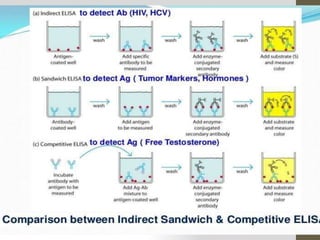
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a widely used laboratory method for measuring concentrations of antibodies or antigens in solutions, employing various techniques including direct, indirect, and sandwich ELISA formats. It involves specific steps such as adsorption of antigens/antibodies, washing, and chromogenic reactions to produce a color change as a signal for spectrophotometric measurement. While ELISA is cost-effective and sensitive, it has limitations, such as the potential for false positives/negatives and dependence on the availability and quality of antibodies.