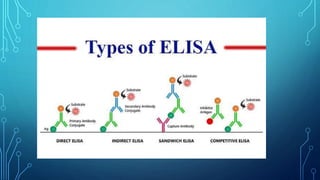
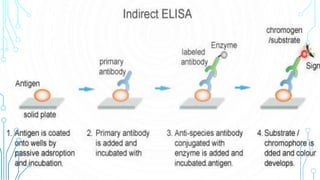
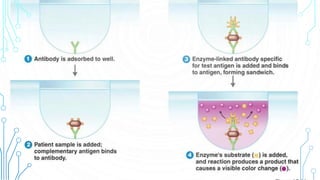
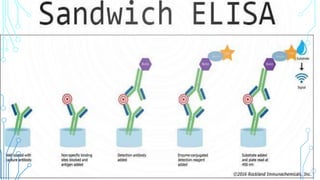
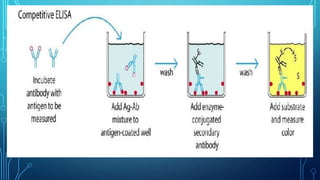
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a technique that uses antibodies or antigens for detection through their interactions. There are four main types of ELISA: indirect, direct, sandwich, and competitive, each with specific procedures for measuring protein concentrations. The method involves coating wells with antibodies, adding samples, and then using enzyme-linked secondary antibodies to produce measurable color changes, allowing quantification of the target proteins.