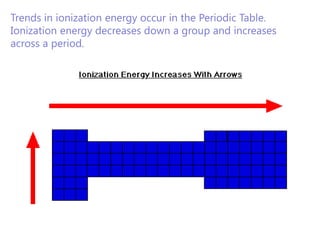
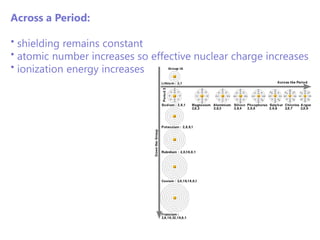
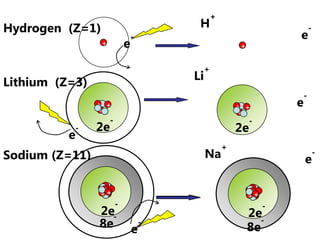
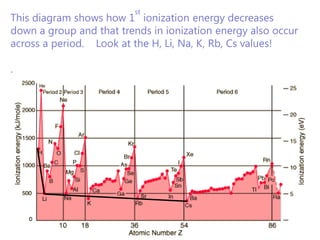
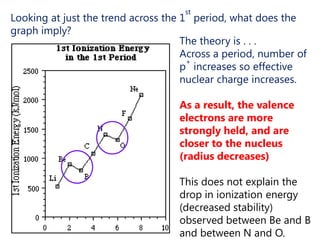
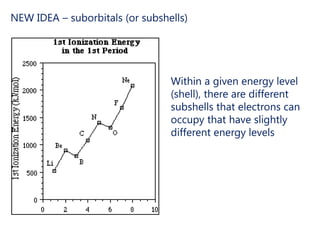
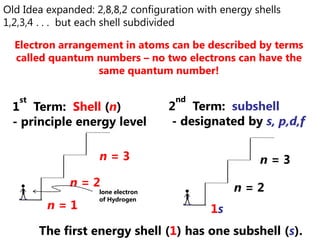
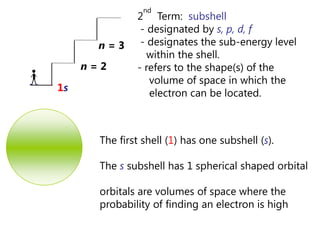
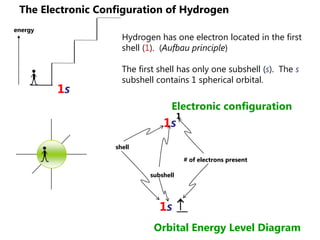
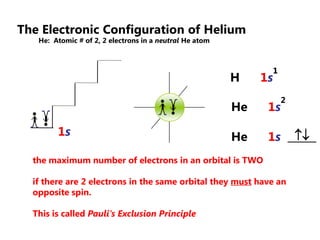
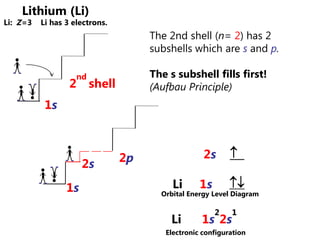
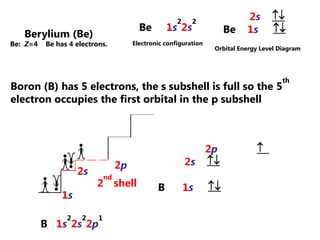
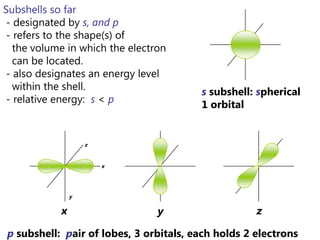
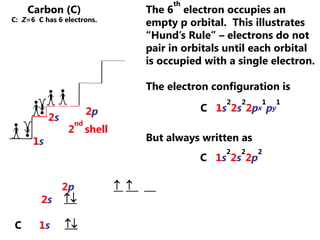
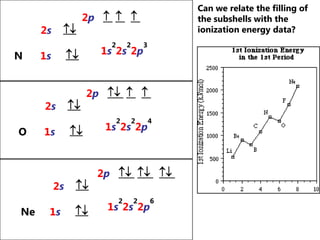
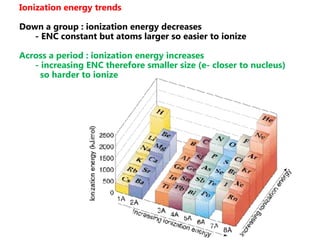
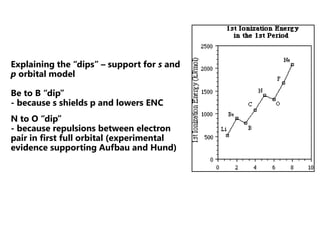
The document discusses electron configuration and trends in ionization energy. It explains that ionization energy decreases down a group and increases across a period due to changes in effective nuclear charge. Electrons fill atomic orbitals according to Aufbau principle and Hund's rule. The document provides examples of writing electron configurations and condensed configurations for various elements. Successive ionization energy data supports the electron configuration model.





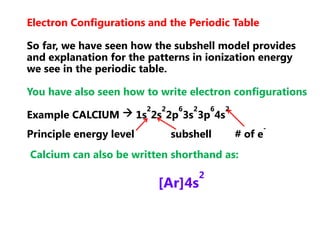

![Electron Configurations and the Periodic TableSo far, we have seen how the subshell model provides and explanation for the patterns in ionization energy we see in the periodic table.You have also seen how to write electron configurationsExample CALCIUM 1s22s22p63s23p64s2Principle energy level subshell # of e-Calcium can also be written shorthand as:[Ar]4s2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011-hlibchemistry-topic12-110906004304-phpapp01/85/2011-hl-ib-chemistry-topic-12-26-320.jpg)
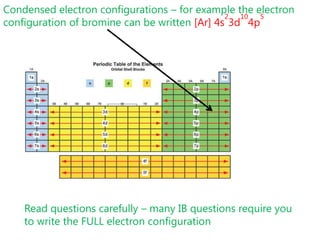


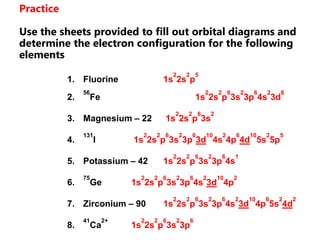
![Condensed electron configurations – for example the electron configuration of bromine can be written [Ar] 4s23d104p5Read questions carefully – many IB questions require you to write the FULL electron configuration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011-hlibchemistry-topic12-110906004304-phpapp01/85/2011-hl-ib-chemistry-topic-12-30-320.jpg)
![Electron configuration of ions:In general, electrons will be removed from orbitals (ionization) in the reverse order that the orbitals were filled. In other words, electrons vacate higher energy orbitals first.The exception: TRANSITION METAL IONSWhen these ions form, electrons are removed from the valence shell sorbitals before they are removed from valence dorbitals when transition metals are ionized.For example: Cobalt has the configuration [Ar] 4s23d7 OR [Ar] 3d7 4s2The Co2+ and Co3+ ions have the following electron configurations. Co2+: [Ar] 3d7Co3+: [Ar] 3d6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011-hlibchemistry-topic12-110906004304-phpapp01/85/2011-hl-ib-chemistry-topic-12-31-320.jpg)
![Condensed electron configurations – for example the electron configuration of bromine can be written [Ar] 4s23d104p5Si ___________________________S2- ___________________________Rb+ ___________________________Se ___________________________Ar ___________________________Nb ___________________________Zn2+ ___________________________Cd ___________________________Sb ___________________________](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2011-hlibchemistry-topic12-110906004304-phpapp01/85/2011-hl-ib-chemistry-topic-12-32-320.jpg)
