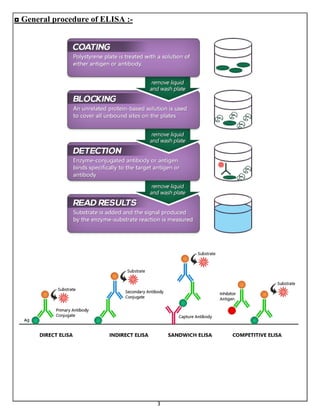
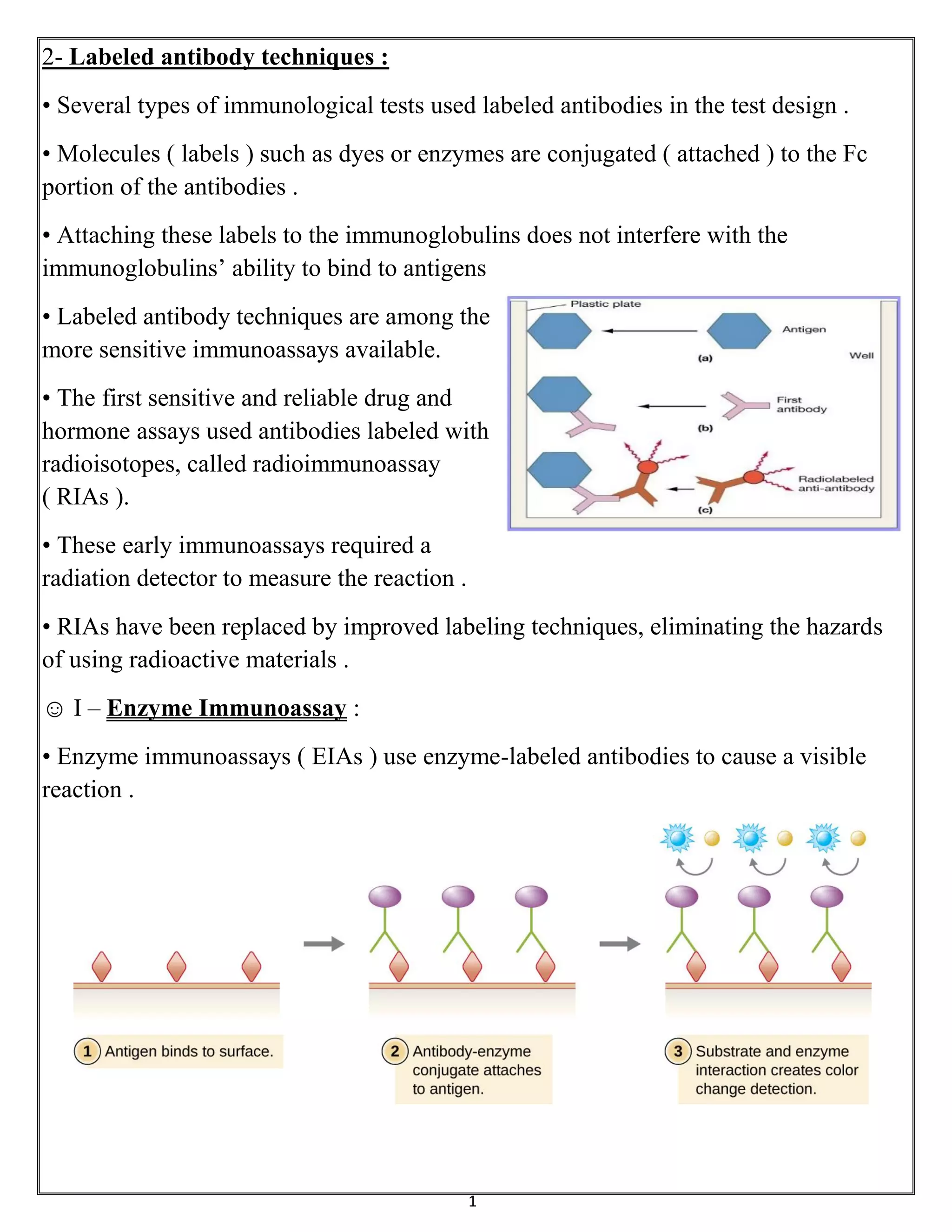
Labeled antibody techniques use antibodies conjugated to labels like enzymes or dyes. Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) use enzyme-labeled antibodies to generate a visible reaction with a substrate. A common type of EIA is the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which uses an enzyme-linked antibody or antigen to detect specific proteins. There are several variations of ELISA that can qualitatively or quantitatively detect antigens or antibodies in samples.
![2
• The tests can be design to detect either antibody or antigen, such as viral antigen, in
a patient specimen .
• Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay ( ELISA ) is a type of EIA .
• It is a very sensitive immunochemical technique used to access the presence and
quantification of specific protein ( antigen or antibody ) in a given sample .
• It is also called solid-phase enzyme immunoassay as it employs an enzyme linked
antigen or antibody as a marker for the detection of a specific protein .
• An enzyme conjugated with an antibody reacts with a colorless substrate to generate
a colored reaction product .
• A number of enzymes have been employed for ELISA, including alkaline
phosphatase ( ALP ) and horseradish peroxidase ( HRP ) .
• The enzyme activity may be monitored directly by measuring the product formed or
by measuring the effect of the product on a coupled reaction .
• Depending on the substrate used, the product can be photometric, fluorometric, or
chemiluminescent .
• For example, a typical photometric reaction using HRP-labeled Ab ( Ab-HRP ) and
the substrate ( a peroxide ) generate the product ( oxygen ) .
• The oxygen can then oxidize a reduced chromogen ( reduced
orthophenylenediamine [ OPD ] ) to produce a colored compound ( oxidized OPD ),
which is measured using a photometer .
Ab-HRP + peroxidase Ab = HRP + O2
O2 + reduced OPD Oxidized OPD + H2o](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec5instrmentalanalysis-180927130824/85/Labeled-antibody-techniques-ELISA-2-320.jpg)