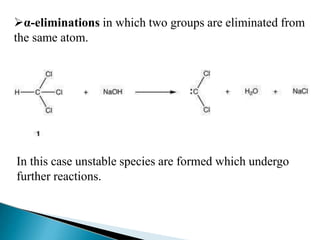
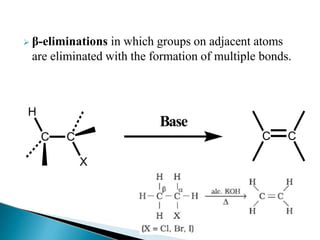
The document discusses elimination reactions in organic chemistry, classifying them into α-eliminations and β-eliminations, each with distinct mechanisms. β-eliminations can occur via E2 or E1 mechanisms, differing in bond cleavage timing, with E2 following second-order kinetics and E1 following first-order kinetics. The document also highlights factors influencing reactivity, including the stability of carbocations, steric hindrance, and the role of nucleophiles.




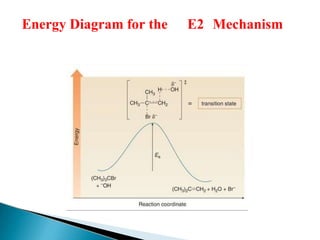
![The E2 elimination
= k [substrate] [base]
Reaction involves a single step: base pulls a proton away from
carbon; simultaneously a halide ion departs and the double
bond forms. Halogen takes its electron pair with it; hydrogen
leaves the electron pair behind, to form the double bond
In this transition
state, two bonds are
being broken: C-H
and C-X.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eliminationreaction-230602052240-28816ce9/85/Elimination-Reaction-pptx-7-320.jpg)