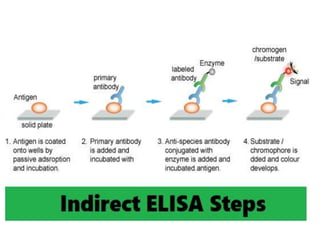
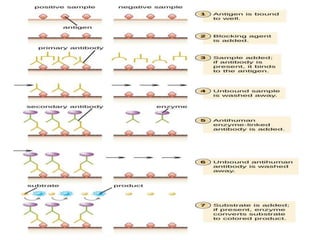
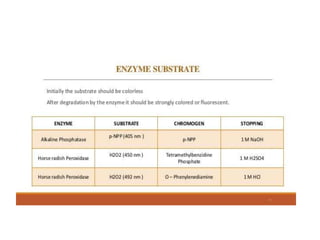
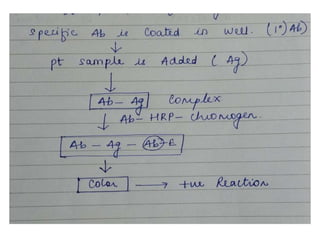
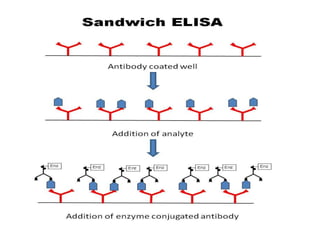
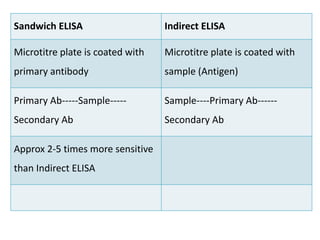
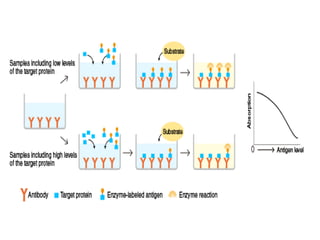
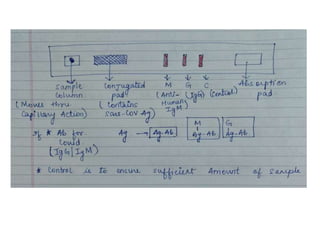
ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) is a sensitive technique used to detect small quantities of antigens, antibodies, or other proteins in biological fluids like blood or urine. There are several types of ELISA including direct, indirect, sandwich, and competitive ELISA. ELISA works by using an enzyme-linked antibody or antigen to detect the presence of a target protein. This allows very small amounts of the target to be detected through the enzyme's catalytic activity.