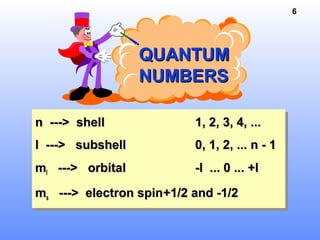
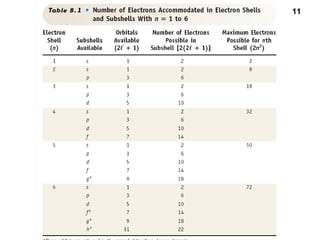
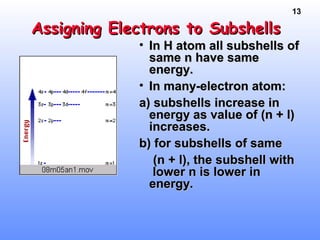
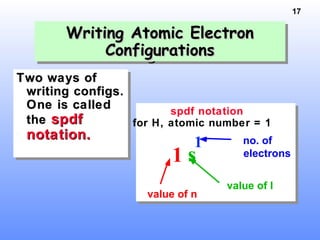
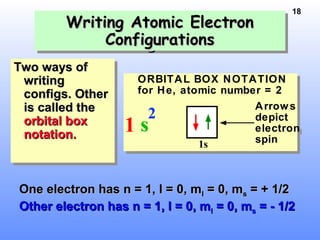
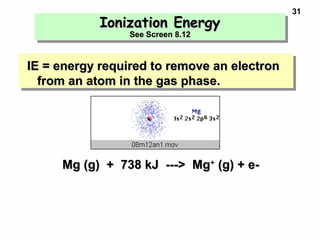
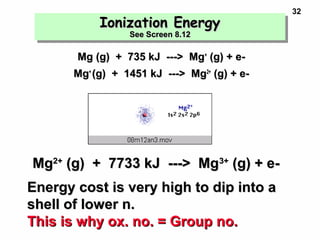
1. Electrons in atoms are arranged in shells, subshells, and orbitals according to their quantum numbers. Each orbital can contain a maximum of two electrons with opposing spins.
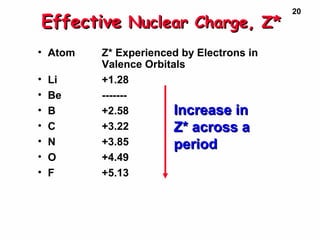
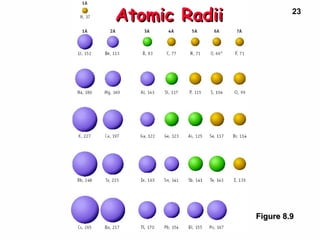
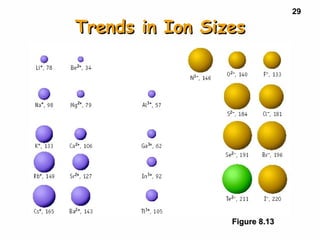
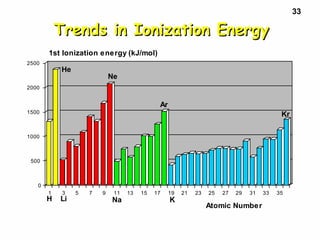
2. Atoms experience an effective nuclear charge that increases across a period, leading to higher ionization energies and smaller atomic and ionic sizes as more protons are exposed.
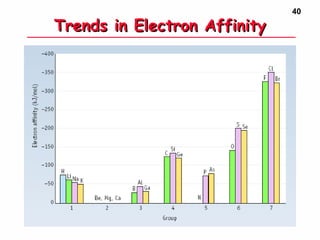
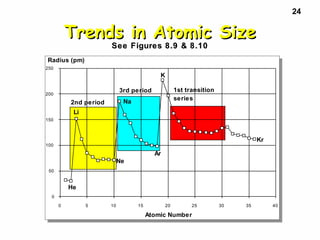
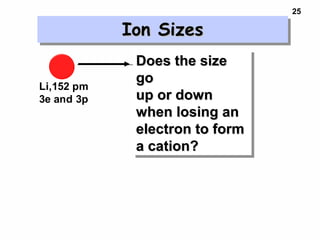
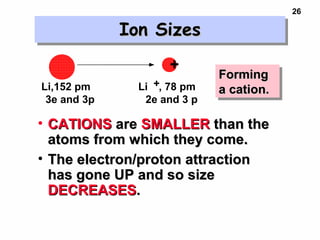
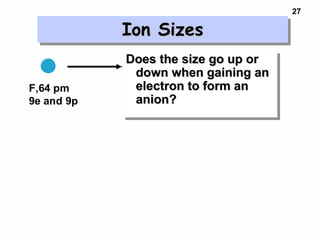
3. Trends in properties like ionization energy, atomic size, and electron affinity are explained by the changing effective nuclear charge experienced by valence electrons.








![15
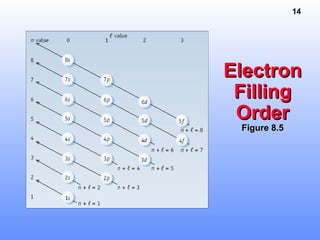
Effective Nuclear Charge, Z*Effective Nuclear Charge, Z*Effective Nuclear Charge, Z*Effective Nuclear Charge, Z*
• Z* is the nuclear chargeZ* is the nuclear charge
experienced by the outermostexperienced by the outermost
electrons.electrons.
• Explains why E(2s) < E(2p)Explains why E(2s) < E(2p)
• Z* increases across a period owing toZ* increases across a period owing to
incomplete shielding by inner electrons.incomplete shielding by inner electrons.
• Estimate Z* by --> [Estimate Z* by --> [ Z - (no. innerZ - (no. inner
electrons)electrons) ]]
• Charge felt by 2s e- in LiCharge felt by 2s e- in Li Z* = 3 -Z* = 3 -
2 = 12 = 1
• BeBe Z* = 4 - 2 = 2Z* = 4 - 2 = 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/periodictablenelectronconfig-150429043514-conversion-gate01/85/Periodic-table-n-electron-config-15-320.jpg)






![37
Electron Affinity of OxygenElectron Affinity of Oxygen
∆∆E isE is EXOEXOthermicthermic
because O hasbecause O has
an affinity for anan affinity for an
e-.e-.
[He] ↓↑ ↓↑ ↑ ↑O atom
EA = - 141 kJ
+ electron
O [He] ↓↑ ↓↑ ↑ ↑- ion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/periodictablenelectronconfig-150429043514-conversion-gate01/85/Periodic-table-n-electron-config-37-320.jpg)
![38
Electron Affinity of NitrogenElectron Affinity of Nitrogen
∆∆E isE is zerozero for Nfor N--
due to electron-due to electron-
electronelectron
repulsions.repulsions.
EA = 0 kJ
[He] ↓↑ ↑ ↑N atom ↑
[He] ↓↑ ↑ ↑N-
ion ↑
+ electron](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/periodictablenelectronconfig-150429043514-conversion-gate01/85/Periodic-table-n-electron-config-38-320.jpg)