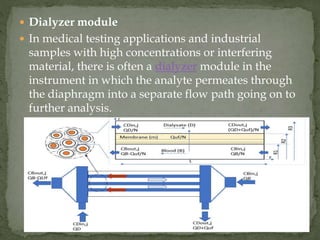
The AutoAnalyzer is an automated analyzer that uses continuous flow analysis, invented in 1957. It has five main parts: the sample pump, mixing chamber, incubator bath, and detector. AutoAnalyzers were mainly used for routine medical and industrial analyses to increase throughput. While still used for some applications, most instruments are now used industrially and for environmental work.







![ Flow Injection Analyzer
Flow Injection Analysis (FIA), conceived in 1975 by
Ruzicka and Hansen, has been described in over
16,000 scientific papers[1] and almost 20 monographs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/poonam-230502072417-cf45cb01/85/Automatic-And-Semi-Automatic-Analyser-Biochemistry-8-320.jpg)