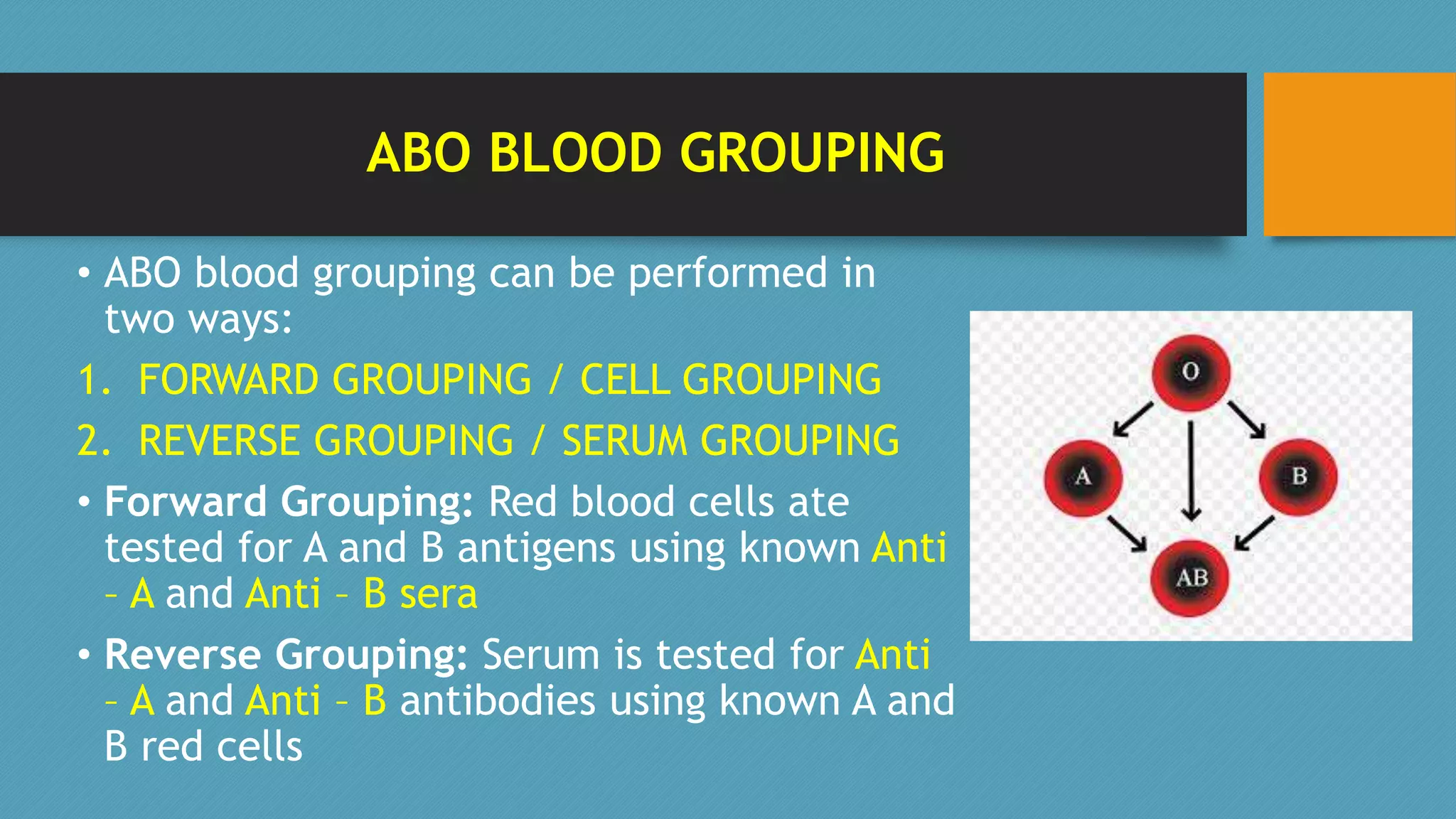
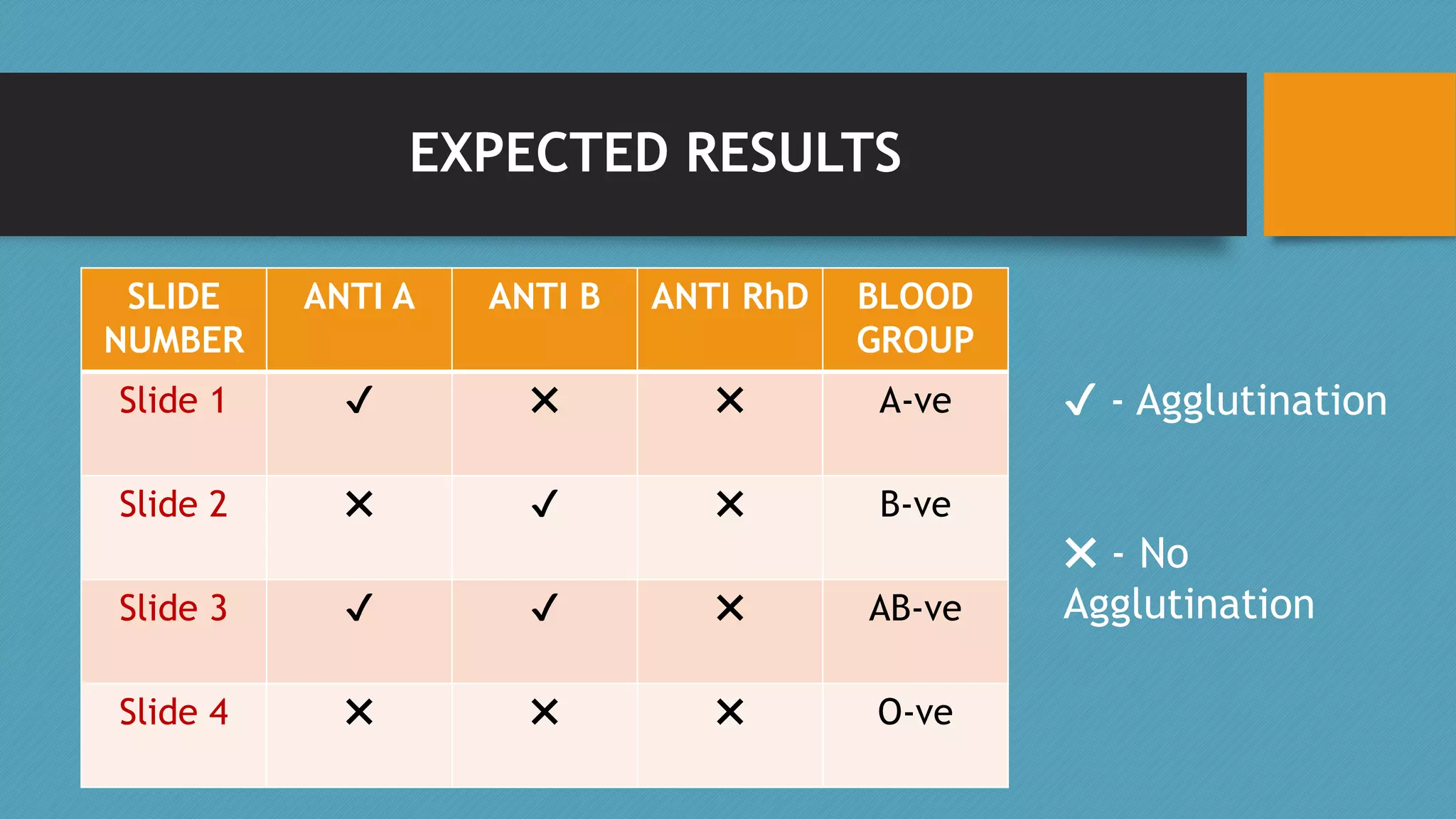
This document discusses blood grouping and the ABO blood type system. It explains that there are four main blood groups - A, B, AB, and O - determined by the presence of antigens on red blood cells. The Rh factor is also discussed, which further divides blood types into positive or negative based on the presence of the RhD antigen. Blood grouping is performed using forward and reverse methods to test red blood cells or serum for antigens and antibodies. The eight main blood group types based on ABO and Rh typing are identified.