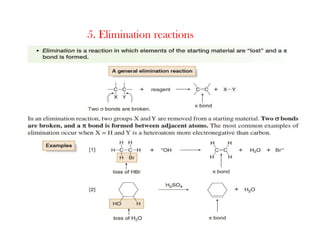
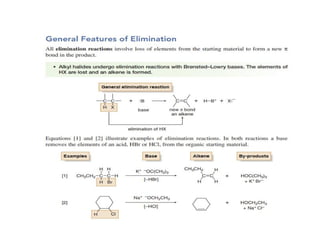
1) Three types of elimination reactions are α-, β-, and γ-elimination which involve the loss of atoms or groups from the 1st, 2nd, and 1st/3rd positions respectively of an organic molecule.
2) The mechanisms of elimination reactions can be E1 or E2. E1 involves carbocation intermediate while E2 is concerted. Kinetic studies can determine the mechanism.
3) Factors like nature of alkyl halide, base, and solvent determine if the reaction follows E1 or E2. E2 is favored with strong base and polar aprotic solvent.




![ E2 reactions are generally run with strong, negatively charged bases like
–OH and –OR.
Two strong, sterically hindered nitrogen bases, called DBN and DBU,
are also sometimes used.
DBN=1,5-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene,
DBU=1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene.
There are close parallels between the E2 and SN2 mechanisms in how the
identity of the base, the leaving group, and the solvent affect the rate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/45992211059958614285-220813094540-fcd42cce/85/Substitution-reaction-7-320.jpg)












![[A]
1) Kinetic isotopic effect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/45992211059958614285-220813094540-fcd42cce/85/Substitution-reaction-20-320.jpg)























