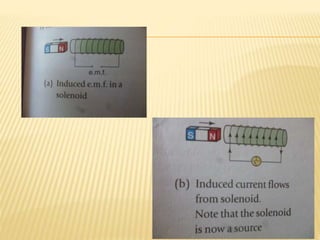
The document discusses electromagnetism induction, which is the production of an electric current from a changing magnetic field. It occurs when there is relative motion between a conductor and magnetic field lines. An induced current is produced when a conductor cuts across magnetic flux lines or when there is a change in the magnetic flux linking a coil. The direction and magnitude of the induced current can be determined by Lenz's law and Faraday's law of induction. Examples of devices that use electromagnetism induction include direct current generators, alternating current generators, and moving coil microphones.